Abstract
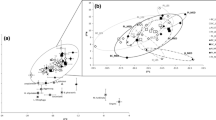
Valuable biological information can be obtained by monitoring the movement of organisms. However, the choice of monitoring method becomes highly restricted when following small organisms (<100 mm), especially in aquatic ecosystems. Stable isotopes are being increasingly used in this respect but rarely at the local spatial scale, i.e. 10–1000 s of metres. We sought to identify movement of small fishes between a main river channel and its tributary. Little overlap in isotope baseline was detected between the two channels despite some temporal variability in δ15N of baseline indicator organisms in the main river. The individuals of two small cyprinid fish species (Leuciscus souffia and Alburnoides bipunctatus) of all the size classes (40–100 mm) caught within the tributary showed considerable heterogeneity in δ15N values. Classification and discriminant analysis on isotope-derived data distinguished two significantly different groups. Moreover, this result was supported by further sampling of fish caught in the main river (in May and December 2006). Alternative hypotheses, such as dietary differences, biological factors, temporal shifts and spatial differences in diet, did not explain δ15N variability. This application of stable isotopes at a relatively small spatial and temporal scales further demonstrates its potential as a tool for ecologists.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bearhop, S., W. Fiedler, R. W. Furness, S. C. Votier, S. Waldron, J. Newton, G. J. Bowen, P. Berthold & K. Farnsworth, 2005. Assortative mating as a mechanism for rapid evolution of a migratory divide. Science 310: 502–504.
Breitenstein, M. & A. Kirchhofer, 1999. Biologie, menaces et protection du spirlin (Alburnoides bipunctatus) en Suisse. Office Fédéral de l’Environnement, des Forêts et du Paysage n°62.
Bridger, C. J. & R. K. Booth, 2003. The effects of biotelemetry transmitter presence and attachment procedures on fish physiology and behaviour. Reviews in Fisheries Science 11: 13–34.
Cabana, G. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1996. Comparison of aquatic food chains using nitrogen isotopes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 10844–10847.
Chappaz, R. & G. Brun, 1992. Données nouvelles sur la biologie et l’écologie d’un poisson cyprinidé du sud de l’Europe Leuciscus (Telestes) soufia (Risso, 1826). Compte Rendu de l’Académie des Sciences de Paris série 3: 35–41.
Ciancio, J. E., M. A. Pascual, F. Botto, M. Amaya-Santi, S. O’Neal, C. Riva Rossi & O. Iribarne, 2008. Stable isotope profiles of partially migratory salmonid populations in Atlantic rivers of Patagonia. Journal of Fish Biology 72: 1708–1719.
Cunjak, R. A., J. M. Roussel, M. A. Gray, J. P. Dietrich, D. F. Cartwright, K. R. Munkittrick & T. D. Jardine, 2005. Using stable isotope analysis with telemetry or mark-recapture data to identify fish movement and foraging. Oecologia 144: 636–646.
Dufour, E. & D. Gerdeaux, 2001. Apports des isotopes stables (13C/12C, 15N/14N, 18O/16O, 36S/34S, 87Sr/86Sr) aux études écologiques sur les poissons. Cybium 25: 369–382.
Everitt, B., 2005. Grouped multivariate data: multivariate analysis of variance and discriminant function analysis. In Everitt, B. (ed.), An R and S-plus Companion to Multivariate Analysis. Springer-Verlag, London: 137–156.
Gannes, L. Z., D. M. O’Brien & C. Martinez del Rio, 1997. Stable isotopes in animal ecology: assumptions, caveats, and a call for more laboratory experiments. Ecology 78: 1271–1276.
Grey, J., 2001. Ontogeny and dietary specialization in brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) from Loch Ness, Scotland, examined using stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 10: 168–176.
Haas, H. L., C. J. Freeman, J. M. Logan, L. Deegan & E. F. Gaines, 2009. Examining mummichog growth and movement: are some individuals making intra-season migrations to optimize growth? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 369: 8–16.
Hansson, S., J. E. Hobbie, R. Elmgren, U. Larsson, B. Fry & S. Johansson, 1997. The stable nitrogen isotope ratio as a marker of food-web interactions and fish migration. Ecology 78: 2249–2257.
Harrington, R. R., B. P. Kennedy, C. P. Chamberlain, J. D. Blum & C. L. Folt, 1998. 15N enrichment in agricultural catchments: field patterns and applications to tracking Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Chemical Geology 147: 281–294.
Harrod, C., J. Grey, T. K. McCarthy & M. Morrissey, 2005. Stable isotope analyses provide new insights into ecological plasticity in a mixohaline population of European eel. Oecologia 144: 673–683.
