Abstract
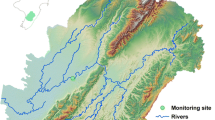
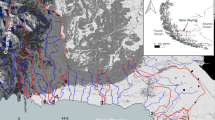
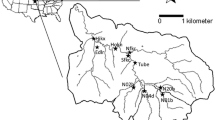
Hydrological changes have the greatest impact on shallow lakes where they alter the water volume and lake depth noticeably. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC), which is markedly affected by hydrological factors, has an important role in many biogeochemical processes. The DOC load supplied to Lake Võrtsjärv, the second largest lake in Estonia, was studied on the scale of the subcatchments discharging into the lake. Daily discharges and biweekly or monthly DOC concentrations were measured close to the river outlets over the years 1990–2002. The stream flow data were separated into groundflow and surface flow by applying local minimum and recursive digital filtering methods. Constituent load estimation software, LOADEST, was used to estimate DOC concentrations and load. LOADEST performed well for three of the four rivers. The total estimated DOC load to Võrtsjärv from all four main rivers varied from 1,320 to 4,934 t year−1. The average annual load over the 13-year period was 3,265 t year−1 or 1.18 g C m−2 year−1. Baseflow separation analysis indicated that the DOC load originating from groundflow contributed 79% and 69% of the total load according to the digital filter and local minimum methods, respectively. The results of our study demonstrate the utility of linking the rating-curve method and baseflow separation to assess the allochthonous DOC load to Võrtsjärv both currently and under changing climatic conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, P. S., W. E. Dietrich, R. Torres, D. R. Montgomery & K. Loague, 1997. Concentration-discharge relationships in runoff from a steep, unchanneled catchment. Water Resources Research 33: 211–225.
Arnold, J. G. & P. M. Allen, 1999. Automated methods for estimating baseflow and ground water recharge from streamflow records. Journal of American Water Resources Association 35: 411–424.
Arvola, L., A. Räike, P. Kortelainen & M. Järvinen, 2004. The effect of climate and landuse on TOC concentrations in Finnish rivers. Boreal Environment Research 9: 381–387.
Boyer, E. W., G. M. Hornberger, K. E. Bencala & D. M. McKnight, 2000. Effects of asynchronous snowmelt on flushing of dissolved organic carbon: a mixing model approach. Hydrological Processes 14: 3291–3308.
Brye, K. R., J. M. Norman, L. G. Bundy & S. T. Gower, 2001. Nitrogen and carbon leaching in agroecosystems and their role in denitrification potential. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 58–70.
Carey, S. K., 2003. Dissolved organic carbon fluxes in a discontinuous permafrost subartic alpine catchment. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes 14: 161–171.
Clark, J. M., P. J. Chapman, J. K. Adamson & S. N. Lane, 2005. Influence of drought-induced acidification on the mobility of dissolved organic carbon in peat soils. Global Change Biology 11: 791–809.
De Lange, H. J., D. P. Morris & C. E. Williamson, 2003. Solar ultraviolet photodegradation of DOC may stimulate freshwater food webs. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 111–117.
Freeman, C., N. Fenner, N. J. Ostle, H. Kang, D. J. Dowrick, B. Reynolds, M. A. Lock, D. Sleep, S. Hughes & J. Hudson, 2004. Export of dissolved organic carbon from peatlands under elevated carbon dioxide levels. Nature 430: 195–198.
Frisk, T., Ä. Bilaletdin, H. Kaipainen, O. Malve & M. Möls, 1999. Modelling phytoplankton dynamics of the eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv, Estonia. Hydrobiologia 414: 59–68.
Hinton, M. J., S. L. Schiff & M. C. English, 1997. The significance of storms for the concentration and export of dissolved organic carbon from two Precambrian Shield catchments. Biogeochemistry 36: 67–88.
Hinton, M. J., S. L. Schiff & M. C. English, 1998. Sources and flowpaths of dissolved organic carbon during storms in two forested watersheds of the Precambrian Shield. Biogeochemistry 41: 175–197.
Inamdar, S. P., S. F. Christopher & M. J. Mitchell, 2004. Export mechanisms for dissolved organic carbon and nitrate during summer storm events in a glaciated forested catchment in New York, USA. Hydrological Processes 18: 2651–2661.
