Abstract
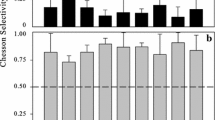
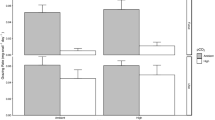
The in situ grazing experiments were performed in the shallow water rocky habitat of the northern Baltic Sea during ice-free season 2002. In the experiments the effects of algal species and choice on the grazing of the mesoherbivores Idotea baltica (Pallas) and Gammarus oceanicus Segerstråle were tested. Salinity, temperature, concentration of nutrients in water and macroalgae and net production of macroalgae were considered as random effects in the analysis. The invertebrate feeding rate was mainly a function of the net photosynthetic activity of Pylaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellman and Fucus vesiculosus L. Feeding rate increased significantly with decreasing algal photosynthetic activity. When the two algal species were incubated together invertebrates fed primarily on P. littoralis. Low selectivity towards P. littoralis coincided with its high photosynthetic activity. The presence of F. vesiculosus did not modify the invertebrate feeding on P. littoralis. The results indicated that (1) the grazing on F. vesiculosus depended on the availability of P. littoralis, (2) the photosynthetic activity of algae explained the best the variation in grazing rate and (3) the grazers are not likely to control the early outbreak of filamentous algae in the northern Baltic Sea by avoiding young and photosynthetically active algae. The likely mechanism behind the relationship is that the increased photosynthetic activity of macroalgae coincides with their higher resistance to herbivory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. B. Adler D. A. Raff W. K. Lauenroth (2001) ArticleTitleThe effect of grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation Oecologia 128 465–479 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420100737
J. Arrontes (1999) ArticleTitleOn the evolution of interactions between marine mesoherbivores and algae Botanica Marina 42 137–155 Occurrence Handle10.1515/BOT.1999.017
S. S. Bell (1991) ArticleTitleAmphipods as insect equivalents? An alternative view Ecology 72 350–354 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1938929
P. B. Birch J. O. Gabrielson K. S. Hamel (1983) ArticleTitleDecomposition of Cladophora I. Field studies in the Peel-Harvey estuarine system, western Australia Botanica Marina 26 165–171 Occurrence Handle10.1515/botm.1983.26.4.165
C. Boström J. Mattila (1999) ArticleTitleThe relative importance of food and shelter for seagrass-associated invertebrates: a latitudinal comparison of habitat choice by isopod grazers Oecologia 120 162–170 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050845
C. E. Boyd (1970) ArticleTitleLosses of mineral nutrients during decomposition of Typha latifolia Archiv für Hydrobiologie 66 511–517
R. Buchsbaum I. Valiela T. Swain M. Dzierzeski S. Allen (1991) ArticleTitleAvailable and refractory nitrogen in detritus of coastal vascular plants and macroalgae Marine Ecology Progress Series 72 131–143
B. A. Byren B. R. Davies (1986) ArticleTitleThe influence of invertebrates on the breakdown of Potamogeton pectinatus L. in a coastal marina (Zandvlei, South Africa) Hydrobiologia 137 141–151 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00004210
E. Cruz-Rivera M. E. Hay (2000) ArticleTitleThe effects of diet mixing on consumer fitness: macroalgae, epiphytes, and animal matter as food for marine amphipods Oecologia 123 252–264 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420051012
J. E. Duffy A. H. Harvilicz (2001) ArticleTitleSpecies-specific impacts of grazing amphipods in an eelgrass-bed community Marine Ecology Progress Series 223 201–211
R. Engvist T. Malm S. Tobiasson (2000) ArticleTitleDensity dependent grazing effects of the isopod Idotea baltica Pallas on Fucus vesiculosus L. in the Baltic Sea Aquatic Ecology 34 253–260 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009919526259
K. Grasshoff (1976) Methods of Seawater Analysis Verlag Chemie New York 317
