Abstract
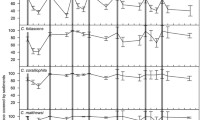
Effects of high suspended-sediment (SS) levels (up to c. 20,000 NTU) from fine clay on 5 species of New Zealand stream insects and the crayfish Paranephrops planifrons were assessed by short-term (24 h) exposures to different SS concentrations. There were no patterns of increasing mortality over 24 h with increasing SS concentrations. Effects of longer-term exposure (14 days) of repeated 4 h exposures to lower SS concentrations (c. 1000 NTU) on the common leptophlebiid mayfly Deleatidium were also investigated. No difference in mortality was found between the test and control solutions. We suggest that so-called ‚sensitive’ invertebrates are tolerant of high SS concentrations, and that even repeated exposures to high SS concentrations have little effect on survival. Absence of these animals from catchments with high SS concentrations thus most likely reflects adverse changes to instream habitat conditions, such as filling of interstitial spaces, contamination of food sources, or both.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Brunke (1999) ArticleTitleColmation and depth filtration within streambeds: retention of particles in hyporheic interstices Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie 84 99–117
Christchurch City Council, 2003. Waterways, wetland and drainage guide – Ko Te Anga Whakaora mo Nga Arawai Repo. Part B: Design. Christchurch City Council. Christchurch
J. J. H. Ciborowski P. J. Pointing L. D. Corkum (1977) ArticleTitleThe effect of current velocity and sediment on the drift of the mayfly Ephemerella subvaria McDunnough Freshwater Biology 7 567–572
C. M. Cooper (1988) ArticleTitleThe toxicity of suspended sediments on selected freshwater invertebrates Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 23 1619–1625
R. J. Davies-Colley C. W. Hickey J. M. Quinn P. A. Ryan (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of clay discharges on streams 1 optical properties and epilithon Hydrobiologia 248 215–234 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00006149
T. J. Doeg G. A. Milledge (1991) ArticleTitleEffect of experimentally increasing concentrations of suspended sediment on macroinvertebrate drift Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 42 519–526
A. A. Graham (1988) ArticleTitleThe impact of fine silt on epilithic periphyton, and possible interactions between periphyton and invertebrate consumers Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 23 1437–1440
M. J. Hall G. P. Closs R. H. Riley (2001) ArticleTitleRelationships between land use and stream invertebrate community structure in a South Island, New Zealand, coastal stream catchment New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 35 591–603
J. S. Harding J. M. Quinn C. W. Hickey (2000) Effects of mining and production forestry K. J. Collier M. J. Winterbourn (Eds) New Zealand Stream Invertebrates: Ecology and Implications for Management New Zealand Limnological Society Christchurch 230–259
J. S. Harding M. J. Winterbourn (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of contrasting landuse on physio-chemical conditions and benthic assemblages of streams in a Canterbury (South Island, New Zealand) river system New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 29 479–492
R. A. Heffner M. J. Butler C. K. Reilly (1996) ArticleTitlePseudoreplication revisited Ecology 77 2558–2562
C. W. Hickey (2000) Ecotoxicology: laboratory and field approaches K. J. Collier M. J. Winterbourn (Eds) New␣Zealand Stream Invertebrates: Ecology and Implications for Management New Zealand Limnological Society Christchurch 313–343
D. M. Hicks G. A. Griffiths (1992) Sediment load M. P. Mosley (Eds) Waters of New Zealand New Zealand Hydrological Society Wellington 229–248
Hicks, D. M., B. Gomez & N. A. Trustrum, 2004a. Event suspended sediment characteristics and the generation of hyperpycnal plumes at river mouths: East Coast continental margin, North Island, New Zealand. The Journal of Geology 112, 471–485
D. M. Hicks J. M. Quinn N. A. Trustrum (2004b) Stream sediment load and organic matter J. S. Harding P. M. Mosley C. P. Pearson B. K. Sorrell (Eds) Freshwaters of New Zealand Caxton Press Christchurch 12.1–12.16
I. D. Hogg R. H. Norris (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of runoff from land clearing and urban development on the distribution and abundance of macroinvertebrates in pool areas of a river Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 42 507–518
S. H. Hurlbert (1984) ArticleTitlePseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments Ecological Monographs 54 187–211
I. G. Jowett J. Richardson B. J. F. Biggs C. W. Hickey J.␣M. Quinn (1991) ArticleTitleMicrohabitat preferences of benthic invertebrates and the development of generalised Deleatidium spp. habitat suitability curves, applied to four New Zealand rivers New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 25 187–199
M. D. Kaller K. J. Hartman (2004) ArticleTitleEvidence of a threshold level of fine sediment accumulation for altering benthic macroinvertebrate communities Hydrobiologia 518 95–104 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025059.82197.35