Jansson, M., A.-K. Bergstrom, P. Blomqvist & S. Drakare, 2000. Allochthonous organic carbon and phytoplankton/bacterioplankton production relationships in lakes. Ecology 81: 3250–3255.
Järvet, A., 2004. Pollution load to Lake Võrtsjärv. In Haberman, J., E. Pihu & A. Raukas (eds), Lake Võrtsjärv. Estonian Encyclopaedia publishers, Tallinn: 151–171.
Laudon, H., S. Köhler & I. Buffam, 2004. Seasonal TOC export from seven boreal catchments in northern Sweden. Aquatic Sciences 66(2): 223–230.
Moore, T. R., 1989. Dynamics of dissolved organic carbon in forested and disturbed catchments, Westland, New Zealand. 1. Maimai. Water Resources Research 25: 1321–1330.
Morris, D. P., H. Zagarese, C. E. Williamson, E. G. Balseiro, B. R. Hargreaves, B. Modenutti, R. Moeller & C. Queimalinos, 1995. The attenuation of solar UV radiation in lakes and the role of dissolved organic carbon. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1381–1391.
Nathan, R. J. & T. A. McMahon, 1990. Evaluation of automated techniques for base flow and recession analyses. Water Resources Research 26: 1465–1473.
Nieminen, M., 2004. Export of dissolved organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus following clear-cutting of three Norway spruce forests growing on drained peatland in southern Finland. Silva Fennica 38: 123–132.
Nõges, P., L. Tuvikene, A. Järvet & T. Nõges, 1998a. The budgets of nitrogen and phosphorus in shallow eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv (Estonia). Hydrobiologia 363: 219–227.
Nõges, T. & P. Nõges, 1998. Primary production of Lake Võrtsjärv. Limnologica 28: 29–40.
Nõges, T., P. Nõges, J. Haberman, V. Kisand, K. Kangur, A. Kangur & A. Järvalt, 1998b. Food web structure in shallow eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv (Estonia). Limnologica 28: 115–128.
Nõges, T. & P. Nõges, 1999. The effect of extreme water level decrease on hydrochemistry and phytoplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 408/409: 277–283.
Reinart, A. & P. Nõges, 2004. Light conditions in Lake Võrtsjärv. In Haberman, J., E. Pihu & A. Raukas (eds), Lake Võrtsjärv. Estonian Encyclopaedia publishers, Tallinn: 141–149.
Runkel, R. L., C. G. Crawford & T. A. Cohn, 2004. Load Estimator (LOADEST): A FORTRAN Program for Estimating Constituent Loads in Streams and Rivers: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods Book 4, Chapter A5, 69 pp.
Schilling, K. & Y.-K. Zhang, 2004. Baseflow contribution to nitrate–nitrogen export from a large, agricultural watershed, USA. Journal of Hydrology 295: 303–316.
Seitzinger, S., J. A. Harrison, J. K. Böhlke, A. F. Bouwman, R. Lowrance, B. Peterson, C. Tobias & G. Van Drecht, 2006. Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes: a synthesis. Ecological Applications 16: 2064–2090.
Sloto, R. A. & M. Y. Crouse, 1996. HYSEP: a computer program for streamflow hydrograph separation and analysis. Water-Resources Investigations. Report 96–4040, US Geological Survey, Reston, VA.
Watts, C. D., P. S. Naden, J. Machell & J. Banks, 2001. Long term variation in water colour from Yorkshire catchments. The Science of the Total Environment 278: 57–72.
Worrall, F., & T. Burt, 2004. Time series analysis of long-term river dissolved organic carbon records. Hydrological Processes 18: 893–912.
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research was provided by Estonian target funding project 03962480s03, by Estonian Science Foundation grant 5738 and by EC project CLIME (EVK1-CT-2002-00121). We used data obtained in frames of the State Monitoring Program of the Estonian Ministry of Environment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: T. Nõges, R. Eckmann, K. Kangur, P. Nõges, A. Reinart, G. Roll, H. Simola & M. Viljanen
European large lakes—Ecosystem changes and their ecological and socioeconomic impacts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamm, T., Nõges, T., Järvet, A. et al. Contributions of DOC from surface and groundflow into Lake Võrtsjärv (Estonia). Hydrobiologia 599, 213–220 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9189-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9189-8