M. E. Hay (1984) ArticleTitlePredictable spatial escapes from herbivory: How do these affect the evolution of herbivore resistance in tropical marine communities? Oecologia 64 396–407 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00379139
A. Hemmi V. Jormalainen (2002) ArticleTitleNutrient enhancement increases performance of a marine herbivore via quality of its food alga Ecology 83 1052–1064 Occurrence Handle10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[1052:NEIPOA]2.0.CO;2
A. Hemmi V. Jormalainen (2004) ArticleTitleGenetic and environmental variation in performance of a marine isopod: effects of eutrophication Oecologia 140 302–311 Occurrence Handle15146322 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00442-004-1574-7
P. Jernakoff A. Brearley J. Nielsen (1996) ArticleTitleFactors affecting grazer epiphyte interactions in temperate seagrass meadows Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review 34 109–162
V. Jormalainen T. Honkanen N. Heikkilä (2001) ArticleTitleFeeding preferences and performance of a marine isopod on seaweed hosts: cost of habitat specialization Marine Ecology Progress Series 220 219–230
P. Kangas H. Autio G. Hällfors H. Luther Å. Niemi H. Salemaa (1982) ArticleTitleA general model of the decline of Fucus vesiculosus at Tvärminne, south coast of Finland in 1977–1981 Acta Botanica Fennica 118 1–27
U. Kautsky H. Kautsky (1995) Coastal productivity in the Baltic Sea A., Eleftheriou A. D. Ansell C. J. Smith (Eds) Biology and Ecology of Shallow Coastal Waters Olsen and Olsen Fredensborg 31–38
Kiirikki, M., 1996. Dynamics of macroalgal vegetation in the northern Baltic Sea – evaluating the effects of weather and eutrophication. Ph.D. Thesis, Walter and Andrée de Nottbeck Foundation Scientific Reports 12: 1–15
J. Köhler (1998) ArticleTitleMeasurement of photosynthetic oxygen production Rostocker Meeresbiologische Beiträge 6 17–21
J. Kotta T. Paalme G. Martin A. Mäkinen (2000) ArticleTitleMajor changes in macroalgae community composition affect the food and habitat preference of Idotea baltica International Review of Hydrobiology 85 697–705 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1522-2632(200011)85:5/6<697::AID-IROH697>3.0.CO;2-0
A. Lehvo S. Bäck M. Kiirikki (2001) ArticleTitleGrowth of Fucus vesiculosus L. (Phaeophyta) in the northern Baltic Proper: energy and nitrogen storage in seasonal environment Botanica Marina 44 345–350 Occurrence Handle10.1515/BOT.2001.044
H. K. Lotze B. Worm (2002) ArticleTitleComplex interactions of climatic and ecological controls on macroalgal recruitment Limnology and Oceanography 47 1734–1741 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.2002.47.6.1734
K. Lüning (1981) Light C. S. Lobban M. J. Wynne (Eds) The Biology of Seaweeds. Botanical Monographs 17 Blackwell Scientific Oxford 326–355
K. H. Mann (1988) ArticleTitleProduction and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine, and coastal marine ecosystems Limnology and Oceanography 33 910–930 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlvFKmur8%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1988.33.4_part_2.0910
G. Martin K. Torn J. Kotta H. Orav-Kotta (2003) ArticleTitleEstonian marine phytobenthos monitoring programme: preliminary results and future perspectives Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences. Biology. Ecology 52 112–124
B. A. Menge (1992) ArticleTitleCommunity regulation: under what conditions are bottom-up factors important on rocky shores? Ecology 73 755–765 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1940155
M. E. Nicotri (1980) ArticleTitleFactors involved in herbivore food preference Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 42 13–26 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-0981(80)90163-X
H. Orav-Kotta J. Kotta (2003) ArticleTitleSeasonal variations in the grazing of Gammarus oceanicus, Idotea baltica, and Palaemon adspersus on benthic macroalgae Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences. Biology. Ecology 52 141–148
H. Orav-Kotta J. Kotta (2004) ArticleTitleFood and habitat choice of the isopod Idotea baltica in the northeastern Baltic Sea Hydrobiologia 514 79–85 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:hydr.0000018208.72394.09
