Abstract
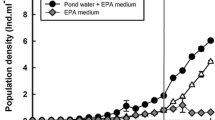
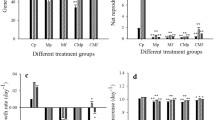
We evaluated the combined effects of food (0.5 × 106, 1.0 × 106 and 2.0 × 106 cells ml−1 of Chlorella vulgaris) and temperature (15, 20 and 25 °C) on life history variables of B. havanaensis. Regardless of Chlorella density there was a steep fall in the survivorship of B. havanaensis at 25 °C. Both food level and temperature affected the fecundity of B. havanaensis. At any given food level, rotifers cultured at 15 °C showed extended but low offspring production. At 25 °C, offspring production was elevated, the duration of egg laying reduced and the fecundity was higher during the latter part of the reproductive period. The effect of food level was generally additive, at any given temperature, and higher densities of Chlorella resulted in higher offspring production. Average lifespan, life expectancy at birth and generation time were 2–3 times longer at 15 °C than at 25 °C. At 20 °C, these remained at intermediate levels. The shortest generation time (about 4 days) was observed at 25 °C. Gross and net reproductive rates and the rate of population increase (r) increased with increasing temperature and generally, at any given temperature, higher algal food levels contributed to higher values in these variables. The r varied from 0.11 to 0.66. The survival patterns and lower rates of reproduction at 15 °C suggest that the winter temperatures (10–15 °C) prevailing in many waterbodies in Mexico City allow this species to sustain throughout the year under natural conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. H. Ahlstrom (1940) ArticleTitleA revision of the rotatorian genera Brachionus and Platyias with descriptions of the new species and two new varieties Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 57 143–184
A. Anaya-Soto S. S. S. Sarma S. Nandini (2003) ArticleTitleLongevity of the freshwater anostracan Streptocephalus mackini (Crustacea: Anostraca) in relation to food (Chlorella vulgaris) concentration Freshwater Biology 48 432–439 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01015.x
Anonymous, 1985. Methods of Measuring the acute Toxicity of Effluents to Freshwater and Marine Organisms. US Environment Protection Agency. EPA/600&4–85/013
M. A. Borowitzka L. J. Borowitzka (1988) Micro-algal Biotechnology Cambridge University Press London
W. R. De Mott R. D. Gulati E. Van Donk ParticleVan (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of dietary phosphorus deficiency on the abundance, phosphorus balance, and growth of Daphnia cucullata in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes Limnology and Oceanography 46 1871–1880
M. Ridder ParticleDe (1981) ArticleTitleSome considerations on the geographical distribution of rotifers Hydrobiologia 85 209–225 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00017611
A. Duncan (1989) ArticleTitleFood limitation and body size in the life cycle of planktonic rotifers and cladocerans Hydrobiologia 186/187 11–28 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00048891
W. T. Edmondson (1965) ArticleTitleReproductive rate of planktonic rotifers as related to food and temperature Ecological Monographs 35 61–111
C. Enrique-García S. Nandini S. S. S. Sarma (2003) ArticleTitleFood type effects on the population growth patterns of littoral rotifers and cladocerans Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica 31 120–133 Occurrence Handle10.1002/aheh.200300480
V. E. Forbes P. Calow (1999) ArticleTitleIs the per capita rate of increase a good measure of population-level effects in ecotoxicology? Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 18 1544–1556 Occurrence Handle10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<1544:ITPCRO>2.3.CO;2
G. Garza-Mouriño M. Silva-Briano S. Nandini S. S. S. Sarma M. E. Castellanos-Páez (2005) ArticleTitleMorphological and morphometrical variations of selected rotifer species in responce to predation: a seasonal study of selected brachionid species from Lake Xochimilco (Mexico) Hydrobiologia 546 169–179
C. N. Guisande Mazuelos (1991) ArticleTitleReproductive pattern of Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas at different food concentrations Journal of Plankton Research 13 279–286
R. D. Gulati W. R. DeMott (1999) ArticleTitleThe role of food quality for zooplankton: remarks on the state-of-the-art, perspectives and priorities Freshwater Biology 38 753–768 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.00275.x
U. Halbach (1973) Life table data and population dynamics of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas as influenced by periodically oscillating temperature W Wieser (Eds) Effects of Temperature on Ectothermic Organisms Springer Verlag Berlin 219–228
Flores-Burgos, F., S. S. S. Sarma & S. Nandini, 2003. Estudio preliminar sobre la fauna de rotı’ feros de Xochimilco (Me’ xico). El agua de cuenca de Me’ xico. Sus problemas histo’ ricos y perspectivas de solucio’ n. Proceedings of the International Conference on XochimilcoEcological Park of Xochimilco, U.A.M. Xochimilco, Mexico City, Mexico, Vol. 1, 163–171.
