Abstract
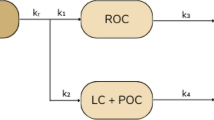
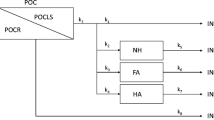
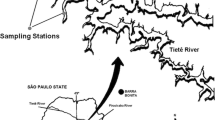
The temporal variation of stoichiometry between consumed oxygen and oxidized carbon was investigated for the aerobic mineralization of leachates from aquatic macrophytes. Seven species of aquatic plants, viz. Cabomba piauhyensis, Cyperus giganteus, Egeria najas, Eichhornia azurea, Salvinia auriculata, Scirpus cubensisand Utricularia breviscapa, were collected from Òleo lagoon located in the floodplain of Mogi-Guacu river (São Paulo State, Brazil). After being collected, the plants were washed, oven-dried and triturated. In order to obtain the leachate, the fragments were submitted to an aqueous extraction (cold). Mineralization chambers were incubated at 20 °C containing leachates dissolved in water samples from Òleo lagoon to a final concentration of ca. 200 mg l−1on carbon basis. The chambers were maintained under aerobic conditions; the concentrations of the organic carbon (particulate and dissolved) and the dissolved oxygen were measured during approximately 80 days. Elemental analysis of the detritus and the concentrations of the remaining material (DOC and POC) were used to determine the amounts of mineralized organic carbon. The data were analyzed with first-order kinetics models, from which the daily rates of consumption (carbon and oxygen) and the stoichiometry (O/C) were determined. In the early phase of mineralization the O/C rates increased before reaching a maximum, after which they tended to decrease. For the mineralization of leachates from C. giganteus, S. auriculata and U. breviscapa, the decrease was relatively slow. For all substrata the initial values were smaller than 1, and ranged from 0.42 (S. cubensis) to 0.81 (C. piauhyensis). The maximum values were within the range from 0.58 (U. breviscapa) to 23.1 (E. najas) and at their highest 26th (C. piauhyensis) and 106th (C. giganteus) days. These variations are believed to be associated with the chemical composition of the leachates, with their transformations and alterations of metabolic pathways involved in the mineralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, J. D., 1996. Stream Ecology-Structure and Function of Running Waters. Chapman & Hall, London.
Anesio, A. M., L. J. Tranvik & W. Granéli, 1999. Production of inorganic carbon from aquatic macrophytes by solar radiation. Ecology 80: 1852-1859.
Bianchini Jr., I., 1997. The degradation process of organic matter in reservoirs. In Rosa, L. P. & M. A. Santos (eds), Hydropower Plants and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. COPPE Report/Ed. Tecnológica, Rio de Janeiro: 6-27.
Bianchini Jr., I., 2000. Decomposição de macrótas aquáticas da lagoa do Infernão: o estado da arte. In Santos, J. E. & Pires, J. S. R. (eds), Estudos Integrados em Ecossistemas-Estaçaão Ecológica de Jataí, vol. 2. Rima, São Carlos, 613-629.
Bianchini Jr., I., 2003. Growth and decomposition models for aquatic macrophytes (in portuguese) In Thomaz, S. M. & L. M. Bini (eds), Ecologia e manejo de macrótas aquáticas. EDUEM, Maringá; 85-126.
Bianchini Jr., I. & R. M. Antonio, 2003. The effect of particle size on the leaching of Scirpus cubensis Poepp & Kunth. Brazilian Journal of Biology 63: 195-205.
Bitar, A. L. & I. Bianchini Jr., 2002. Mineralisation essays of some organic resources of aquatic systems. Brazilian Journal of Biology 62: 557-564.
Brum, P. R., V. F. Farjalla, J. F. Gonçalves Jr., A. M. Santos, M. T. Pôrto, E. D. R. Vieira, F. M. Ferreira & I. Bianchini Jr., 1999. Aspects of uptake of dissolved oxygen in Cabiúnas and Imboassica lagoons (Macaé, RJ). Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 42(4): 433-440.
Chapra, S. C. & K. H. Reckhow, 1983. Engineering Approaches for Lake Management, vol. 2. Mechanistic Modeling. Woburn, Butterworth/Ann Arbor.
