Abstract
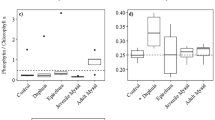
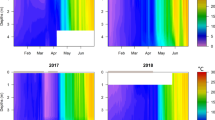
Plankton data from 1997 to 2005 were used to examine impacts of a managed draw-down, subsequent drought and resulting historic low water levels (during 2000 and 2001) on the zooplankton of Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Prior to the drought the lake supported less than 150 ha of submerged vegetation. Following the drought, over 15,000 ha of submerged vegetation developed around the lake shore and conditions favored greater survival of age 0 fish. The zooplankton changed significantly from the pre- to post-drought period, including: (a) a near-complete loss of all dominant species of cladocerans and rotifers; and (b) an abrupt transition to a community with over 80% of total biomass comprised of Arctodiaptomus dorsalis, a calanoid copepod previously described as being resistant to fish predation. These changes persisted over a 5 year post-drought sampling period. In contrast, there were no systematic changes in biomass of bacteria, phytoplankton, inedible cyanobacteria, algal cell size, suspended solids, or any other physical or chemical attributes known to affect zooplankton in shallow lakes. Evidence points towards increased predation by fish, and perhaps invertebrates, as factors responsible for loss of cladocerans and rotifers following the drought, and indicates a need for future research to link changes in water level to shifts in predation pressure in this and other shallow lakes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, 1989. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Auer, B., U. Elzer & H. Arndt, 2004. Comparison of pelagic food webs in lakes along a trophic gradient and with seasonal aspects: influence of resource and predation. Journal of Plankton Research 26: 697–709.
Bartsch, L. A., W. B. Richardson & M. B. Sandheinrich, 2004. Zebra mussels (Driessena polymorpha) limit food for larval fish (Pimephales promelas) in turbulent systems: a bioenergetics analysis. Hydrobiologia 495: 59–72.
Bays, J. S. & T. L. Crisman, 1983. Zooplankton and trophic state relationships in Florida lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 40: 1813–1819.
Beaver, J. R. & K. E. Havens, 1996. Seasonal and spatial variation in zooplankton community structure and their relation to possible controlling variables in Lake Okeechobee. Freshwater Biology 36: 45–56.
Benndorf, J. B., H. Schultz, A. Benndorf, A., R. Unger, E. Penz, H. Kneschke, K. Kossatz, R. Dumke, U. Hornig, R. Kruspe, S. Reichel & A. Kohler, 1988. Food-web manipulation by enhancement of piscivorous fish stocks: long-term effects in the hypereutrophic Bautzen Reservoir. Limnologica 19: 97–110.
Brandl, Z. & C. H. Fernando, 1978. Prey selection by the cyclopoid copepods Mesocyclops edax and Cyclops vicinus. Verhandlungen der Internationale Vereinigung der Limnologie 20: 2505–2510.
Brandl, Z. & C. H. Fernando, 1981. The impact of predation by cyclopoid copepods on zooplankton. Verhandlungen der Internationale Vereinigung der Limnologie 21: 1573–1577.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Bull, L. A., D. D. Fox, D. W. Brown, L. J. Davis, S. J. Miller & J. G. Wullschleger, 1995. Fish distribution in limnetic areas of Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Advances in Limnology 45: 333–342.
Chigbu, P., 2004. Assessment of the potential impact of the mysid shrimp, Neomysis mercedis, on Daphnia. Journal of Plankton Research 26: 295–306.
Crisman, T. L. & J. R. Beaver, 1990. Applicability of biomanipulation for managing eutrophication in the subtropics. Hydrobiologia 200: 177–185.
Dockendorf, K. J. & M. S. Allen, 2005. Age-0 black crappie abundance and size in relation to zooplankton density, stock abundance, and water clarity in three Florida lakes. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 134: 172–183.
Dodson, S. I., 1974. Zooplankton competition and predation: an experimental test of the size-efficiency hypothesis. Ecology 55: 605–613.
Elmore, J. L., B. C. Cowell & D. S. Vodopich, 1984. Biological communities of three subtropical Florida lakes of different trophic character. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 100: 455–478.
Gliwicz, Z. M. & W. Lampert, 1990. Food thresholds in Daphnia species in the absence and presence of blue-green filaments. Ecology 71: 691–702.
Guest, W. C., R. W. Drenner, S. T. Threlkeld, F. D. Martin & J. D. Smith, 1990. Effects of gizzard shad and threadfin shad on zooplankton and young-of-the-year white crappie production. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 100: 529–536.
Havens, K. E., 2003. Submerged aquatic vegetation correlations with depth and light attenuating materials in a shallow subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 493: 173–186.
Havens, K. E., T. L. East & J. R. Beaver, 1996. Experimental studies of zooplankton – phytoplankton—nutrient interactions in a large subtropical lake (Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA). Freshwater Biology 36: 579–597.
Havens, K. E., T. L. East, J. Marcus, P. Essex, B. Bolan, S. Raymond & J. R. Beaver, 2000. Dynamics of the exotic Daphnia lumholtzii and native macro-zooplankton in a subtropical chain-of-lakes in Florida, USA. Freshwater Biology 45: 21–32.
Havens, K. E., D. D. Fox, S. Gornak & C. Hanlon, 2005. Aquatic vegetation and largemouth bass population responses to water level variations in Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Hydrobiologia 539: 225–237.
Havens, K. E., M. C. Harwell, M. A. Brady, B. Sharfstein, T. L. East, A. J. Rodusky, D. Anson & R. P. Maki, 2002. Large-scale mapping and predictive modeling of submerged aquatic vegetation in a shallow eutrophic lake. The Scientific World Journal 2: 949–965.
