Abstract
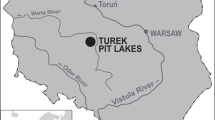
The environment of Lake Carey, a large salt lake in the goldfields of Western Australia, has been subjected to mining for the past 100 years. The effect of discharge of hypersaline water to the playa as a result of pit dewatering has been a grave concern. The aim of this paper was to investigate the influences of seasonal parameters and mining activity on the physico-chemical and biological attributes of Lake Carey. Assessment of water and sediment chemistry and benthic microbial communities (BMCs) has been carried out opportunistically since 1999, with particular emphasis on the differences between sites receiving dewatering discharge currently or in the past (Impacted Sites), and those which have never received dewatering discharge (Control Sites). Results of water and sediment analyses indicated that the impacts of dewatering discharge on Lake Carey were localised and evident in the vicinity of the discharge sites. However, large rainfall events, such as the cyclonic rainfall in 2004, could result in flushing and amelioration of sediments. This was also reflected in the sites which were historically impacted by dewatering discharge. The sites directly impacted by dewatering discharge displayed poor abundance and species richness of diatoms compared to the sites unaffected by dewatering discharge. However, recovery of these sites in terms of species richness and abundance is also initiated by large rainfall events, as shown by data collected from the historical dewatering discharge sites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACMER, 2003. Workshop on Water quality issues in final voids, salt lakes and ephemeral streams, Perth, Western Australia.
ANZECC, 2000. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality. ANZECC, Canberra.
Beard, J. S., 1974. Vegetation Survey of Western Australia—Great Victoria Desert. University of Western Australia Press, Perth.
Blinn, D. W., 1993. Diatom community structure along physicochemical gradients in saline lakes. Ecology 74: 1246–1263.
Blinn, D. W. & P. C. E. Bailey, 2001. Land-use influence on stream water quality and diatom communities in Victoria, Australia: a response to secondary salinization. Hydrobiologia 466: 231–244.
Blinn, D. W., S. A. Halse, A. M. Pinder, R. J. Shiel & J. M. McRae, 2004. Diatom and micro-invertebrate communities and environmental determinants in the western Australian wheatbelt: a response to salinization. Hydrobiologia 528: 229–248.
Boulton, A. J. & M. A. Brock, 1999. Australian Freshwater Ecology—Processes and Management. Gleneagles Publishing, South Australia.
Brearley, D. R., J. N Dunlop & J. M. Osborne, 1997. The terrestrial flora and fauna of Lake Carey. Internal Report to Placer Granny Smith. Published by the Mine Rehabilitation Group, Curtin University of Technology, Perth.
Bureau of Meteorology, 2006. Available online www.bom.wa.gov.au.
Chaplin, S. & J. John, 1999. A preliminary sampling of the aquatic organisms of Lake Carey. Curtin Consultancy Report 3397.2, Western Australia, 20 pp.
Clarke, K. R. & R. N Gorley, 2006. Primer V6: User Manual/Tutorial, Primer-E Ltd Plymouth.
Coleman, M., 1999. Potential impact of discharging groundwater from the Placer Granny Smith Pty Ltd, Sunrise Mine and the Acacia Resources Sunrise Dam Gold Mine into Lake Carey. Internal Report actis Environmental Services, Perth, Western Australia.
Commander, P., 1999. Hydrogeology of salt lakes in Western Australia. In Proceedings of the Salt Lake Ecology Seminar. Centre of Land Rehabilitation, Perth.
Davey, B., 2000. Lake Carey Fringing Flora Monitoring 2000. Internal report for AngloGold Australasia. Placer Granny Smith and Sons of Gwalia Ltd.
Erhlich, A., 1995. Atlas of the inland-water diatom flora of Israel, Flora Palestina. Publications of the Israel Academy of Science and Humanities, Israel.
Finucane, S., K. Lee & D. Foy, 2002. Environmental monitoring of mine water discharge to Lake Miranda. Proceedings of the 2002 Goldfields Environmental Management Group Workshop “The boundary fence and beyond”. Kalgoorlie, Western Australia.
Finucane, S., M. Boisvert & K. Ariyaratnam, 2003. Water quality monitoring at Lake Miranda. Workshop on Water Quality Issues in Final Voids, Salt Lakes and Ephemeral Streams, ACMER, Perth, Western Australia.
