Abstract
Diatom analyses of sediment cores extracted from three lakes in coastal southeastern South Australia reveal that, for most of the mid-late Holocene, they were shallow, brackish to saline systems with limited flow of water from continental sources. The construction of a substantial network of drains in the early years of settlement, to maximise transportation and agricultural production through wet winters, lead to abrupt freshening of the lakes. Interestingly, despite substantial nutrient loads to Lake Bonney SE (there are two Lakes Bonney and Frome in South Australia, which is why the lakes in the southeast of the state are differentiated with ‘SE’) associated with the commissioning and expansion of pulp and paper mills, a wastewater treatment plant discharge and agricultural runoff, there is only moderate evidence of nutrient enrichment in the lake, possibly because the post-impact assemblages are dominated by taxa with broad ecological preferences. Despite being preserved within a conservation park, eutrophication associated with agriculture is evident in the diatom assemblages of Lake Frome SE, which has a catchment more than twice that of Lake Bonney SE. Mullins Swamp, on the other hand, supports few indicators of eutrophic conditions. The freshening of these lakes is against the tide of salinisation from rising saline groundwaters in most wetlands across southeastern Australia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird, E., 2000. Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester.
Bennion, H., 1994. A diatom-phosphorous transfer function for shallow, eutrophic ponds in southest England. Hydrobiologia 275/276: 391–410.
Bennion, H., P. G. Appleby & G. L. Phillips, 2001. Reconstructing nutrient histories in the Norfolk Broads, UK: implications for the role of diatom-total phosphorus transfer functions in shallow lakes management. Journal of Paleolimnology 26: 181–204.
Chambers, J. W. & N. G. Cameron, 2001. A rod-less piston corer for lake sediments: an improved, rope-operated percussion corer. Journal of Paleolimnology 25: 117–122.
Commonwealth of Australia, (2001) Australia: State of the Environment 2001. CSIRO, Canberra, Australia.
Croft, T., G. House, A. Oppermann, A. Shaw Rungie & T. Zubrinich, 1999. Biodiversity Plan for the South East of South Australia: Summary. Department of Environment, Heritage and Aboriginal Affairs.
Dean, W., 1974. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 44(1): 242–248.
Dearing, J., 1994. Environmental Magnetic Susceptibility: Using the Bartington MS2 System. Chi Publishing, England.
Department for Environment and Heritage, 2003. Lake Frome SE Conservation Park Management Plan, South Australia. DEH, Adelaide.
Espinosa, M. A., 1994. Diatom paleoecology of the Mar Chiquita Lagoon delta, Argentina. Journal of Paleolimnology 10: 17–23.
Gasse, F., P. Barker, P. Gell, S. C. Fritz & F. Chalie, 1997. Diatom-Inferred Salinity in Palaeolakes: an indirect tracer of climate change. Quaternary Science Reviews 16: 547–563.
Gell, P. A., 1997. The development of diatom database for inferring lake salinity, Western Victoria, Australia: towards a quantitative approach for reconstructing past climates. Australian Journal of Botany 45: 389–423.
Gell, P., J. Tibby, J. Fluin, P. Leahy, M. Reid, K. Adamson, S. Bulpin, A. MacGregor, P Wallbrink, G. Hancock & B. Walsh, 2005. Accessing limnological change and variability using fossil diatom assemblages, south-east Australia. River Research and Applications 21: 257–269.
Glover, B. 1975. Lake Bonney SE (S.E.) Ecological Study. Engineering and Water Supply Department, Report No. 3662/70.
Grimm, E. C., 1987. CONISS: a FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Computers and Geosciences 13: 13–35.
Grimm, E. C., 1993. TILIA Version 2.0.b.4. Illinois State Museum, Research and Collections Centre.
Holmes, J. W. & J. D. Waterhouse, 1983. Hydrology. In Tyler, M. J., C. R. Twidale, J. K. Ling & J. W. Holmes (eds), Natural History of the South East. Occasional Publications of the Royal Society of South Australia Inc., Adelaide.
Hynynen, J., A. Palomaki, J. Merilainen, A. Witick & K. Mantykoski, 2004. Pollution history and recovery of a boreal lake exposed to a heavy bleached pulping effluent load. Journal of Paleolimnology 32: 351–374.
Jones, R. N., T. A. McMahon & J. M. Bowler, 2001. Modelling historical lake levels and recent climate change at three closed lakes, Western Victoria, Australia (c.1840– 990). Journal of Hydrology 246: 159–180.
Jowsey, P. C., 1966. An improved peat sampler. New Phytologist 65: 245–248.
Juggins, S., 2003. C2 User guide. Software for ecological and palaeoecological data analysis and visualisation. University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK.
Kershaw, A. P., 1997. A modification of the Troels-Smith system of sediment description and portrayal. Quaternary Australasia 15: 63–66.
Kinhill Engineers Pty. Ltd., 1990. Apcel Pulp Mill Redevelopment Project. Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Consultants Report to Apcel Pty. Ltd. Adelaide, Concord Printing Pty. Ltd.