Havens, K. E., E. J. Phlips, M. F. Cichra & B. L. Li, 1998. Light availability as a possible regulator of cyanobacteria species composition in a shallow subtropical lake. Freshwater Biology 39: 547–556.
Havens, K. E., B. Sharfstein, M. A. Brady, T. L. East, M. C. Harwell, R. P. Maki & A. J. Rodusky, 2004. Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical lake in Florida, USA. Aquatic Botany 78: 67–82.
Hessen, D. O., 1992. Nutrient element limitation of zooplankton production. American Naturalist 140: 799–814.
Hobbie, J. E., R. J. Daley & J. Jasper, 1977. Use of Nucleopore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 33: 1225–1228.
Holanov, S. H. & J. C. Tash, 1978. Particulate and filter feeding in threadfin shad, Dosoroma petenense, at different light intensities. Journal of Fish Biology 13: 619–625.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard & T. Lauridsen, 1997. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 342: 151–164.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, K. E. Havens, O. Anneville, L. Carvalho, M. F. Coveney, R. Deneke, M. T. Dokulil, R. Foy, D. Gerdeaux, S. E. Hampton, S. Hilt, K. Kangur, J. Kohler, E. H. H. R. Lammens, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Manca, M. R. Miracle, B. Moss, P. Noges, G. Persson, G. Phillips, R. Portielge, S. Romo, C. L. Schelske, D. Straile, I. Tatrai, E. Willen & M. Widner, 2005a. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading – an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50: 1747–1771.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, C. Branco, B. Huszar & F. Scasso, 2005b. Lake restoration and biomanipulation in temperate lakes: relevance for subtropical and tropical lakes. In Reddy, M. V. (ed.). Tropical Eutrophic Lakes: Their Restoration and Management. Science Publishers, Enfield, 331–359.
Jones, B. I., 1987. Lake Okeechobee eutrophication research and management. Aquatics 9: 21–26.
Kirk, K. L. & J. J. Gilbert, 1990. Suspended clay and the population dynamics of planktonic rotifers and cladocerans. Ecology 71: 1741–1755.
Lund, J. W. G., C. Kipling & E. D. LeCren, 1958. The inverted microscope method for estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis for estimations by counting. Hydrobiologia 11: 393–424.
McCauley, E., 1984. The estimation of the abundance and biomass of zooplankton in samples. In Downing, J. A. & F. H. Rigler (eds), A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivity in Fresh Waters. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, 228–265.
Meerhoff, M., J. M. Clemente, F. Teixeira de Mello, C. Iglesias, A. R. Pedersen & E. Jeppesen (in press). Littoral trophic structure and effects on aquatic plants differ substantially between temperate and subtropical shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology.
Mitra, A. & K. J. Flynn, 2005. Predator-prey interactions: is ecological stoichiometry sufficient when good food goes bad? Journal of Plankton Research 27: 393–399.
Moss, B., J. Madgwick & G. Phillips, 1997. A guide to the restoration of nutrient-enriched shallow lakes. W.W. Hawes, U.K.
Nordlie, F. G., 1976. Plankton communities of three central Florida lakes. Hydrobiologia 48: 65–78.
Ortega-Mayagoitia, E., X. Armengol & C. Rojo, 2000. Structure and dynamics of zooplankton in a semi-arid wetland, the national park of Las Tablas de Daimiel (Spain). Wetlands 20: 629–638.
Phlips, E. J., F. J. Aldridge, P. Hansen, P. V. Zimba, J. Ihnat, M. Conroy & P. Ritter, 1993. Spatial and temporal variability of trophic state parameters in a shallow subtropical lake (Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 128: 437–458.
PlaВman, T., G. Maier & H. B. Stich, 1997. Predation impact of Cyclops vicinus on the rotifer community in Lake Constance in spring. Journal of Plankton Research 19: 1069–1079.
Riessen, H. P., W. J. O’Brien & B. Loveless, 1984. An analysis of the components of Chaoborus predation on zooplankton and the calculation of relative prey vulnerabilities. Ecology 65: 514–522.
Rogers, M. & M. Allen (in press). Affects of altered hydrology on ecosystem resilience to hurricanes. Ecosystems.
Schriver, P., J. Bøgestrand, E. Jeppesen & M. Søndergaard, 1995. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions: large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshwater Biology 33: 255–270.
Stansfield, J. H., M. R. Perrow, L. D. Tenchm, A. J. D. Jowitt & A. A. L. Taylor, 1997. Submerged macrophytes as refuges for grazing Cladocera against fish predation: observations on seasonal changes in relation to macrophyte cover and predation pressure. Hydrobiologia 342: 229–240.
Tugend, K. I. & M. S. Allen, 2000. Temporal dynamics of zooplankton community composition and mean size at Lake Wauberg, Florida. Florida Scientist 63: 142–154.
Warren, G. L., M. J. Vogel & D. D. Fox, 1995. Trophic and distributional dynamics of Lake Okeechobee sublittoral benthic invertebrate communities. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Advances in Limnology 45: 317–332.
Williamson, C., 1984. Laboratory and field experiments on the feeding ecology of the cyclopoid copepod Mesocyclops edax. Freshwater Biology 14: 575–585.
Williamson, C., 1986. The swimming and feeding behavior of Mesocyclops. Hydrobiologia 134: 11–19.
Young, J. D. & H. P. Riessen, 2005. The interaction of Chaoborus size and vertical distribution determines predation effects on Daphnia. Freshwater Biology 50: 993–1006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: S.I. Dodson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havens, K.E., East, T.L. & Beaver, J.R. Zooplankton response to extreme drought in a large subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 589, 187–198 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0738-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0738-y