Abstract
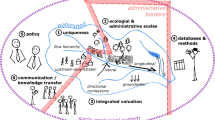
This paper discusses and summarizes the major conclusions of the special issue entitled ‘Living rivers: trends and challenges in science and management’ of Hydrobiologia/Developments in Hydrobiology. It is structured along three lines: (1) Functioning of river systems; (2) Ecological rehabilitation of river systems; (3) Challenges and obstacles to sustainable management. Sustainable river basin management requires a thorough understanding of natural, physical, chemical and ecological processes as well as socio-economic functioning. Environmental rehabilitation of river systems inevitably requires an ecosystem-based approach involving solutions supported by the public. The challenge is to combine ecological and socio-economic sustainability. Rethinking our efforts in both directions must lead to more innovative solutions than those available at present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Admiraal G. Velde Particlevan der H. Smit W. G. Cazemier (1993) ArticleTitleThe rivers Rhine and Meuse in the Netherlands: present state and signs of ecological recovery Hydrobiologia 265 97–128
C. Ahn D. M. Johnston R. E. Sparks D. C. White (2006) ArticleTitleAnalysis of naturalization alternatives for the recovery of moist-soil plants in the floodplain of the Illinois River Hydrobiologia 565 217–228 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1915-5
Anonymous, 2003. Freude am Fluss project, Interreg IIIB North-West Europe, Application Form Radboud University Nijmegen. Interreg IIIB NWE Secretariat ENO, Lille.
M. J. Baptist M. Haasnoot P. Cornelissen J. Icke G. Wedden Particlevan der H. J. Vriend Particlede G. Gugić (2006) ArticleTitleFlood detention, nature development and water quality along the lowland river Sava, Croatia Hydrobiologia 565 243–257 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1917-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XkvVWls7k%3D
A. Bij de Vaate R. Breukel G. Velde Particlevan der (2006) ArticleTitleLong-term developments in ecological rehabilitation of the main distributaries in the Rhine delta: fish and macroinvertebrates Hydrobiologia 565 229–242 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1916-4
J. Bohannon M. Enserink (2005) ArticleTitleHurricane Katrina. Scientists weigh options for rebuilding New Orleans Science 309 1808–1809 Occurrence Handle16166494 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtVWms73O Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.309.5742.1808
G. Brouwer (2003) ArticleTitleThe creeping storm Civil Engineering – ASCE 73 46–55
InstitutionalAuthorNameBrundtland Commission (1987) Our Common Future. World Commission on Environment and Development of the United Nations Oxford University Press Oxford
Buijse, A., F. Klijn, R. S. E. W. Leuven, H. Middelkoop, F. Schiemer, J. Thorp & H. Wolfert, 2005. Rehabilitation of large rivers: references, achievements and integration into river management. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplement 155(1–4) Large Rivers 15(1–4): 715–738.
W. T. Groot ParticleDe H. J. R. Lenders (2006) ArticleTitleEmergent principles for river management Hydrobiologia 565 309–316 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1921-7
R. J. W. Nooij ParticleDe W. C. E. P. Verberk H. J. R. Lenders R. S. E. W. Leuven P. H. Nienhuis (2006) ArticleTitleThe importance of hydrodynamics for protected and endangered biodiversity of lowland rivers Hydrobiologia 565 153–162 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1911-9
M. Fischetti (2001) ArticleTitleDrowing New Orleans Scientific American 285 76–85 Occurrence Handle11570045 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MritlKmtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/scientificamerican1001-76
G. W. Geerling A. M. J. Ragas R. S. E. W. Leuven J. H. Berg Particlevan den M. Breedveld D. Liefhebber A. J. M. Smits (2006) ArticleTitleSuccession and rejuvenation in floodplains along the River Allier (France) Hydrobiologia 565 71–86 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1906-6
A. Hollander M. A. J. Huijbregts A. M. J. Ragas D. Meent Particlevan de (2006) ArticleTitleBasinBox: a generic multimedia fate model for the predicting of the fate of chemicals in river catchments Hydrobiologia 565 21–38 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1903-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XkvVWls7s%3D
C. A. Johnston R. J. Naiman (1990) ArticleTitleBrowse selection by beaver: effects on riparian forest composition Canadian Journal of Forest Research 20 1036–1043
Knip, K. 2005. Overstroming New Orleans was zoals voorspeld. NRC Handelsblad 7 September 2005 (in Dutch).