Cunha, M. B. & I. Bianchini Jr., 1998. Mineralization aeróbia de Cabomba piauhyensis e Scirpus cubensis. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 10(1): 81-91.
Cunha, M. B. & I. Bianchini Jr., 2001. Formação de compostos húmicos a partir da degradaçãode Scirpus cubensis e Cabomba piauhyensis. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 13(2): 35-43.
Cunha-Santino, M. B. & I. Bianchini Jr., 2002a. Estequiometria da decomposição aeróbia de galhos, cascas serapilheira e folhas. In Espíndola, E. (ed.), Recursos hidroenergéticos: usos, impactos e planejamento integrado São Carlos, Rima: 185-197.
Cunha-Santino, M. B. & I. Bianchini Jr., 2002b. Humic substance mineralization in a tropical oxbow lake (São Paulo, Brazil). Hydrobiologia 468: 33-43.
Davis, M. L. & Cornwell, D. A., 1991. Introduction to Environmental Engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Dilly, O., 2001. Microbial respiratory quotient during basal metabolism and after glucose amendment in soils and litter. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 33: 117-127.
Farjalla, V. F., C. C. Marinho & F. A. Esteves, 1999. The uptake of oxygen in the initial stages of decomposition of aquatic macrophytes and detritus from terrestrial vegetation in a tropical coastal lagoon. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 11(2): 185-193.
Godinho, M. J. L., 2000. Ecologia de Microrganismos Lacustres. PPGERN-UFSCar, São Carlos.
Imai, A., T. Fukushima, K. Matsushige & Y. H. Kim, 2001. Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake, it 's in. owing rivers, and other organic matter sources. Water Research 35(17): 4019-4028.
Jorgensen S. E., 1986. Fundamentals of Ecological Modelling. Developments in Environmental Modelling, 9. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Lehninger, A. L., D. L. Nelson & M. M. Cox, 1993. Principles of Biochemistry. 2nd edn. Worth Publishers, New York.
Lemos, R. M. A., I. Bianchini Jr. & J. B. N. Mauro, 1998. Decomposition kinetics of aquatic macrophyte Scirpus cubensis under the in. uence of dissolved phosphate levels. R. Esc. Minas, Ouro Preto 51(3): 28-31.
Lousier, J. D. & D. Parkinson, 1976. Litter decomposition in a cool temperate deciduous forest. Canadian Journal of Botany 54: 419-436.
Lush, D. L. & H. B. N. Hynes, 1978. The uptake of dissolved organic matter by small spring stream. Hydrobiologia 60(3): 271-275.
McLatchey, G. P. & K. R. Reddy, 1998. Regulation of organic matter decomposition and nutrient release in a wetland soil. Journal of Environmental Quality 17: 1268-1274.
Pacobahyba, L. D., 2002. Decomposiçãode Staurastrum c.f. iversenii NYGAARD var. americanum: Efeitos da qualidade do recurso, da disponibilidade de oxigênio e da temperatura. UFSCar, São Carlos.
Pomeroy, L. R. & W. J. Wiebe, 1988. Energetic of microbial food webs. Hydrobiologia 156: 7-18.
Press, W. H., S. A., Teukolsky, W. T. Vetterling & S. A. Flannery, 1993. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge University Press, New York.
Stumm, W. & J. J. Morgan, 1981. Aquatic Chemistry. Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Swift, M. J., D. W. Heal & J. M. Anderson, 1979. Studies in Ecology. Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Blackwell, Oxford.
USEPA-United States Environmental Protection Agency., 1985. Rates, Constants and Kinetics Formulations in Surface Water Quality Modeling. 2nd edn. EPA/600/3-85/040. U. S. Government Printing Office, Athens.
Wetzel, R. G., 1983. Limnology. 2nd edn. Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia.
Wetzel, R. G., 1992. Gradient-dominated ecosystems: sources and regulatory functions of dissolved organic matter in freshwater ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 229: 181-198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peret, A., Bianchini, I. Stoichiometry of aerobic mineralization (O/C) of aquatic macrophytes leachate from a tropical lagoon (São Paulo –Brazil). Hydrobiologia 528, 167–178 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-2340-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-2340-x