Abstract
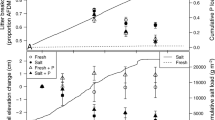
To investigate the effects of the simultaneous occurrence of salt stress and tidal sea-level rise on mangroves, potted Kandelia candel seedlings were treated under deep flooding (flooded 40 cm above the soil surface for 16 h per day, inundating the entire plant) and shallow flooding (flooded just above the soil surface for 8 h per day) at salinity levels of 5, 15, and 25 ppt over 14 months. Deep flooding enhanced stem elongations at all salinity levels but increased stem biomass only at 5 ppt. Deep flooding increased both leaf production and leaf fall; leaf biomass increased at 5 ppt, but decreased at 15 and 25 ppt. Biomass ratios of root/shoot (R/S) of deep flooding treatments were significantly lower than those of shallow flooding treatments. Under deep flooding, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities did not show significant change between 5 and 15 ppt, but increased at 25 ppt. With increasing salinity level, peroxidase (POD) activities increased, and the difference between shallow and deep flooding was enhanced. Malonaldehyde (MDA) content significantly decreased at 25 ppt with 40 cm flooding, but was not affected by other treatments. These results demonstrated that the growth and physiological responses of K. candel seedlings under deep flooding conditions varied with salinity level; growth was enhanced at low salinity level but inhibited at high salinity level. It is therefore probable that K. candel will shift from downstream to upstream, where the influence of fresher river water resources will ameliorate the effects of increased salinities that accompany deeper tidal flooding in these mangrove ecosystems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. A., K. W. Krauss & R. D. Hauff, 2003. Factors limiting the intertidal distribution of the mangrove species Xylocarpus granatum. Oecologia 135: 110–121.
Aziz, I. & M. A. Khan, 2001. Experimental assessment of salinity tolerance of Ceriops tagal seedlings and saplings from the Indus delta Pakistan. Aquatic Botany 70: 259–268.
Ball, M. C., 1998. Mangrove species richness in relation to salinity and waterlooging: a case study along the Adelaide River floodplain, northern Australia. Global Ecology and Biogeography 7: 73–82.
Ball, M. C., 2002. Interactive effects of salinity and irradiance on growth: implications for mangrove forest structure along salinity gradients. Trees – Structure and Function 16: 126–139.
Ball, M. C. & G. D. Farquhar, 1984. Photosynthetic and stomatal responses of the two mangrove species, Aegiceras corniculatum and Avicennia marina, to long term salinity and humidity conditions. Plant Physiology 74: 1–6.
Ball, M. C. & S. M. Pidsley, 1995. Growth responses to salinity in relation to distribution of two mangrove species, Sonneratia alba and S. lanceolata, in northern Australia. Functional Ecology 9: 77–85.
Ball, M. C., M. J. Cochrane & H. M. Rawson, 1997. Growth and water use of the mangroves Rhizophora apiculata and R. stylosa in response to salinity and humidity under ambient and elevated concentrations of atmospheric CO2. Plant, Cell & Environment 20: 1158–1166.
Bowler, C., M. V. Montagu & D. Inze, 1992. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 43: 83–116.
Cardona-Olarte, P., R. R. Twilley, K. W. Krauss & V. Rivera-Monroy, 2006. Responses of neotropical mangrove seedlings grown in monoculture and mixed culture under treatments of hydroperiod and salinity. Hydrobiologia 569: 325–341.
Chen, R. & R. R. Twilley, 1998. A gap dynamic model of mangrove forest development along gradients of soil salinity and nutrient resources. Journal of Ecology 86: 37–52.
Chen, L. Z., W. Q. Wang & P. Lin, 2005. Photosynthetic and physiological responses of Kandelia candel L. Druce seedlings to duration of tidal immersion in artificial seawater. Environmental and Experimental Botany 54: 256–266.
Christian, R., 2005. Interactive effects of salinity and irradiance on photoprotection in acclimated seedlings of two sympatric mangroves. Trees – Structure and Function 19: 596–606.
Cintrón, G. & Y. S. Novelli, 1984. Methods for studying mangrove structure. In Snedaker, S. C. & J. G. Snedaker (eds), The Mangrove Ecosystem: Research Methods. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization Publisher, Richard Clay (The Chaucer Press), UK: 91–113.