L. P. M. Lamers R. Loeb A. M. Antheunissen M. Miletto E. C. H. E. T. Lucassen A. W. Boxman A. J. P. Smolders J. G. M. Roelofs (2006) ArticleTitleBiogeochemical constraints on the ecological rehabilitation of wetland vegetation in river floodplains Hydrobiologia 565 165–186 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1912-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XkvVWls7g%3D
Lenders, H. J. R. & L. Knippenberg, 2005. The temporal and social dimensions of river rehabilitation: towards a multi-dimensional research perspective. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplement 155 (1–4) Large Rivers 15 (1–4): 119–131.
R. S. E. W. Leuven A. J. M. Smits P. H. Nienhuis (2000) From integrated approaches to sustainable river basin management A. J. M. Smits P. H. Nienhuis R. S. E. W. Leuven (Eds) New Approaches to River Management Backhuys Publishers Leiden 329–347
R. S. E. W. Leuven P. J. M. Heuvel Particlevan den M. M. Katwijk Particlevan P. M. J. Herman G. Velde Particlevan der A. M. J. Ragas (2006a) ArticleTitlePieter Hendrik Nienhuis: aquatic ecologist and environmental scientist Hydrobiologia 565 1–18 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1902-x
Leuven, R. S. E. W., A. M. J. Ragas, A. J. M. Smits & G. van der Velde (eds), 2006b. Living rivers: trends and challenges in science and management. Hydrobiologia 565: 1–367.
P. H. Nienhuis R. S. E. W. Leuven A. M. J. Ragas (Eds) (1998) New Concepts for Sustainable Management of River Basins Backhuys Publishers Leiden
P. H. Nienhuis R. S. E. W. Leuven (1998) Ecological concepts for the sustainable management of lowland river basins: a review P. H. Nienhuis R. S. E. W. Leuven A. M. J. Ragas (Eds) New Concepts for Sustainable Management of River Basins Backhuys Publishers Leiden 7–34
P. H. Nienhuis A. D. Buijse R. S. E. W. Leuven A. J. M. Smits R. J. W. Nooij Particlede E. M. Samborska (2002) ArticleTitleEcological rehabilitation of the lowland basin of the river Rhine (NW Europe) Hydrobiologia 478 53–72 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021070428566
P. H. Nienhuis (2006) ArticleTitleWater and values: Ecological research as the basis for water management and nature management Hydrobiologia 565 261–275 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1918-2
Peters, B., E. Kater & G. W. Geerling, 2005. Handboek Cyclisch Beheer – Omgaan met Spontane Natuur en Hydraulische Opstuwing. Staatsbosbeheer, Rijkswaterstaat, Stichting Ark & Radboud Universiteit, Nijmegen (in Dutch).
G.E. Petts J. Nestler R. Kennedy (2006) ArticleTitleAdvancing science for water resources management Hydrobiologia 565 277–288 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1919-1
B. J. A. Pollux A. Korosi W. C. E. P. Verberk P. M. J. Pollux G. Velde Particlevan der (2006) ArticleTitleReproduction, growth and migration of fishes in a regulated lowland tributary: Potential recruitment to the river Meuse Hydrobiologia 565 105–120 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1908-4
D. Ryder A. J. Boulton (2005) ArticleTitleRedressing the limnological imbalance: trends in aquatic ecology, management and conservation in Australia Hydrobiologia 552 159–166 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1513-6
A. J. M. Smits P. H. Nienhuis R. S. E. W. Leuven (Eds) (2000) New Approaches to River Management Backhuys Publishers Leiden
A. J. M. Smits P. H. Nienhuis H. L. F. Saeijs (2006) ArticleTitleChanging estuaries, changing views Hydrobiologia 565 339–355 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1924-4
M. W. Straatsma H. Middelkoop (2006) ArticleTitleAirborne laser scanning as a tool for lowland floodplain vegetation monitoring Hydrobiologia 565 87–103 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1907-5
K. Tockner I. Klaus C. Baumgartner J. V. Ward (2006) ArticleTitleAmphibian diversity and nestedness in a dynamic floodplain river (Tagliamento, NE-Italy) Hydrobiologia 565 121–133 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1909-3
G. Velde ParticleVan der I. Nagelkerken S. Rajagopal A. bij de Vaate (2002) Invasions by alien species in inland freshwater bodies in western Europe: the Rhine delta E. Leppäkoski S. Gollasch S. Olenin (Eds) Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management. Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht 360–372
Van der Velde, G., R. S. E. W. Leuven & I. Nagelkerken, 2004. Types of river ecosystems. In: Fresh surface water. Water Sciences, Engineering and Technology Resources. Encyclopedia of life support systems (EOLSS). UNESCO, EOLSS Publishers, Oxford, 1–29 (http://www.eolss.net/).
