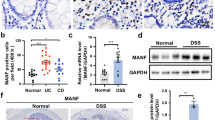
Abstract
The activation of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) has been reported to attenuate astrocytes injury in central nervous system, but its effect on enteric glial cells (EGCs) remains unknown. Here, we confirmed that the residence of EGCs was regulated by TLR3 agonist (polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid, PIC) or TLR3/dsRNA complex inhibitor in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced mice. In vitro, TLR3 signaling prevented apoptosis in EGCs and drove the secretion of EGCs-derived glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid and S-nitrosoglutathione. PIC preconditioning enhanced the protective effects of EGCs against the dysfunction of intestinal epithelial barrier and the development of colitis in DSS-induced mice. Interestingly, PIC stimulation also promoted the effects of EGCs on converting macrophages to an M2-like phenotype and regulating the levels of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-10, in DSS-induced mice. These findings imply that TLR3 signaling in EGCs may provide a potential target for the prevention and treatment of colitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Brun P, Giron MC, Qesari M et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal inflammation by controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 145:1323–1333
Bush TG, Savidge TC, Freeman TC et al (1998) Fulminant jejuno-ileitis following ablation of enteric glia in adult transgenic mice. Cell 93:189–201
Cader MZ, Kaser A (2013) Recent advances in inflammatory bowel disease: mucosal immune cells in intestinal inflammation. Gut 62:1653–1664
Capaldo CT (2023) Claudin barriers on the brink: how conflicting tissue and cellular priorities drive IBD pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 24:8562
Coelho-Aguiar Jde M, Bon-Frauches AC, Gomes AL et al (2015) The enteric glia: identity and functions. Glia 63:921–935
Cornet A, Savidge TC, Cabarrocas J et al (2001) Enterocolitis induced by autoimmune targeting of enteric glial cells: a possible mechanism in Crohn’s disease? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:13306–13311
Dharmasiri S, Garrido-Martin EM (2021) Human intestinal macrophages are involved in the pathology of both ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 27:1641–1652
Fuenzalida P, