Abstract
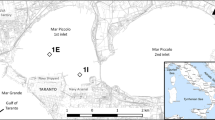
Depth profiles of Fe, Mn, (HS)t, Cu and Cd concentrations in pore water were determined on a seasonal scale in intertidal sediments of Ria Formosa. Concentrations of Cu and Cd were also determined in near-bottom water during the short period that water inundates the sediment. A maximum near the sediment-water interface was observed in depth profiles of Mn and Fe concentrations followed by a decrease with depth. Otherwise, depth profiles of (HS−)t were irregular but peak concentrations was observed below Mn and Fe maximum. Although subsurface maximum was observed at deeper layers for Cu and Cd, the profiles shape varied among sites and sampling dates. This suggests site specificity and alterations associated with early diagenetic reactions. In order to assess exchanges of Cu and Cd across the sediment water interface, diffusive fluxes and advective transport were estimated. Both contribute substantially to the daily transfer of Cd from intertidal sediments to the water column of Ria Formosa. In the case of Cu, the flux associated with tidal flooding (advective flux) was the major contributor. Presumably, the exchange of trace elements between the sediment-water interface in intertidal areas of macro- and meso-tidal systems are underestimated since do not take into consideration the pulse contribution associated with tidal flooding.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, R., 1994. The sedimentary Mn cycle in long island sound: Its role as intermediate oxidant and the influence of bioturbation, O2 and Corg flux on diagenetic reaction balances. Journal of Marine Research 52: 259–295.
Aller, R., 1998. Mobile deltaic and continental shelf muds as suboxic, fluidized bed reactors. Marine Chemistry 61: 143–155.
Anschutz, P., B. Sundby, L. Lefrançois, G. Luther & A. Mucci, 2000. Interactions between metal oxides and species of nitrogen and iodine in bioturbated marine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 64: 2751–2763.
Bebianno, M., 1995. Effects of pollutants in the Ria Formosa lagoon, Portugal. Science of the Total Environment 171: 107–115.
Bebianno, M. & A. Serafim, 2003. Variation of metal and metallothionein concentrations in a natural population of Ruditapes decussatus. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 44: 53–66.
Benjamin, M. & J. Leckie, 1981. Multiple-site adsorption of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb on amorphous iron oxyhydroxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 79: 209-221.
Berner, R., 1980. Early diagenesis. A Theoretical Approach. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
Blasco, J., V. Sáenz & A. Gómez-Parra, 2000. Heavy metal fluxes at sediment–water interface of three coastal ecosystems from south-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Science of Total Environment 247: 189–199.
Brotas, V., A. Ferreira, C. Vale & F. Catarino, 1990. Oxygen profiles in intertidal sediments of Ria Formosa (S. Portugal). Hydrobiologia 207: 123–129.
Caetano, M., (1998). Biogeoquímica do manganês, ferro, cobre e cádmio em sedimentos da Ria Formosa. [PhD Thesis]. Universidade de Algarve, Faro.
Caetano, M., M. Falcão, C. Vale & M. Bebianno, 1997. Tidal flushing of ammonium, iron and manganese from inter-tidal sediment pore waters. Marine Chemistry 58: 203–211.
Caetano, M., M. Madureira, C. Vale, M. Bebianno & M. Gonçalves, 1995. Variations of Mn, Fe and S concentrations in sediment pore waters of Ria Formosa at different time scales. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 29: 275–281.
Caetano, M. & C. Vale, 2003. Trace elemental composition of seston and plankton along the portuguese coast. Acta Oecologica 24: S341–S349.
Caetano, M., C. Vale & M. Bebianno, 2002. Distribution of Fe, Mn, Cu and Cd in upper sediments and sediment-trap material of Ria Formosa (Portugal). Journal of Coastal Research SI36: 118–123.
Cheevaporn, V., G. Jacinto & M. san Diego-McGlone, 1995. Heavy metals in Bang Pakong River Estuary, Thailand: sedimentary vs diffusive fluxes. Marine Pollution Bulletin 31: 290–294.
Ciceri, G., S. Maran, W. Martinotti & G. Queirazza, 1992. Geochemical cycling of heavy metals in a marine coastal area: benthic flux determination from pore water profiles and in situ measurements using benthic chambers. Hydrobiologia 235: 501–517.
Dai, M., J.-M. Martin & G. Cauwet, 1995. The significance role of colloids in the transport and transformation of organic carbon and associated metals (Cd, Cu and Ni) in the Rhone delta (France). Marine Chemistry 51: 159–175.
Danielsson, L., B. Magnusson & S. Westerlund, 1978. An improved metal extraction procedure for the determination of trace metals in sea water by atomic absorption spectrometry with electrotermal atomization. Analytica Chimica Acta 98: 47–57.
