Abstract
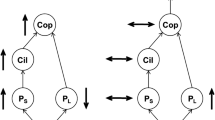
We developed a mechanistic model of nutrient, phytoplankton, zooplankton and fish interactions to test the effects of phytoplankton food quality for herbivorous zooplankton on planktonic food web processes. When phytoplankton food quality is high strong trophic cascades suppress phytoplankton biomass, the zooplankton can withstand intense zooplanktivory, and energy is efficiently transferred through the food web sustaining higher trophic level production. Low food quality results in trophic decoupling at the plant-animal interface, with phytoplankton biomass determined primarily by nutrient availability, zooplankton easily eliminated by fish predation, and poor energy transfer through the food web. At a given nutrient availability, food quality and zooplanktivory interact to determine zooplankton biomass which in turn determines algal biomass. High food quality resulted in intense zooplankton grazing which favored fast-growing phytoplankton taxa, whereas fish predation favored slow-growing phytoplankton. These results suggest algal food quality for herbivorous zooplankton can strongly influence the nature of aquatic food web dynamics, and can have profound effects on water quality and fisheries production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren, G., 1987. Temperature functions in biology and their application to algal growth constants. Oikos 49: 177–190.
Arditi, R. & L. R. Ginzburg, 1989. Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. Journal of Theoretical Biology 139: 311–326.
Arhonditsis, G. B. & M. T. Brett, 2004. Evaluation of the current state of mechanistic aquatic biogeochemical modeling. Marine Ecology Progress Series 271: 13–26.
Arhonditsis, G. B. & M. T. Brett, 2005. Eutrophication model for Lake Washington (USA): part I—Model description and sensitivity analysis. Ecological Modelling 187: 140–178.
Arhonditsis, G., M. T. Brett & J. Frodge, 2003. Environmental control and limnological impacts of a large recurrent spring bloom in Lake Washington, USA. Environmental Management. 31: 603–618.
Boersma, M. & J. Vijverberg, 1994. Resource depression in Daphnia galeata, Daphnia cucullata and their interspecific hybrid: life history consequences. Journal of Plankton Research 16: 1741–1758.
Brendonck, L., L. De-Meester & N. G. Hairston Jr. (ed.). 1998. Evolutionary and ecological aspects of crustacean diapause. Archiv für Hydrobiologie—Advances in Limnology, 52.
Brett, M. T., L. Martin & T. J. Kawecki, 1992. An experimental test of the egg-ratio method-Estimated versus observed death rates. Freshwater Biology 28: 237–248.
Brett, M. T. & C. R. Goldman, 1996. A meta-analysis of the freshwater trophic cascade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 7723–7726.
Brett, M. T. & C. R. Goldman, 1997. Consumer versus resource control in freshwater pelagic food webs. Science 275: 384–386.
Brett, M. T. & D. C. Müller-Navarra, 1997. The role of highly unsaturated fatty acids in aquatic food-web processes. Freshwater Biology 38: 483–499.
Brett, M. T., D. C. Müller-Navarra & S.-K. Park, 2000. Empirical analysis of the effect of phosphorus limitation on algal food quality for freshwater zooplankton. Limnology & Oceanography 45: 1564–1575.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size and the composition of the plankton. Science 150: 28.
Carmichael, W. W., 1994. The toxins of cyanobacteria. Scientific American January, 78–102.
Carpenter, S. R., J. F. Kitchell & J. R. Hodgson, 1985. Cascading trophic interactions and lake productivity. BioScience 35: 634–639.
Chapra, S. C., 1997. Surface Water-Quality Modeling. McGraw-Hill, New York, New York, USA, 784 pp.
DeMelo, R., R. France & D. J. McQueen, 1992. Biomanipulation: hit or myth? Limnology & Oceanography 37: 192–207.
Elser, J. J., W. F. Fagan, R. F. Denno, D. R. Dobberfuhl, A. Folarin, A. Huberty, S. Interlandi, S. S. Kilham, E. McCauley, K. L. Schulz, E. H. Siemann & R. W. Sterner, 2000. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 408: 578–580.
Falconer, I. R., 1999. An overview of problems caused by toxic blue–green algae (cyanobacteria) in drinking and recreational water. Environmental Toxicology 14: 5–12.
Fasham, M. J. R., H. W. Ducklow & S. M. McKelvie, 1990. A nitrogen-based model of plankton dynamics in the oceanic mixed layer. Journal of Marine Research 48: 591–639.
Gasol, J. M., P. A. del Giorgio & C. M. Duarte, 1997. Biomass distribution in marine planktonic communities. Limnology & Oceanography 42: 1353–1363.
Grover, J. P., 1989. Phosphorus-dependent growth-kinetics of 11 species of freshwater algae. Limnology & Oceanography 34: 341–348.
Grover, J. P., 1991. Resource competition in a variable environment-phytoplankton growing according to the variable-internal-stores model. American Naturalist 138: 811–835.
Grover, J. P., 1995. Competition, herbivory, and enrichment: nutrient-based models for edible and inedible plants. American Naturalist 145: 746–774.
Hansson, L. A., 1996. Algal recruitment from lake sediments in relation to grazing, sinking, and dominance patterns in the phytoplankton community. Limnology & Oceanography 41: 1312–1323.
Harris, G. P., 1994. Pattern, process and prediction on aquatic ecology. A limnological view of some general ecological problems. Freshwater Biology 32: 143–160.