Clarke, P. J. & W. G. Allaway, 1993. The regeneration niche of the grey mangrove (Avicennia marina): effects of salinity, light, and sediment factors on establishment, growth and survival in the field. Oecologia 93: 548–556.
Clarke, P. J. & R. A. Kerrigan, 2002. The effects of seed predators on the recruitment of mangroves. Journal of Ecology 90: 728–736.
Clarke, P. J. & P. J. Myerscough, 1993. The intertidal distribution of the grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) in southeastern Australia: the effects of physical conditions, interspecific competition, and predation on propagule establishment and survival. Australian Journal of Ecology 18: 307–315.
Clough, B. F., 1984. Growth and salt balance of the mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. and Rhizophora stylosa Griff. in relation to salinity. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology 11: 419–430.
Delgado, P., P. F. Hensel, J. A. Jiménez & J. W. Day, 2001. The importance of propagule establishment and physical factors in mangrove distributional patterns in a Costa Rican estuary. Aquatic Botany 71: 157–178.
Ellison, A. M. & E. J. Farnsworth, 1993. Seedling survivorship, growth, and response to disturbance in Belizean mangal. American Journal of Botany 80: 1137–1145.
Ellison, A. M. & E. J. Farnsworth, 1996. Spatial and temporal variability in growth of Rhizophora mangle saplings: links with insolation, herbivory and local sedimentation regimes on Belizean coral cays. Journal of Ecology 84: 717–731.
Ellison, A. M. & E. J. Farnsworth, 1997. Simulated sea level change alters anatomy, physiology, growth, and reproduction of red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle L.). Oecologia 112: 435–446.
Farnsworth, E. J. & A. M. Ellison, 1996. Sun-shade adaptability of the red mangrove, Rhizophora mangle (Rhizophoraceae): changes through ontogeny at several levels of biological organization. American Journal of Botany 83: 1131–1143.
Field, C. D., 1995. Impact of expected climate change on mangroves. Hydrobiologia 295: 75–81.
He, B., T. Lai, H. Fan, W. Wang & H. Zheng, 2007. Comparison of flooding tolerance in four mangrove species in a diurnal tidal zone in the Beibu Gulf. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 74: 254–262.
Hovenden, M. J., M. Curran, M. A. Cole, P. F. E. Goulter, N. J. Skelton & W. G. Allaway, 1995. Ventilation and respiration in roots of one-year-old seedlings of grey mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Hydrobiologia 295: 23–29.
Kao, W. Y., H. C. Tsai & T. T. Tsai, 2001. Effect of NaCl and nitrogen availability on growth and photosynthesis of seedlings of a mangrove species, Kandelia candel (L.) Druce. Journal of Plant Physiology 158: 841–846.
Kitaya, Y., V. Jintana, S. Piriyayotha, D. Jaijing, K. Yabuki, S. Izutani, A. Nishimiya & M. Iwasaki, 2002. Early growth of seven mangrove species planted at different elevations in a Thai estuary. Trees – Structure and Function 16: 150–154.
Krauss, K. W. & J. A. Allen, 2003a. Influences of salinity and shade on seedling photosynthesis and growth of two mangrove species, Rhizophora mangle and Bruguiera sexangula, introduced to Hawaii. Aquatic Botany 77: 311–324.
Krauss, K. W. & J. A. Allen, 2003b. Factors influencing the regeneration of the mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza (L.) Lamk. on a tropical Pacific island. Forest Ecology and Management 176: 49–60.
Krauss, K. W., C. E. Lovelock, K. L. McKee, L. López-Hoffman, S. M. L. Ewe & W. P. Sousa, 2008. Environmental drivers in mangrove establishment and early development: a review. Aquatic Botany 89: 105–127.
Li, N., S. Chen, X. Zhou, C. Li, J. Shao, R. Wang, E. Fritz, A. Hüttermann & A. Polle, 2008. Effect of NaCl on photosynthesis, salt accumulation and ion compartmentation in two mangrove species, Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorhiza. Aquatic Botany 88: 303–310.
Lin, P., 1999. Mangrove Ecosystem in China. Science Press, Beijing.
Lin, G., & L. da S. L. Sternberg, 1992. Effects of growth form, salinity, nutrient, and sulphide on photosynthesis, carbon isotope discrimination and growth of red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle L). Australian Journal of Plant Physiology 19: 509–517.
Lin, G., & L. da S. L. Sternberg, 1993. Effect of salinity fluctuation on photosynthetic gas exchange and plant growth of the red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle L.). Journal of Experimental Botany 44: 9–16.
