Abstract
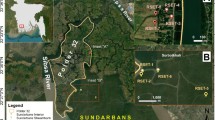
The spatial and temporal variability of water levels was investigated across a section of floodplain in the Pantanal that represents typical geomorphic and ecological complexity of these environments. A series of 11 staff gauges were installed along a 12-km transect running perpendicularly from the Cuiabá River into the floodplain. The staff gauges were monitored fortnightly during the flood seasons from 2004 to 2007. Contrary to what is often assumed, the water surface profile was never level, and it was particularly variable when there was less water on the floodplain. Water surface slope varied from 1.4 × 10−4 (unitless) to 1.3 × 10−3 indicating substantial water movement that was verified by flow observations. The spatial patterns of water level variation were repeated across years, even though there was considerable interannual variation in magnitude and duration of floodplain inundation. In 2004 and 2005, the duration of inundation was 121 and 120 days, respectively, but in 2006 and 2007, inundation lasted 166 and 157 days, respectively. These observations reveal considerable small-scale spatial variability in the water surface profile, but with persistent patterns over space and time that are related to the river hydrograph and the channels that convey flood waters across the area. This study contributes to our understanding of inundation hydrology and its linkages to ecosystem processes, and additionally provides a valuable data set for calibration and validation of remote sensing approaches to measurement of inundation area and water movement across floodplains.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsdorf, D. E., P. Bates, J. Melack, M. Wilson & T. Dunne, 2007a. The spatial and temporal complexity of the Amazon flood measured from space. Geophysical Research Letters 34: L08402. doi:10.1029/2007GL029447.
Alsdorf, D. E., E. Rodriguez & D. Lettenmaier, 2007b. Measuring surface water from space. Review of Geophysics 45: RG2002. doi:10.1029/2006RG000197.
Amoros, C. & A. L. Roux, 1988. Interaction between waterbodies within the floodplain of large rivers: function and development of connectivity. In Schreiber, K. F. (ed.), Connectivity in Landscape Ecology. Proceedings of the Second International Seminar of the International Association of Landscape Ecology, Münstersche Geographische Arbeiten, Vol. 29, Münster: 125–130.
Arieira, J. & C. N. Cunha, 2006. Phytosociology of a monodominant flooded forest of Vochysia divergens Pohl (Vochysiaceae) in North Pantanal, Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Acta Botanica Brasilica 20: 569–580.
Benke, A. C., I. Chaubey, G. Milton & E. L. Dunn, 2000. Flood pulse dynamics of an unregulated river floodplain in the southeastern U.S. coastal plain. Ecology 81: 2730–2741.
Buffagni, A., G. A. Crosa, D. M. Harper & J. L. Kemp, 2000. Using macroinvertebrate species assemblages to identify river channel habitat units: an application of the functional habitats concept to a large, unpolluted Italian river (River Ticino, northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 435: 213–225.
Cuffney, T. F. & J. B. Wallace, 1987. Leaf litter processing in coastal plain streams and floodplains of southeastern Goergia, USA. Archiv für Hydrobiologie - Supplement 76: 1–24.
Da Silva, C. J., 2000. Ecological basis for the management of the Pantanal—Upper Paraguay River basin. In Smits, A. J. M., P. H. Nienhuis & R. S. E. W. Leuven (eds), New Approaches to River Management. Bachuys Publishers, Leiden: 97–117.
Da Silva, C. J. & P. Girard, 2004. New challenges in the management of the Brazilian Pantanal and catchment area. Wetlands Ecology and Management 12: 553–561.
Depetris, C., O. Orfeo & J. J. Neiff, 1992. Atenuación del escurrimiento fluvial por bosques de “aliso”. Ambiente Subtropical 2: 33–43.
Fantin-Cruz, I., 2008. Dinâmica da Inundação em Meso-Escala na Planície do Rio Cuiabá, Pantanal, Brasil. Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso, Master thesis dissertation: 28 pp.
Fantin-Cruz, I., S. M. Loverde-Oliveira & P. Girard, 2008. Morphometric characterization and its limnological implications in Northern Pantanal lakes. Acta Scientiarum Biological Sciences 30: 133–140.
