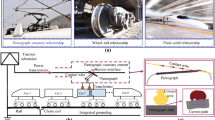
Special high-voltage busbar (current carrier) designs are widely used to connect various objects in stations and substations (generators, transformers, switchgear, etc.) and individual components of these systems (e.g., switchgear cells). Connecting various high-voltage objects at stations and substations with flexible wires is a thing of the past; this is now done with rigid non-corona busbars with air insulation, gas-filled current carriers, and current carriers with polymer insulation. In recent years, highly compact busbars have mainly involved the use of new insulating media (primarily gases and polymer dielectrics with high breakdown strengths), along with improvements in the technology for production and application of these materials. Various types of high-voltage busbars are currently in use: shielded air busbars, busbars with cast polymer insulation, sealed shielded busbars with primary insulation by high breakdown-strength gases. Losses in busbars are reduced by using technical solutions employing insulating media with low dielectric constants and the busbars are built to avoid corona at the rated working voltage. The solutions for busbar construction at present have various advantages and disadvantages, depending on the design of the busbar and the object on which it is used. Further improvements in high-voltage busbars will involve the creation of new polymer materials, technologies for their use, and the development and application of new gases with high breakdown strengths.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Mayer, “Profile extrusion of/with thermoplastic elastomers,” TPE Magazine, June, 26 – 31 (2009).
K. I. Chernyak, Epoxy Compounds and Their Applications [in Russian], Sudpromgiz, Leningrad (1963).
V. Zhuravlev, “Filling and impregnation in electrical technology. Latest technologies for Russian industry,” Nov. Élektrotekh., No. 5(113) – 6(114), (2018).
V. N. Varivodov, Internal Insulation of Gas-Filled Equipment for Super-High and Ultra-High Voltages. Doctoral Thesis [in Russian], Moscow (2000).
V. N. Varivodov, A. A. Demkin, and L. I. Emel’yanov, “Dependence of the electrical breakdown strength of cast epoxy insulation on dimensions in weakly nonuniform electric fields,” Élektrotekhnika, No. 1, 33 – 36 (1983).
E. I. Nesis, Boiling of Liquids [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1973).
J. Sato, S. Kinoshita, O. Sakaguchi, M. Miyagawa, T. Shimizu, and M. Homma, “Solid Insulated Switchgear and Investigation of its Mechanical and Electrical Reliability,” Electr. Eng. Japan, 174(4), (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Élektricheskie Stantsii, No. 10, October 2020, pp. 31 – 39.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varivodov, V.N., Kovalev, D.I., Zhulikov, S.S. et al. Technological Aspects of the Use of Cast Polymer Insulation for High-Voltage Switchgear and Busbars. Power Technol Eng 54, 915–922 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10749-021-01306-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10749-021-01306-2