R. J. Orth J. Montfrans ParticleVan (1984) ArticleTitleEpiphyte–seagrass relationship with an emphasis on the role of micrograzing: a review Aquatic Botany 18 43–69 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3770(84)90080-9
T. Paalme H. Kukk J. Kotta H. Orav (2002) ArticleTitle“In vitro” and “in situ” decomposition of nuisance macroalgae Cladophora glomerata and Pilayella littoralis Hydrobiologia 475/476 469–476 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020364114603
Paalme, T. & A. Mäkinen, 1997. Variation in primary productivity of different Baltic macroalgal species in different seasons, NorFa project report nr.9630.002-M Nordisk Forskerutdanningsakademi Oslo
M. F. Pedersen J. Borum (1996) ArticleTitleNutrient control of algal growth in estuarine waters. Nutrient limitation and the importance of nitrogen requirements and nitrogen storage among phytoplankton and species of macroalgae Marine Ecology Progress Series 142 261–272 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXosVeltQ%3D%3D
R. J. Putman (1986) Grazing in Temperate Ecosystems: Large Herbivores and the Ecology of the New Forest Croom Helm London 210
D. G. Raffaelli J. Raven L. Poole (1998) ArticleTitleEcological impact of macroalgal blooms Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review 36 97–125
P. Raimbault G. Slawyk (1991) ArticleTitleA semiautomatic, wet-oxidation method for the determination of particulate organic nitrogen collected on filters Limnology and Oceanography 36 405–408 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlsVWrtb8%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1991.36.2.0405
P. F. Shacklock (1991) ArticleTitleBiology of Idotea baltica in Chondrus aquaculture Bulletin of the Aquaculture Association of Canada 91 39–40
L. Solorzano J. H. Sharp (1980) ArticleTitleDetermination of total dissolved nitrogen in natural waters Limnology and Oceanography 25 751–754 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXnsFSh
Sokal R. R. & Rohlf F. J., 1981. Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 2nd ed. Freeman W.H., San Francisco, California, USA, p. 859
R. S. Steneck L. Watling (1982) ArticleTitleFeeding capabilities and limitations of herbivorous molluscs: a functional group approach Marine Biology 68 299–319 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00409596
I. Valiela J. McClelland J. Hauxwell P. J. Behr D. Hersh K. Foreman (1997) ArticleTitleMacroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences Limnology and Oceanography 42 1105–1118 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1997.42.5_part_2.1105
B. Worm (2000) ArticleTitleConsumer versus resource control in rocky shore food webs: Baltic Sea and Northwest Atlantic Ocean Berichte aus dem Institut für Meereskunde an der Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel 316 1–147
B. Worm H. K. Lotze C. Boström R. Engkvist V. Labanauskas U. Sommer (1999) ArticleTitleMarine diversity shift linked to interactions among grazers, nutrients and propagule banks Marine Ecology Progress Series 185 309–314
B. Worm H. K. Lotze U. Sommer (2000) ArticleTitleCoastal food web structure, carbon storage, and nitrogen retention regulated by consumer pressure and nutrient loading Limnology and Oceanography 45 339–349 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVKrt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.2000.45.2.0339
B. Worm U. Sommer (2000) ArticleTitleRapid direct and indirect effects of a single nutrient pulse in a seaweed–epiphyte–grazer system Marine Ecology Progress Series 202 283–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0251-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonne, K., Helen, OK., Tiina, P. et al. Seasonal Changes in situ Grazing of the Mesoherbivores Idotea baltica and Gammarus oceanicus on the Brown Algae Fucus vesiculosus and Pylaiella littoralis in the Central Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Hydrobiologia 554, 117–125 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1011-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1011-x