C. E. King (1982) The evolution of lifespan H. J. P. Dingle Hegmann (Eds) Evolution and Genetics of Life Histories Springer Verlag New York 121–128
C. J. Krebs (1985) Ecology EditionNumber3 Harper & Row New York 800
S. Nandini R. Pérez-Chávez S. S. S. Sarma (2003) ArticleTitleThe effect of prey morphology on the feeding behaviour and population growth of the predatory rotifer Asplanchna sieboldi: a case study using five species of Brachionus (Rotifera) Freshwater Biology 48 2131–2140 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01149.x
T. Nogrady R. L. Wallace T. W. Snell (1993) Rotifera 1. Biology, Ecology and Systematics. Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World, NumberInSeriesVol. 84. SBP Academic Publishers The Hague 142
P. Ramírez-García S. Nandini S. S. S. Sarma E. Robles-Valderrama I. Cuesta D. Hurtado-Maria (2002) ArticleTitleSeasonal variations of zooplankton abundance in the freshwater reservoir Valle de Bravo (Mexico) Hydrobiologia 467 99–108 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014953119507
E. Ramos-Rodríguez J. M. Conde-Porcuna (2003) ArticleTitleNutrient limitation on a planktonic rotifer: life history consequences and starvation resistance Limnology and Oceanography 48 933–938
K. O. Rothhaupt (1990) ArticleTitlePopulation growth rates of two closely related rotifer species: effects of food quantity, particle size, and nutritional quality Freshwater Biology 23 561–570
L. O. Sanoamuang (1993) ArticleTitleThe effect of temperature on morphology, life history and growth rate of Filinia terminalis (Plate) and Filinia cf. pejleri Hutchinson in culture Freshwater Biology 30 257–267
S. S. S. Sarma T. R. Rao (1990) ArticleTitleThe population dynamics of Brachionus patulus Müller in relation to food and temperature Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences (Animal Sciences) 99 335–343
S. S. S. Sarma T. R. Rao (1991) ArticleTitleThe combined effects of food and temperature on the life history parameters of Brachionus patulus Muller (Rotifera) Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie 76 225–239
S. S. S. Sarma S. Nandini (2001) ArticleTitleLife table demography and population growth of Brachionus variabilis Hampel, 1896 in relation to algal (Chlorella vulgaris) density Hydrobiologia 446/447 75–83 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017577206815
S. S. S. Sarma S. Nandini (2002) ArticleTitleComparative life table demography and population growth of Brachionus macracanthus Daday, 1905 and Platyias quadricornis Ehrenberg, 1832 (Rotifera, Brachionidae) in relation to algal (Chlorella vulgaris) food density Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica 30 128–140 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1521-401X(200211)30:2/3<128::AID-AHEH128>3.0.CO;2-W
S. S. S. Sarma M. A. Fernández-Araiza S. Nandini (1999) ArticleTitleCompetition between Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas and Brachionus patulus (Müller) (Rotifera) in relation to algal food concentration and initial population density Aquatic Ecology 33 339–345 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009912816400
S. S. S. Sarma P. S. Larios-Jurado S. Nandini (2001) ArticleTitleEffect of three food types on the population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus and Brachionus patulus (Rotifera: Brachionidae) Revista de Biología Tropical 49 75–82
S. S. S. Sarma E. L. Pavón-Meza S. Nandini (2003a) ArticleTitleComparative population growth and life table demography of the rotifer Asplanchna girodi at different prey (Brachionus calyciflorus and Brachionus havanaensis) (Rotifera) densities Hydrobiologia 491 309–320 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1024440610204
S. S. S. Sarma H. E. Trujillo-Hernández S. Nandini (2003b) ArticleTitlePopulation growth of herbivorous rotifers and their predator (Asplanchna) on urban wastewaters Aquatic Ecology 37 243–250 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025896703470
R. R. Sokal F. J. Rohlf (2000) Biometry W.H. Freeman and Company San Francisco
B. R. E. Torres-Orozco S. A. Zanatta (1998) ArticleTitleSpecies composition, abundance and distribution of zooplankton in a tropical eutrophic lake: Lake Catemaco, Mexico Revista de Biología Tropical 46 285–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavón-Meza, E.L., Sarma, S.S.S. & Nandini, S. Combined Effects of Algal (Chlorella vulgaris) Food Level and Temperature on the Demography of Brachionus havanaensis (Rotifera): a Life Table Study. Hydrobiologia 546, 353–360 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4245-8
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4245-8