Girard, P., 2010. Hydrology of surface and ground waters in the Pantanal floodplains. In Junk, W. J, C. J. da Silva, C. Nunes da Cunha & K. M. Wantzen (eds), The Pantanal: Ecology, Biodiversity and Sustainable Management of a Large Neotropical Seasonal Wetland. Pensoft Publishers, Sofia.
Girard, P., C. J. Da Silva & M. Abdo, 2003. River–groundwater interactions in the Brazilian Pantanal. The case of the Cuiabá River. Journal of Hydrology 283: 57–66.
Hamilton, S. K., 1999. Potential effects of a major navigation project (the Paraguay-Paraná Hidrovía) on inundation in the Pantanal floodplains. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management 15: 289–299.
Hamilton, S. K., 2002. Hydrological controls of ecological structure and function in the Pantanal wetland (Brazil). In McClain, M. (ed.), The Ecohydrology of South American Rivers and Wetlands. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, Special Publication 6: 133–158.
Hamilton, S. K., S. J. Sippel & J. M. Melack, 1995. Oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide and methane production in waters of the Pantanal wetland of Brazil. Biogeochemistry 30: 115–141.
Hamilton, S. K., S. J. Sippel & J. M. Melack, 1996. Inundation patterns in the Pantanal wetland of South America determined from passive microwave remote sensing. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 137: 1–23.
Hamilton, S. K., S. J. Sippel, D. F. Calheiros & J. M. Melack, 1997. An anoxic event and other biogeochemical effects of the Pantanal wetland on the Paraguay River. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 257–272.
Hamilton, S. K., O. C. Souza & M. E. Coutinho, 1998. Dynamics of floodplain inundation in the alluvial fan of the Taquari River (Pantanal, Brazil). Verhandlungen International Vereiniging Limnology 26: 916–922.
Hamilton, S. K., S. J. Sippel & J. M. Melack, 2002. Comparison of inundation patterns in South American floodplains. Journal of Geophysical Research 107: Art No. 8038. doi:10.1029/2000JD000306.
Harvey, J. W., R. W. Schaffranek, G. B. Noe, L. G. Larsen, D. J. Nowacki & B. L. O’Connor, 2009. Hydroecological factors governing surface water flow on a low-gradient floodplain. Water Resources Research 45: W03421. doi:10.1029/2008WR007129.
Junk, W. J. & K. M. Wantzen, 2004. The flood pulse concept: new aspects, approaches and applications – an update. In Welcomme, R. L. & T. Petr (eds), Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Management of Large Rivers for Fisheries. Volume 2. Food and Agriculture Organization and Mekong River Commission. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific. RAP Publication, Bangkok: 117–149.
Junk, W. J., P. B. Bailey & R. E. Sparks, 1989. The flood pulse concept in river–floodplain systems. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 106: 110–127.
Junk, W. J., C. N. Cunha, K. M. Wantzen, P. Petermann, C. Strussmann, M. I. Marques & J. Adis, 2006. Biodiversity and its conservation in the Pantanal of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Aquatic Sciences 68: 278–309.
Lamouroux, N., J. M. Olivier, H. Capra, M. Zylberblat, A. Chandesris & P. Roger, 2006. Fish community changes after minimum flow increase: testing quantitative predictions in the Rhône River at Pierre-Bénite, France. Freshwater Biology 51: 1730–1743.
Loverde-Oliveira, S. M., V. L. M. Huszar & I. Fantin-Cruz, 2007. Implications of the flood pulse on morphometry of a Pantanal lake (Mato Grosso state, Central Brazil). Acta Limnologica Brasiliense 19: 453–461.
Mertes, L. A. K., 1997. Documentation and significance of the perirheic zone on inundated floodplains. Water Resources Research 33: 1749–1762.
Neiff, J. J., 1990. Ideas for an ecological interpretation of the Paraná. Interciencia 156: 424–441.
Neiff, J. J., 1996. Large rivers of South America: toward the new approach. Verhandlungen International Vereiniging Limnology 26: 167–180.
