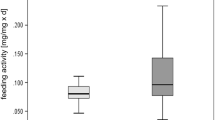
Abstract
A specific landfill leachate that contained 1.036 mgl−1of 2-chlorobiphenyl was used in the study (255 mg l−1 COD and 133 mg l−1 BOD5). Three, 2-l semi-continuous batch reactors (SBRs) were used to simulate the treatment potential of this method on a small scale. Aerobic digestion effectively reduced the leachates COD concentration. Regardless of dilution, the leachates COD reached a <20 mg l−1 equilibrium after 96 h exposure to aerobic digestion, however, increasing the level of dilution accelerated the process. In untreated leachate, the LC50 for Asellus aquaticus was 57% v/v leachate in deionised water and 5% for Gammarus pulex (96 h, static LC50 tests without nutrition and oxygen depleting conditions). After being exposed to aerobic digestion, these values rose to 95% and 40%, respectively. Prolonged exposure to a 1:20 sub-lethal dilution of the aforementioned leachate has been previously shown to affect the breeding colony size of Asellus aquaticus and a 1:66 dilution influenced the fecundity of a Gammarus pulex population. After remediation by aerobic digestion, however, the population dynamics of both test species remained unaltered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BOD5:
-
5 day biochemical oxygen demand
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- LC50:
-
Lethal concentration in which 50% of the test animals died
- Mgl−1:
-
Milligram per litre
- Ml:
-
Millilitre
- MLSS:
-
Mixed liquor suspended solids
- PCB:
-
Polychlorinated Biphenyl
- v/v:
-
Dilution
References
J. J. Arensdorf D. D. Focht (2004) ArticleTitleFormation of chlorocatechol meta cleavage products by a pseudomonad during metabolism of monochlorobiphenyls Applied Environmental Microbiology 60 2884–2889
Bloor. M. C., 2004. To assess how landfilling could affect the ecology of the far-field aquatic environment. PhD Thesis, School of Civil Engineering and the Environment, University of Southampton, UK: 1–177.
S. D. Bridgham (1988) ArticleTitleChronic effects of 2,2′- dichlorobiphenyl on reproduction, mortality, growth and respiration of Daphnia pulicaria Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 17 731–740 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01061979 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlsVCitLs%3D
L. A. Buikema SuffixJr. B. R. Niederlehner J. Cairns SuffixJr. (1982) ArticleTitleBiological monitoring part iv - Toxicity testing Water Research 16 239–262 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(82)90188-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xit1alsrY%3D
B. Clement G. Persoone C. Janssen A. Le Du-Delepierre (1996) ArticleTitleEstimation of the hazard of landfills through toxicity testing of leachates 1. Determination of leachate toxicity with a battery of acute tests Chemosphere 33 2303–2320 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntVKlsLc%3D
InstitutionalAuthorNameCouncil of the European Communities (1980) ArticleTitleDirective on the protection of the groundwater against pollution caused by certain dangerous substances (80/86/EEC) Official Journal of the European Communities L20 43–47
E. Diamadopoulos P. Samaras X. Dabou G. P. Sakellaro poulos (1997) ArticleTitleCombined treatment of landfill leachate and domestic sewage in a sequencing batch reactor Water Science and Technology 36 61–68 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00370-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnvFaqtLo%3D
M. Y. Gross D. S. Maycock M. C. Thorndyke D. Morritt M. Crane (2001) ArticleTitleAbnormalities in sexual development of the amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.) found below sewage treatment works Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 20 1792–1797 Occurrence Handle11491564 Occurrence Handle10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<1792:AISDOT>2.0.CO;2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlsVKqu7k%3D
L. Maltby (1995) ArticleTitleSensitivity of the crustaceans Gammarus pulex (L.) and Asellus aquaticus (L.) to short-term exposure to hypoxia and unionised ammonia: observations and possible mechanisms Water Research 29 781–787 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(94)00231-U Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjs1Wltrk%3D
C. P. McCahon D. Pascoe (1988) ArticleTitleCulture techniques for three freshwater macro-invertebrate species and their use in toxicity tests Chemosphere 17 2471–2480 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0045-6535(88)90157-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhtV2msLw%3D
C. P. McCahon M. J. Poulton C. P. Thomas Q. Xu D. Pascoe C. Turner (1991) ArticleTitleLethal and sub-lethal toxicity of field simulated farm waste episodes to several freshwater invertebrate species Water Research 25 661–671 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(91)90041-N Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXks1KnsLo%3D
F. L. Mayer P. M. Mehrle H. O. Sanders (1977) ArticleTitleResidue dynamics and biological effects of polychlorinated biphenyls in aquatic organisms Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 5 501–511 Occurrence Handle407851 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02220928 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXls1antrw%3D
D. Pascoe R. W. Edwards (1989) Single species toxicity tests A. Boudou F. Ribeyre (Eds) Aquatic Ecotoxicology, Fundamental Concepts and Methodologies CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 93–126
E. T. H. M. Peeters T. J. Jager ParticleDe J. A. J. Beijer A. A. Koelmans (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of benzo(a)pyrene and size of organic matter particles on bioaccumulation and growth of Asellus aquaticus Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 39 307–314 Occurrence Handle10948280 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntlOmtrk%3D
Rowe, R. K., 1998. From the past to the future of landfill engineering through case histories. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering, St Louis: 145–166.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 1998. In L.S. Clesceri, et al. (eds), Water Environment Federation, USA: 5–3 and 5–15.
S. E. Strand (2004) ArticleTitleAerobic biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls CEWA, ESC, MICRO 518 1–10
R. A. Voyer J. F. Heltshe (1984) ArticleTitleFactor interactions and aquatic toxicity testing Water Research 18 441–447 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(84)90152-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXhsl2rsbo%3D
Westholm, L. J., 2003. Leachate treatment with use of SBR-technology combined with a constructed wetland system at the Isatra landfill site, Sweden. In Christensen et al. (eds), Proceedings of the 9th International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium. Sardinia, Italy CISA Press, London Paper No. 535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bloor, M.C., Banks, C.J. Acute and Sub-lethal Toxicity of Landfill Leachate Towards Two Aquatic Macro-invertebrates: Demonstrating the Remediation Potential of Aerobic Digestion. Hydrobiologia 556, 387–397 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1201-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1201-6