S. T. Larnard M. R. Scarsbrook T. H. Snelder B. J. F. Biggs (2004) ArticleTitleWater quality in low-elevation streams and rivers of New Zealand: recent state and trends in contrasting land-cover classes New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 38 347–366
J. R. Maxted B. F. Evans M. R. Scarsbrook (2003) ArticleTitleDevelopment of standard protocols for macroinvertebrate assessment of soft-bottomed streams in New Zealand New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 37 793–807
G. W. Minshall (1984) Aquatic Insect-Substratum Relationships V. H. Resh D. M. Rosenberg (Eds) The Ecology of Aquatic Insects Praeger New York 358–400
J. H. Mol P. E. Ouboter (2003) ArticleTitleDownstream effects of erosion from small-scale gold mining on the instream habitat and fish community of a small neotropical rainforest stream Conservation Biology 18 201–214 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1523-1739.2004.00080.x
P. M. Nuttall (1972) ArticleTitleThe effects of sand deposition upon the macroinvertebrate fauna of the River Camel Freshwater Biology 2 181–186
L. Oksanen (2001) ArticleTitleLogic of experiments in ecology: is pseudoreplication a pseudoissue? Oikos 94 27–38 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0706.2001.11311.x
M. J. Paul J. L. Meyer (2001) ArticleTitleStreams in the Urban Landscape Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 32 333–365 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114040
J. M. Quinn (2000) Effects of pastoral development K. J. Collier M. J. Winterbourn (Eds) New Zealand Stream Invertebrates: Ecology and Implications for Management New Zealand Limnological Society Christchurch 208–229
J. M. Quinn A. B. Cooper (1997) ArticleTitleLand-water interactions at Whatawhata, New Zealand: introduction and synthesis New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 31 569–577
J. M. Quinn M. J. Stroud (2002) ArticleTitleWater quality and nutrient export from New Zealand hill-land catchments of contrasting land use New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 36 409–429
J. M. Quinn A. B. Cooper R. J. Davis-Colley J. C. Rutherford R. B. Williamson (1997) ArticleTitleLand use effects on habitat, water quality, periphyton, and benthic invertebrates in Waikato, New Zealand, hill-country streams New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 31 579–597
J. M. Quinn R. J. Davies-Colley, C. W. Hickey, M. L. Vickers, P. A. Ryan (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of clay discharges on streams 2. Benthic invertebrates Hydrobiologia 248 235–247 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00006150
B. A. Richardson (1985) ArticleTitleThe impact of forest road construction on the benthic invertebrate and fish fauna of a coastal stream in southern New South Wales Australian Society of Limnology Bulletin 10 65–88
D. M. Rosenberg A. P. Wiens (1975) ArticleTitleExperimental sediment addition studies on the Harris River, NWT, Canada: the effect on macroivertebrate drift Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Linmologie 19 1568–1574
D. M. Rosenberg A. P. Wiens (1978) ArticleTitleEffects of sediment addition on macrobenthic invertebrates in a northern Canadian river Water Research 12 753–763 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(78)90024-6
P. A. Ryan (1991) ArticleTitleEnvironmental effects of sediment on New Zealand streams: a review New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 25 207–221
A. M. Suren ( 2000) Effects of urbanisation K. J. Collier M. J. Winterbourn (Eds) New Zealand Stream Invertebrates: Ecology and Implications for Management New Zealand Limnological Society Christchurch 260–288
A. M. Suren I. G. Jowett (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of deposited sediment on invertebrate drift: an experimental study New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 35 725–737
S. M. Wagener J. D. LaPerriere (1985) ArticleTitleEffects of placer mining on the invertebrate communities of interior Alaska streams Freshwater Invertebrate Biology 4 208–214
T. F. Waters (1995) ArticleTitleSediment in streams Sources, biological effects, and control American Fisheries Society Monograph 7 1–251
R. B. Williamson (1993) ArticleTitleUrban Runoff Data Book Water Quality Centre Publication 20 1–51
P. J. Wood K. B. Armitage (1997) ArticleTitleBiological effects of fine sediment in the lotic environment Environmental Management 21 203–217 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002679900019 Occurrence Handle9008071
Y. F. Wu (1931) ArticleTitleA contribution to the biology of Simulium (Diptera) Papers of the Michigan Acadamy of Sciences, Arts and Letters 13 543–599
H. Yamada F. Nakamura (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of fine sediment deposition and channel works on periphyton biomass in the Makomanai River, Northern Japan River Research and Applications 18 481–493 Occurrence Handle10.1002/rra.688
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suren, A.M., Martin, M.L. & Smith, B.J. Short-Term Effects of High Suspended Sediments on Six Common New Zealand Stream Invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 548, 67–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4167-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4167-5