G. A. Duinen ParticleVan Y. Zhuge W. C. E. P. Verberk A. M. T. Brock H. H. Kleef Particlevan R. S. E. W. Leuven G. Velde Particlevan der H. Esselink (2006) ArticleTitleEffects of rewetting measures in Dutch raised bog remnants on assemblages of aquatic Rotifera and microcrustaceans Hydrobiologia 565 187–200 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1913-7
W. H. J. M. Eck ParticleVan J. P. M. Lenssen H. M. Steeg Particlevan de C. W. P. M. Blom H. Kroon Particlede (2006) ArticleTitleSeasonal dependent effects of flooding on plant species survival and zonation: a comparative study of ten grassland species Hydrobiologia 565 59–69 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1905-7
H. H. Kleef ParticleVan W. C. E. P. Verberk R. S. E. W. Leuven H. Esselink G. Velde Particlevan der G. A. Duinen Particlevan (2006) ArticleTitleBiological traits successfully predict the effects of restoration management on macroinvertebrates in shallow softwater lakes Hydrobiologia 565 201–216 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1914-6
M. C. Riel ParticleVan G. Velde Particlevan der S. Rajagopal S. Marguillier F. Dehairs A. bij Vaate Particlede (2006) ArticleTitleTrophic relationships in the lower Rhine food web during invasion and after establishment of the Ponto-Caspian invader Dikerogammarus villosus Hydrobiologia 565 39–57 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1904-8
H. T. C. Stokkom ParticleVan A. J. M. Smits R. S. E. W. Leuven (2005) ArticleTitleFlood defense in the Netherlands: a new era, a new approach Water International 30 76–87 Occurrence Handle10.1080/02508060508691839
P. Vugteveen R. S. E. W. Leuven M. A. J. Huijbregts H. J. R. Lenders (2006) ArticleTitleRedefinition and elaboration of river ecosystem health: perspective for river management Hydrobiologia 565 289–308 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1920-8
A. G. Wetzel (2001) Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems EditionNumber3 Academic Press San Diego
M. A. Wiering B. J. M. Arts (2006) ArticleTitleDiscursive shifts in Dutch river management: ‘deep’ institutional change or adaptation strategy? Hydrobiologia 565 327–338 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-5923-2
S. Wijnhoven G. Velde Particlevan der R. S. E. W. Leuven A. J. M. Smits (2005) ArticleTitleFlooding ecology of voles, mice and shrews: the importance of geomorphological and vegetational heterogeneity in river floodplains Acta Theriologica 50 453–473
S. Wijnhoven G. Velde Particlevan der R. S. E. W. Leuven A. J. M. Smits (2006) ArticleTitleModelling recolonisation of heterogeneous river floodplains by small mammals Hydrobiologia 565 135–152 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1910-x
J. V. Witter H. T. C. Stokkom Particlevan G. Hendriksen (2006) ArticleTitleFrom river management to river basin management: a water manager’s perspective Hydrobiologia 565 317–325 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1922-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Velde, G., Leuven, R.S.E.W., Ragas, A.M.J. et al. Living Rivers: Trends and Challenges in Science and Management. Hydrobiologia 565, 359–367 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1925-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1925-3