Neiff, J. J., 1999. El régimen de pulsos en ríos y grandes humedales de Sudamérica. In Malvarez, A. I. & P. Kandus (eds), Tópicos sobre grandes humedales sudamericanos. ORCYT-MAB (UNESCO): 97–145.
Neiff, J. J., 2001. Humedales de la Argentina: sinopsis, problemas y perspectivas futuras. In Cirelli, A. F. (ed.), El Agua en Iberoamérica, Funciones de los humedales, calidad de vida y agua segura. Publ. CYTED: 83–112.
Neiff, J. J., M. H. Iriondo & R. Carignan, 1994. Large tropical South American wetlands: an overview. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Ecology and Management of Aquatic-Terrestrial Ecotones, Washington, Seattle, USA: 156–165.
Neiff, J. J., C. A. E. Patiño & S. L. Casco, 2005. Atenuación de las crecidas por los humedales del Bajo Paraguay. In Capatto, J. & J. Peteán (eds), Humedales fluviales de América del Sur, Hacia un manejo sustentable. Fundación Proteger: 261–276.
Penha, J. M., C. J. Da Silva & I. Bianchini, 1999. Productivity of the aquatic macrophytes Pontederia lanceolata Nutt. (Pontederiaceae) on the floodplains of the Pantanal Mato-grossense, Brazil. Wetlands Ecology and Management 7: 155–163.
Poff, N. L., J. D. Allan, M. B. Bain, J. R. Karr, K. L. Prestegaard, B. D. Richter, R. E. Sparks & J. C. Stromberg, 1997. The natural flow regime. A paradigm for river conservation and restoration. BioScience 47: 769–784.
Pulliam, W. M., 1993. Carbon dioxide and methane exports from a southeastern floodplain swamp. Ecological Monographs 63: 29–53.
RAMSAR, 2004. The List of Wetlands of International Importance: 1–34. http://www.ramsar.org/index.html. Accessed December 14, 2007.
Reynolds, C. S., J. Padisák & U. Sommer, 1993. Intermediate disturbance in the ecology of phytoplankton and the maintenance of species diversity: a synthesis. Hydrobiologia 249: 183–188.
Silva, J. S. V., M. M. Abdon, A. Boock & M. P. Silva, 1998. Fitofisionomias dominantes em parte das sub-regiões do Nabileque e Miranda, Sul do Pantanal. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira 33: 1713–1719.
Sippel, S. J., S. K. Hamilton, J. M. Melack & E. M. M. Novo, 1998. Passive microwave observations of inundation area and area/stage in the Amazon River floodplain. International Journal of Remote Sensing 19: 3055–3074.
Thomaz, S. M., T. A. Pagioro, L. M. Bini, M. C. Roberto & R. R. A. Rocha, 2004. Limnological characterization of the aquatic environments and influence of hydrometric levels. In Thomaz, S. M., A. A. Agostinho & N. S. Hahn (eds), The Upper Paraná and its Floodplain: Physical Aspects, Ecology and Conservation. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 75–102.
Tockner, K., F. Malard & J. V. Ward, 2000. An extension of the flood pulse concept. Hydrological Processes 14: 2861–2883.
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted with support from the Long-term Ecological Research Program (PELD-12/CNPq), the Pantanal Research Center (CPP), and the Nucleus for Ecological Research of the Mato Grosso Pantanal (NEPA). We would like to express our appreciation for the grant awarded by CNPq to Ibraim Fantin da Cruz and for the logistical support provided by SESC-Pantanal for the development of this research. We are indebted to the researchers Drs. Juan José Neiff and Alexandre Silveira for their corrections and helpful suggestions, and to the technicians Enésio Francisco and Francisco Modesto, as well as the park guards of the RPPN SESC-Pantanal, for their assistance with the fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: J. M. Melack
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girard, P., Fantin-Cruz, I., de Oliveira, S.M.L. et al. Small-scale spatial variation of inundation dynamics in a floodplain of the Pantanal (Brazil). Hydrobiologia 638, 223–233 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0046-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0046-9