López-Hoffman, L., N. P. R. Anten, M. Martı′nez-Ramos & D. Ackerly, 2007. Salinity and light interactively affect neotropical mangrove seedlings at the leaf and whole plant levels. Oecologia 150: 545–556.
Misra, S., A. Choudhury, A. Ghosh & J. Dutta, 1984. The role of hydrophobic substances in leaves in adaptation of plants to periodic submersion by tidal water in a mangrove ecosystem. Journal of Ecology 72: 621–625.
Naidoo, G., 1985. Effects of waterlogging and salinity on plant–water relations and on the accumulation of solutes in three mangrove species. Aquatic Botany 22: 133–143.
Naidoo, G., 1987. Effects of salinity and nitrogen on growth and relations in the mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. New Phytologist 107: 317–325.
Parida, A. K., A. B. Das & B. Mittra, 2003. Effects of NaCl stress on the structure, pigment complex composition, and photosynthetic activity of mangrove Bruguiera parviflora chloroplasts. Photosynthetica 41: 191–200.
Parida, A. K., A. B. Das, Y. Sanada & P. Mohanty, 2004. Effects of salinity on biochemical components of the mangrove, Aegiceras corniculatum. Aquatic Botany 80: 77–87.
Pezeshki, S. R., R. D. DeLaune & W. H. Patrick, 1990. Differential response of selected mangroves to soil flooding and salinity: gas exchange and biomass partitioning. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 20: 869–874.
Pezeshki, S. R., R. D. DeLaune & J. F. Meeder, 1997. Carbon assimilation and biomass partitioning in Avicennia germinans and Rhizophora mangle seedlings in response to soil redox conditions. Environmental and Experimental Botany 37: 161–171.
Purnobasuki, H. & M. Suzuki, 2004. Aerenchyma formation and porosity in root of a mangrove plant, Sonneratia alba (Lythraceae). Journal of Plant Research 117: 465–472.
Skelton, N. J. & W. G. Allaway, 1996. Oxygen and pressure changes measured in situ during flooding in roots of the gray mangrove Avicennia marina (Forssk) Vierh. Aquatic Botany 54: 165–175.
Takemura, T., N. Hanagata, K. Sugihara, S. Baba, I. Karube & Z. Dubinsky, 2000. Physiological and biochemical responses to salt stress in the mangrove, Bruguiera gymnorrhiza. Aquatic Botany 68: 15–28.
Tuffers, A., G. Naidoo & D. J. vonWillert, 2001. Low salinities adversely affect photosynthetic performance of the mangrove Avicennia marina. Wetlands Ecology and Management 9: 235–242.
Wang, W. Q. & P. Lin, 2000. Study on the membrane lipid peroxidation of the leaves of Kandelia candel seedlings to long-term and short-term salinity. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 22: 49–54.
Ye, Y. & N. F. Y. Tam, 2002. Growth and physiological responses of Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza to livestock wastewater. Hydrobiologia 479: 75–81.
Ye, Y., N. F. Y. Tam, Y. S. Wong & C. Y. Lu, 2003. Growth and physiological responses of two mangrove species (Bruguiera gymnorrhiza and Kandelia candel) to waterlogging. Environmental and Experimental Botany 49: 209–221.
Ye, Y., N. F. Y. Tam, Y. S. Wong & C. Y. Lu, 2004. Does sea level rise influence propagule establishment, early growth and physiology of Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 306: 197–215.
Ye, Y., Y. S. Wong & N. F. Y. Tam, 2005. Acclimation of a dominant mangrove plant (Kandelia candel) to soil texture and its response to canopy shade. Hydrobiologia 539: 109–119.
Youssef, T. & P. Saenger, 1996. Anatomical adaptive strategies and rhizosphere oxidation in mangrove seedlings. Australian Journal of Botany 44: 297–313.
Zheng, W. J. & P. Lin, 1990. Effect of salinity on the growth characteristics and water metabolism of seedlings of Kandelia candel. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) 29: 575–579.
Acknowledgments
The work described in this paper is supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project no. 40276036, 40476040) and New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Karen McKee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Gu, Y.T., Gao, H.Y. et al. Combined effects of simulated tidal sea-level rise and salinity on seedlings of a mangrove species, Kandelia candel (L.) Druce. Hydrobiologia 641, 287–300 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0099-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0099-9