Davies-Colley, R., P. Nelson & K. Williamson, 1985. Sulfide control of cadmium and copper concentrations in anaerobic estuarine sediments. Marine Chemistry 16: 173–186.
Dhakar, S. & D. Burdige, 1996. A coupled, non-linear, steady state model for diagenetic processes in pelagic sediments. American Journal of Science 296: 296–330.
Falcão, M. & C. Vale, 1990. Study of the Ria Formosa ecosystem: benthic nutrient remineralization and tidal variability of nutrients in the water. Hydrobiologia 207: 137–146.
Falcão, M. & C. Vale, 1995. Tidal flushing of ammonium from intertidal sediments of Ria Formosa, Portugal. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 29: 239–244.
Fones, G., W. Davison & J. Hamilton-Taylor, 2004. The fine scale remobilization of metals in the surface sediment of the North-East Atlantic. Continental Shelf Research 24: 1485–1504.
Gobeil, C., N. Silverberg, B. Sundby & D. Cossa, 1987. Cadmium diagenesis in Laurentian trough sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 51: 589–596.
Hemond, H., W. Nuttle, R. Burke & K. Stolzenbach, 1984. Surface infiltration in salt marshes: Theory, measurement, and biogeochemical implications. Water Resources Research 20: 591-600.
Huettel, M., W. Ziebis, S. Forster & G. Luther, 1998. Advective transport affecting metal and nutrient distributions and interfacial fluxes in permeable sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 62: 613–631.
Hyacinthe, C., P. Anschutz, P. Carbonel, J. Jouanneau & F. Jorinssen, 2001. Early diagenetic processes in muddy sediments of the Bay of Biscay. Marine Geology 177: 111-128.
Kerner, M. & K. Wallmann, 1992. Remobilization events involving Cd and Zn from intertidal flat sediments in the Elbe estuary during the tidal cycle. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 35: 371–393.
Li, Y. & S. Gregory, 1974. Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 38: 703–714.
Luther, G., A. Giblin & R. Varsolona, 1985. Polarographic analysis of sulphur species in marine porewater. Limnology and Oceanography 30: 727–736.
Luther, G. & E. Tsamakis, 1989. Concentration and form of dissolved sulphide in the oxic water column of the ocean. Marine Chemistry 27: 165–177.
Naylor, C., W. Davison, M. Motelica-Heino, G. van Den Berg & L. van der Heijdt, 2004. Simultaneous release of sulfide with Fe, Mn, Ni and Zn in marine harbour sediment measured using metal/sulphide DGT probe. Science of the Total Environment 328: 275–286.
Petersen, W., K. Wallman, L. Pinglin, F. Schroeder & H. Knauth, 1995. Exchange of trace elements at the sediment–water interface during early diagenesis processes. Marine Freshwater Research 46: 19–26.
Rocha, C., 1997. Rhythmic ammonium regeneration and flushing in intertidal sediments of the Sado estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 823–831.
Shaw, T., J. Gieskes & R. Jahnke, 1990. Early diagenesis in different depositional environments: The response of transition metals in pore water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 54: 1233–1246.
Skrabal, S., J. Donat & D. Burdige, 2000. Pore water distributions of dissolved copper and copper-complexing ligands in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 64: 1843–1857.
Sundby, B., P. Martinez & C. Gobeil, 2004. Comparative geochemistry of cadmium, rhenium, uranium and molybdenum in continental margin sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 68: 2485–2494.
Tessier, A., D. Fortin, N. Belzile, R. De Vitre & G. Leppard, 1996. Metal sorption to diagenetic iron and manganese oxyhydroxides and associated organic matter: narrowing the gap between field and laboratory measurements. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 60: 387–404.
Thomson, J., S. Nixon, I. Croudace, T. Pedersen, L. Brown, G. Cook & A. MacKenzie, 2001. Redox-sensitive element uptake in North-East Atlantic ocean sediments (benthic boundary layer experiment sites). Earth and Planetary Science Letters 184: 535–547.
Van Cappellen, P. & Y. Wang, 1996. Cycling of iron and manganese in surface sediments: A general theory for the coupled transport and reaction of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, iron and manganese. American Journal of Science 296: 197–243.
Winderlund, A., 1996. Early diagenetic remobilization of copper in near-shore marine sediments: a quantitative pore-water model. Marine Chemistry 54: 41–53.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank their colleague, Miguel Quintans for helping with fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caetano, M., Madureira, MJ. & Vale, C. Exchange of Cu and Cd across the sediment-water interface in intertidal mud flats from Ria Formosa (Portugal). Hydrobiologia 587, 147–155 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0673-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0673-y