Abstract
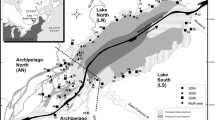
Aquatic macroinvertebrate communities were sampled between 1994 and 1996 at 13 sites downstream of phosphorus (P)-enriched canal inflows in a northern Everglades marsh to determine the effects of nutrient enrichment on community structure and function. Sampling was performed using sweep nets and Hester–Dendy (HD) samplers. Data were analyzed to assess changes in taxa richness and diversity, species composition, and functional group composition along the gradient. Environmental conditions at each site were characterized to interpret spatial changes in these metrics. Mean water-column total P (TP) increased from ≤10μg lminus;1at sites in the marsh interior to as high as 160 μg lminus;1at sites closest to the canal. Vegetation and habitat composition changed dramatically along the gradient, with sawgrass and slough-wet prairie habitats accounting for most vegetative cover in the interior and cattail accounting for nearly 100%of the cover near the canal. These differences in TP concentrations and vegetation were used to classify sites as reference, enriched, and highly enriched. Daytime dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations averaged ≥3mg lminus;1at reference sites as compared with concentrations ≤2mg lminus;1at enriched and highly enriched sites. Total macroinvertebrate densities were significantly higher in sweep samples and significantly lower in HD samples from highly enriched sites as compared with the reference condition. Taxa richness and diversity in sweep samples did not change significantly along the gradient, but declined with enrichment on the HD samplers. Insects were the dominant organisms at all sites, but declined in percent abundance with enrichment in sweep samples due to decreases in dipterans, trichopterans and odonates and an increase in oligochaetes. Changes in major invertebrate classes were less pronounced on HD samplers, although amphipods showed significant declines with enrichment. Principal components analysis revealed a clear distinction in taxonomic composition between reference sites and both enriched and highly enriched sites for sweep samples as common chironomid taxa at reference sites declined with enrichment while pollution-tolerant chironomid and oligochaete taxa increased. A similar, but less dramatic trend was found for HD samples, with selected amphipod, chironomid, and gastropod taxa declining with enrichment and pollution-tolerant taxa reaching peak abundance at enriched sites. The functional composition in sweep samples showed modest changes with enrichment, including a shift in dominance from epibenthic collector–gatherers/deposit feeders, which were predominantly chironomids, to subsurface taxa, which were predominantly oligochaetes. Shifts in invertebrate functional composition on HD samplers with enrichment were attributable to declines in the dominance of shredders and collector-filterer/suspension-feeders. Portions of the Everglades exposed to P-enriched runoff are showing characteristic shifts in macroinvertebrate taxonomic composition related to eutrophication. This shift has occurred without a change in species diversity and with an increase in total invertebrate abundance indicative of an overall increase in marsh productivity. The transition from an oligotrophic to eutrophic community signals a decline in the biological integrity of the Everglades ecosystem in response to P enrichment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. P. Batzer S. A. Wissinger (1996) ArticleTitleEcology of insect communities in nontidal wetlands Annual Review of Entomology 41 75–100
W. M. Beck SuffixJr. (1954) ArticleTitleStudies in stream pollution biology: I. A simplified ecological classification of organisms Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Science 17 211–227
W. M. Beck SuffixJr. (1977) Environmental Requirements and Pollution Tolerance of Common Freshwater Chironomidae EPA-600/4-77-024 Cincinnati, Ohio
T. V. Belanger D. J. Scheidt J. R. Platko SuffixII (1989) ArticleTitleEffects of nutrient enrichment on the Florida Everglades Lake and Reservoir Management 5 101–111
L. Berner M. L. Pescador (1988) The Mayflies of Florida (revised edition) University Presses of Florida Gainesville
R.S Brightman (1984) Benthic macroinvertebrate response to secondarily treated wastewater in north-central Florida cypress domes K. C. Ewel H. T. Odum (Eds) Cypress Swamps University of Florida Press Gainesville 151–157
J. C. Davis (1975) ArticleTitleMinimal dissolved oxygen requirements of aquatic life with emphasis on canadian species: a review Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 32 2295–2332
J. A. Epler (1995) Chironomidae of Florida (revised) Report to the Florida Department of Environmental Protection Tallahassee, Florida
G. A. Graves D. G. Strom B. E. Robson (1998) ArticleTitleStormwater impact to the freshwater Savannas Preserve marsh, Florida, USA Hydrobiologia 379 111–122
L. H. Gunderson W. F. Loftus (1993) The Everglades W. H. Martin S. G. Boyce A. C. Echternacht (Eds) Biodiversity of the Southeastern United States: Terrestrial Communities John Wiley and Sons, New York 123–344
C. Hart S. W. Jr. L. H. Fuller (1974) Pollution Ecology of Freshwater Invertebrates Academic Press New York
F. E. Hester J. S. Dendy (1962) ArticleTitleA multiple sampler for aquatic macroinvertebrates Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 91 420–421
M. Hollander D. A. Wolfe (1973) Nonparametric Statistical Methods John Wiley & Sons New York
R. K. Johnson T Wiederholm (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations, and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates D. M. Rosenberg V. H. Resh (Eds) Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates Routledge, Chapman Hall New York: 40–158
J. R. Karr D. R. Dudley (1981) ArticleTitleEcological perspectives on water quality goals Environmental Management 5 55–68
R. S. King J. C. Brazner (1999) ArticleTitleCoastal wetland insect communities along a trophic gradient in Green Bay, Lake Michigan Wetlands 19 426–437
R. S. King C. J. Richardson (2002) ArticleTitleEvaluating subsampling approaches and macroinvertebrate taxonomic resolution for wetland bioassessment Journal of the North American Benthological Society 21 150–171
G. A. Lamberti (1996) The role of periphyton in benthic food webs In Stevenson R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Academic Press, New York: 533–573
M. Lentner T. Bishop (1986) Experimental Design and Analysis Valley Book Blacksburg, Virginia
S. S. Light J. W. Dineen (1994) Water control in the Everglades: S. M. Davis J. C. Ogden (Eds) a historical perspective Everglades: The Ecosystem and Its Restoration. St. Lucie Press, Delray Beach, Florida 47–84
A. E. Magurran (1988) Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement Princeton University Press Princeton, New Jersey
P. McCormick M. V. B. O’Dell (1996) ArticleTitleQuantifying periphyton responses to phosphorus enrichment in the Florida Everglades: a synoptic-experimental approach Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15 450–468
P. V. McCormick J. E. Laing (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of increased phosphorus loading on dissolved oxygen in a subtropical wetland, the Florida Everglades Wetlands Ecology and Management 11 199–216
P. McCormick P. V. K. S. Rawlik E. Lurding P. Smith F. H. Sklar (1996) ArticleTitlePeriphyton-water quality relationships along a nutrient gradient in the northern Everglades Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15 433–449
P. V. McCormick R. B. E. Shuford SuffixIII J. G. Backus W. C. Kennedy (1998) ArticleTitleSpatial and seasonal patterns of periphyton biomass and productivity in the northern Everglades, Florida, USA Hydrobiologia 362 185–208
P. V. McCormick S. Newman S. L. Miao D. Gawlik D. Marley K. R. Reddy T. D. Fontaine (2001a) Effects of anthropogenic phosphorus inputs on the Everglades In Porter J. W. K. G. Porter (Eds) The Everglades, Florida Bay, and Coral Reefs of the Florida Keys: An Ecosystem Sourcebook CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida 83–126
P. McCormick M. V. R.B. O’Dell J.B. E. Shuford III W.G. Backus C. Kennedy (2001b) ArticleTitlePeriphyton responses to experimental phosphorus enrichment in an Everglades slough Aquatic Botany 71 119–139
R. W. Merritt K. W. Cummins (1996) Aquatic Insects of North America, 3rd edn Kendall/Hunt Publishing Dubuque, Iowa
S. L. Miao W. F. DeBusk (1999) Effects of phosphorus enrichment on structure and function of sawgrass and cattail communities in Florida wetlands K. R. Reddy , G. A. O’Connor C. L. Schelske (Eds) Phosphorus Biogeochemistry of Subtropical Ecosystems CRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida 275–300
A. V. Nebeker S. T. Onjukka D. G. Stevens G. A. Chapman S. E. Dominguez (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of low dissolved oxygen on survival, growth and reproduction of Daphnia, Hyalella, and Gammarus Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 11 373–379
R. W. Pennak (1989) Freshwater Invertebrates, 3rd edn John Wiley & Sons New York
R. B. Rader (1994) ArticleTitleMacroinvertebrates of the northern Everglades: species composition and trophic structure Florida Scientist 57 22–33
R. B. Rader C. J. Richardson (1992) ArticleTitleThe effects of nutrient enrichment on algae and macroinvertebrates in the Everglades: a review Wetlands 12 121–135
R. B. Rader C. J. Richardson (1994) ArticleTitleResponse of macroinvertebrates and small fish to nutrient enrichment in the northern Everglades Wetlands 14 134–146
D. Rosenberg V. M. H. Resh (Eds) (1993) Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates Routledge, Chapman & Hall New York
H. R. Rudolph D. G. Strom (1990) Macroinvertebrates Associated with Macrophytes in Lake Okeechobee, Florida 1986–1987 Florida Department of Environmental Regulation Port St. Lucie, Florida
K. Rutchey L. Vilchek (1999) ArticleTitleAir photo interpretation and satellite imagery analysis techniques for mapping cattail coverage in a northern impoundment Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 65 185–191
R. P. Rutter (2003) A Bioassessment of Two Lakes in Highlands County and One Lake in Charlotte County, Florida, in Winter and Summer 2002 With Emphasis on the Macroinvertebrate Fauna Florida Department of Environmental Protection Punta Gorda, Florida
O. A. Saether (1979) ArticleTitleChironomid communities as water quality indicators Holarctic Ecology 2 65–74
E. P. Smith P. V. McCormick (2001) ArticleTitleLong-term relationship between phosphorus inputs and wetland phosphorus concentrations in a northern Everglades marsh Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 68 153–176
J. H. Thorp A. P. Covich (2001) Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates Academic Press San Diego, California
A. M. Turner J. C. Trexler (1997) ArticleTitleSampling aquatic invertebrates from marshes: evaluating the options Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16 694–709
A. M Turner J. C. Trexler C. F. Jordan S. J. Slack P. Geddes J. H. Chick W. F. Loftus (1999) ArticleTitleTargeting ecosystem features for conservation: standing crops in the␣Florida Everglades Conservation Biology 13 898–911
InstitutionalAuthorNameUSEPA (1990a) Water Quality Standards for Wetlands: National Guidance EPA-440/S-90-011 Office of Water Regulations and Standards, United States Environmental Protection Agency Washington, D.C.
InstitutionalAuthorNameUSEPA (1990b) Biological Criteria: National Program Guidance for Surface Waters, EPA 440-5-90-004 Office of Water Regulations and Standards, United States Environmental Protection Agency Washington, D.C.
P. Vaithiyanathan C. J. Richardson (1999) ArticleTitleMacrophyte species changes in the Everglades: examination along a eutrophication gradient Journal of Environmental Quality 28 1347–1358
D. K. Voigts (1976) ArticleTitleAquatic invertebrate abundance in relation to changing marsh vegetation American Midland Naturalist 95 313–322
W. W. Walker SuffixJr. (1995) ArticleTitleDesign basis for Everglades stormwater treatment areas Water Resources Bulletin 31 671–685
E. B. Welch (1980) Ecological Effects of Waste Water Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mccormick, P.V., Shuford, R.B. & Rawlik, P.S. Changes in macroinvertebrate community structure and function along a. Hydrobiologia 529, 113–132 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-5737-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-5737-7