Foster, J., 2004. Salt Lakes and Mine Dewatering Discharge: Cause, Effect and Recovery. Goldfields Environmental Management Group, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia.
Gell, P. A., 1997. The development of a diatom database for inferring lake salinity, western Victoria, Australia: towards a quantitative approach for reconstructing past climates. Australian Journal of Botany 45: 389–723.
Gell, P. A. & F. Gasse, 1990. Relationships between salinity and diatom flora from some Australian saline lakes. In Kociolek, J. P. (ed.) Proceedings of the 11th International Diatom Symposium. California Academy of Science Memoir 17. San Francisco, CA: 631–647.
Gregory, S. J., M. J. Ward & V. S. Campagna, 2006. Classification of Inland Salt Lakes in Western Australia. Proceedings of the Goldfields Environmental Management Group Conference, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia.
Hirst, H., I. Juttner & S. J. Ormerod, 2002. Comparing the responses of diatoms and macroinvertebrates to metals in upland streams of Wales and Cornwall. Freshwater Biology 47: 1752–1765.
Jasper, D., 1999. Salt Lake Ecology Seminar—A synthesis of issues raised in group discussion. In Proceedings of the Salt Lake Ecology Seminar, Perth, WA.
John, J., 1983. The Diatom Flora of the Swan River Estuary, Western Australia. J. Cramer, Germany.
John, J. 2000. A guide to diatoms as indicators of urban stream health. LWRRDC Occasional paper 14/99. Urban Sub Program, Report No. 7.
Keighery, G. J., N. J. Hall & A. V. Milewski, 1994. Vegetation and flora. Records of the Western Australian Museum Supplement 47: 24–50.
Mann, A. W., 1982. Hydrogeochemistry and weathering on the Yilgarn Block, Western Australia—ferrolysis and heavy metals in continental brines. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 47: 181–190.
Minitab Inc, 2003. MINITAB Statistical Software, Release 14 for Windows, State College, Pennsylvania. MINITAB® is a registered trademark of Minitab Inc.
OES, 2001. Regional biological monitoring: Lake Carey, December 2001. Internal report for the Lake Carey Catchment Management Group.
OES, 2004. Lake Carey regional study, July 2004. Internal report for the Lake Carey Catchment Management Group.
Pringle, H. J. R., A. M. E. Van Vreeswyk & S. A. Gilligan, 1994. An inventory and condition survey of rangelands in the north-eastern Goldfields, Western Australia. Technical Bulletin, No. 87, Department of Agriculture, Western Australia.
Saros, J. E. & S. C. Frtiz, 2002. Resource competition among saline-lake diatoms under varying N/P ratio, salinity and anion composition. Freshwater Biology 47: 87–95.
Smith, R., R. Jeffree, J. John & P. Clayton, 2004. Review of methods for water quality assessment of temporary stream and lake systems. ACMER, QLD.
Timms, B. V., 1992. Lake Geomorphology. Gleneagles Publishing, Adelaide.
Timms, B. V., 2006. The geomorphology and hydrology of saline lakes of the middle Paroo, arid zone Australia. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 127: 157–174.
Timms, B. V., B. Datson & M. Coleman, 2006. The wetlands of the Lake Carey catchment, northeast Goldfields of Western Australia, with special reference to large branchiopods. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia 89: 175–183.
van Etten, E., B. Sommer & P. Horwitz, 2000. Monitoring study of Lake Austin following 14 months of dewatering discharge form the Cuddingwarra Mine. Centre for Ecosystem Management, Edith Cowan University, Perth.
Acknowledgements
This work has been sponsored by the Lake Carey Catchment Management Group (LCCMG), which consists of mining companies present on the peripheries of the lake. The assistance of Belinda Bastow, Paul Ritchie, Nicole Mittan, Sarah Pollock, Tim Stevens, Sophie Gaunt of the LCCMG is acknowledged. Our thanks to Fiona Taukulis and Veronica Campagna for help with diatom identification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editors: J. John & B. Timms
Salt Lake Research: Biodiversity and Conservation—Selected papers from the 9th Conference of the International Society for Salt Lake Research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregory, S.J., Ward, M.J. & John, J. Changes in the chemistry and biota of Lake Carey: a large salt lake impacted by hypersaline discharge from mining operations in Western Australia. Hydrobiologia 626, 53–66 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9744-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9744-6