Jónasdóttir, S. H., 1994. Effects of food quality on the reproductive success of Acartia tonsa and Acartia hudsonica: laboratory observations. Marine Biology 121: 67–81.
Jorgensen, S. E., S. N. Nielsen & L. A. Jorgensen, 1991. Handbook of Ecological Parameters and Ecotoxicology. Pergamon Press, Amsterdam.
Kerfoot, W. C., C. Levitan & W. R. DeMott, 1988. Daphnia-phytoplankton interactions: density-dependent shifts in resource quality. Ecology 69: 1806–1825.
Kleppel, G. S., C. A. Burkart & L. Houchin, 1998. Nutrition and the regulation of egg production in the calanoid copepod Acartia tonsa. Limnology & Oceanography 43: 1000–1007.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems. Second edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Lampert, W., 1981. Inhibitory and toxic effects of blue-green algae on Daphnia. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 66: 285–288.
Lampert, W., 1987. Laboratory studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 483–490.
Lampert, W., W. Fleckner, H. Rai & B. E. Taylor, 1986. Phytoplankton control by grazing zooplankton: a study on the spring clear water phase. Limnology & Oceanography 31: 478.
Lampert, W. & U. Sommer, 1997. Limnoecology: The Ecology of Lakes and Streams. Oxford University Press, New York, USA, 382.
Leibold, M. A., 1989. Resource edibility and the effects of predators and productivity on the outcome of the trophic interactions. American Naturalist 134: 922–949.
Loladze, I., Y. Kuang & J. J. Elser, 2000. Stoichiometry in producer-grazer systems: linking energy flow with element cycling. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 62: 1137–1162.
McQueen, D. J., J. R. Post & E. L. Mills, 1986. Trophic relationships in freshwater pelagic ecosystems. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 43: 1571–1581.
Micheli, F., 1999. Eutrophication, fisheries, and consumer-resource dynamics in marine pelagic ecosystems. Science 285: 1396–1398.
Muller, E. B., R. M. Nisbet, S. A. L. M. Koojman, J. J. Elser & E. McCauley, 2001. Stoichiometric food quality and herbivore dynamics. Ecology Letters 4: 519–529.
Müller-Navarra, D. C., M. T. Brett, A. Liston & C. R. Goldman, 2000. A highly unsaturated fatty acid predicts carbon transfer between primary producers and consumers. Nature 403: 74–77.
Müller-Navarra, D. C., M. T. Brett, S.-K. Park, S. Chandra, A. P. Ballantyne, E. Zorita & C. R. Goldman, 2004. Unsaturated fatty acid content in seston and tropho-dynamic coupling in lakes. Nature 427: 69–72.
Oksanen, L., S. D. Fretwell, J. A. Arruda & P. Niemela, 1981. Exploitation ecosystems in gradients of primary productivity. American Naturalist 118: 240–261.
Pauly, D. & V. Christensen, 1995. Primary production required to sustain global fisheries. Nature 374: 255–257.
Polis, G. A., L. W. Sears-Anna, G. R. Huxel, D. R. Strong & J. L. Maron, 2000. When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 15: 473–475.
Ravet, J. L. & M. T. Brett, 2006. Essential fatty acid and phytoplankton phosphorus content constraints on Daphnia somatic growth and reproduction. Limnology & Oceanography 51: 2438–2452.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Sarnelle, O., 1996. Predicting the outcome of trophic manipulation in lakes-a comment on Harris (1994). Freshwater Biology 35: 339–342.
Schoenberg, S. A. & R. E. Carlson, 1984. Direct and indirect effects of zooplankton grazing on phytoplankton in a hypereutrophic lake. Oikos 42: 291–302.
Sommer, U., Z. M. Gliwicz, W. Lampert & A. Duncan, 1986. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 106: 433–471.
Straile, D., 1997. Gross growth efficiencies of protozoan and metazoan zooplankton and their dependence on food concntration, predator-prey weight ration, and taxonomic group. Limnology & Oceanography 42: 1375–1385.
Sterner, R. W. & D. O. Hessen, 1994. Algal nutrient limitation and the nutrition of aquatic herbivores. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics 25: 1–25.
Tilman, D., 1982. Resource Competition and Community Structure: Monographs in Population Biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Vollenweider, R. A., 1976. Advances in defining critical loading levels for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Memorie dell’Istituto Italiano d’Idrobiologia 33: 53–83.
von Elert, E., D. Martin-Creuzburg & J. R. Le Coz, 2003. Absence of sterols constrains carbon transfer between cyanobacteria and a freshwater herbivore (Daphnia galeata). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B-Biological Sciences, 270: 1209–1214.
Welch, E. B., 1992. Ecological Effects of Wastewater. Chapman & Hall, London, UK.
Zar, J. H., 1999. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 663 pp.
Zison, S. W., W. B. Mills, D. Diemer & C. W. Chen, 1978. Rates, Constants, and Kinetic Formulations in Surface Water Quality Modeling. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 317 pp.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NSF grant DEB-0075616 to MTB and a University of Washington Valle Scandinavian Exchange Fellowship to MGD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: D. Hamilton
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danielsdottir, M.G., Brett, M.T. & Arhonditsis, G.B. Phytoplankton food quality control of planktonic food web processes. Hydrobiologia 589, 29–41 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0714-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0714-6