Lawrie, K. & M. A. J. Williams, 2004. Improving salinity hazard predictions by factoring in a range of human impacts in the context of climate change. In Roach, I.C. (ed.), Regolith, 2004. CRC LEME, 199–203.
Lepŝ, J. & P. Šmilauer, 2003. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Luttenton, M. & R. Lowe, 2006. Response of a lentic periphyton community to nutrient enrichment at low N:P ratios. Journal of Phycology 42: 1007–1015.
McCormac, F. G., A. G. Hogg, P. G. Blackwell, C. E. Buck, T. F. G. Higham & P. J. Reimer, 2004. SHCal04 Southern Hemisphere Calibration 0–11.0 cal kyr BP. Radiocarbon 46: 1087–1092.
Macumber, P. G., 1991. Interaction between groundwater and surface systems in northern Victoria. Department of Conservation and Environment, Melbourne.
Manning, P., 1990. Review of Water Quality and Biological Monitoring 1972–1990. Engineering and Water Supply Department, S.A., Adelaide.
Marks, J. & M. Power, 2001. Nutrient induced changes in the species composition od epiphytes on Cladophora glomerata Kűtz. (Chlorophyta). Hydrobiologia 450: 187–196.
Michelutti, N., M. Douglas & J. Smol, 2002. Tracking recent recovery from eutrophication in a high arctic lake (Meretta Lake, Cornwallis Island, Nunavut, Canada) using fossil diatom assemblages. Journal of Paleolimnology 28: 377–381.
Ogden, R. W. 1996. The impacts of farming and river regulation on billabongs of the southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Unpublished PhD thesis, Australian National University.
Radke, L., K. Howard & P. Gell, 2002. Chemical diversity in south-eastern Australian saline lakes I: geochemical causes. Marine and Freshwater Research 53: 941–959.
Radke, L., S. Juggins, S. Halse, P. De Dekker & T. Finston, 2003. Chemical diversity in south-eastern Australian saline lakes II: biotic implications. Marine and Freshwater Research 54: 895–912.
Reid, M. A., J. Tibby, D. Penny & P. Gell, 1995. The use of diatoms to assess past and present water quality. Australian Journal of Ecology 20: 57–64.
Schwebel, D. A. 1984. Quaternary stratigraphy and sea-level variation in the south-east of South Australia. In Thom, B. G. (ed.), Coastal Geomorphology in Australia. Academic Press, 291–311.
South East Drainage Board (SEDB), 1980a. Digging Through Time: A Display Illustrating the History of Drainage in the South-East of South Australia. SEDB, South Australia.
South East Drainage Board (SEDB), 1980b. Environmental Impact Study on the Effect of Drainage in the South East of South Australia. SEDB, South Australia.
Sonneman, J. A., C. J. Walsh, P. F. Breen & A. K. Sharpe, 2001. Effects of urbanization on streams of the Melbourne region, Victoria, Australia. II. Benthic diatom communities. Freshwater Biology 46(4): 553–565.
Stuiver, M. & P. J. Reimer, 2005. Radiocarbon calibration program CALIB rev5.0.2, http://calib.qub.ac.uk/calib/calib.html, accessed on 22.1.2007.
Sylvetre, F., B. Beck-Eichler, W. Duleba & J. Debenay, 2001. Modern benthic diatom distribution in a hypersaline coastal lagoon: the Lagoa de Araruama (R.J.), Brazil. Hydrobiologia 443: 213–231.
ter Braak, C. J. F. & P. Šmilauer, 1999. Canoco for Windows Version 4.02. Centre for Biometry, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Tibby, J., 2004. Development of a diatom-based model for inferring total phosphorus in southeastern Australian water storages. Journal of Paleolimnology 31: 23–36.
van Dam, H., A. Mertens & J. Sinkeldam, 1994. A coded checklist and eclogical indicator values of freshwater diatoms from the Netherlands. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 28(1): 117–133.
Verb, R. & M. Vis, 2000. Comparison of benthic diatom assemblages from streams draining abandoned and reclaimed coal mines and nonimpacted sites. Journal of North American Benthological Society 19(2): 274–288.
Vos, P. C. & H. Wolf, 1993. Diatoms as a tool for reconstructing sedimentary environments in coastal wetlands; methodological aspects. Hydrobiologia 269–270(1): 285–296.
Acknowledgements
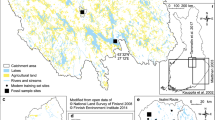
Dr. Frances Williams and Professor John Prescott undertook OSL analyses. Dr. Fiona Petchey, Radiocarbon Dating Laboratory, University of Waikato (NZ), provided the AMS-14C ages. Kimberly-Clark Australia supported the project in collaboration with the EPA (SA). Cameron Barr, Asta Cox, Fiona Little, Brendan Walsh and Craig McVeigh assisted with fieldwork. Chris Crothers drafted Figure 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haynes, D., Gell, P., Tibby, J. et al. Against the tide: the freshening of naturally saline coastal lakes, southeastern South Australia. Hydrobiologia 591, 165–183 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0802-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0802-7