Hershey, A. E., J. Pastor, B. J. Peterson & G. W. Kling, 1993. Stable isotopes resolve the drift paradox for Baetis Mayflies in an Arctic river. Ecology 74: 2315–2325.
Hobson, K. A., 1999. Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: a review. Oecologia 120: 314–326.
Hobson, K. A., 2008. Isotopic tracking of migrant wildlife. In Michener, R. & K. Lajtha (eds), Stable Isotope in Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2nd ed. Blackwell Publishing, Singapore: 155–175.
Hobson, K. A. & L. I. Wassenaar, 1997. Linking breeding and wintering grounds of neotropical migrant songbirds using stable hydrogen isotopic analysis of feathers. Oecologia 109: 142–148.
Hobson, K. A., L. I. Wassenaar & O. R. Taylor, 1999. Stable isotopes (δD and δ13C) are geographic indicators of natal origins of monarch butterflies in eastern North America. Oecologia 120: 397–404.
Huet, M., 1959. Aperçu des relations entre la pente et les populations piscicoles des eaux courantes. Revue Suisse d’Hydrologie 11: 332–351.
Kneitel, J. M. & J. M. Chase, 2004. Trade-offs in community ecology: linking spatial scales and species coexistence. Ecology Letters 7: 69–80.
Lévêque, C. (ed.), 2003. Ecology: From Ecosystem to Biosphere. Science Publishers, Enfield: 490 pp.
Litvin, S. Y. & M. P. Weinstein, 2004. Multivariate analysis of stable isotope ratios to infer movements and utilization of estuarine organic matter by juvenile weakfish (Cynoscion regalis). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 61: 1851–1861.
Lucas, M. C. & E. Baras (eds), 2001. Migration of Freshwater Fishes. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford: 440 pp.
Marra, P. P., K. A. Hobson & R. T. Holmes, 1998. Linking winter and summer events in a migratory bird by using stable-carbon isotopes. Science 282: 1884–1886.
Matthews, B. & A. Mazumder, 2004. A critical evaluation of intrapopulation variation of δ13C and isotopic evidence of individual specialisation. Oecologia 140: 361–371.
McCutchan, J. H., W. M. Lewis, C. Kendall & C. C. McGrath, 2003. Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulphur. Oikos 102: 378–390.
Perga, M. E. & D. Gerdeaux, 2005. ‘Are fish what they eat’ all year round? Oecologia 144: 598–606.
Rasmussen, J. B., V. Trudeau & G. Morinville, 2009. Estimating the scale of fish feeding movements in rivers using δ13C signature gradients. Journal of Animal Ecology 78: 674–685.
Rifflart, R., G. Carrel, Y. Le Coarer & B. Nguyen The Fontez, 2009. Spatio-temporal patterns of fish assemblages in a large regulated alluvial river. Freshwater Biology 54: 1544–1559.
Rubenstein, D. R. & K. A. Hobson, 2004. From birds to butterflies: animal movement patterns and stable isotopes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 19: 256–263.
Schwarz, M., 1998. Biologie, menaces et protection du blageon (Leuciscus souffia) en Suisse. Office Fédéral de l’Environnement, des Forêts et du Paysage n°59.
Smith, R. J. F., 1991. Social behaviour, homing and migration. In Winfield, I. J. & J. S. Nelson (eds), Cyprinid Fishes: Systematics, Biology and Exploitation. Chapman & Hall, London: 509–529.
Tachet, H., P. Richoux, M. Bournaud & P. Usseglio-Polatera (eds), 2000. Invertébrés d’eau douce: Systématique, biologie, écologie. CNRS Editions, Paris: 588 pp.
Venables, W. N. & B. D. Ripley, 1998. Modern applied statistics with S-plus. In Venables, W. N. & B. D. Ripley (eds), Statistics and Computing, 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag, New York: 548.
Webster, M. S., P. P. Marra, S. M. Haig, S. Bensch & R. T. Holmes, 2002. Links between worlds: unraveling migratory connectivity. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 17: 76–83.
Wocher, H. & R. Rosch, 2006. Migrations of soufie (Leuciscus souffia agassizii, Val. 1844) in a natural river and a tributary determined by mark-recapture. Archiv fur Hydrobiologia 165: 77–87.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank D. Salducci, B. Barascud, F. Martel, G. Morello-Fenouillet and T. Reynier for their invaluable help provided during sampling. This study received financial support from EDF (Electricité de France). EDF funded the PhD studies of M.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: M. Power
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durbec, M., Cavalli, L., Grey, J. et al. The use of stable isotopes to trace small-scale movements by small fish species. Hydrobiologia 641, 23–31 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0051-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0051-z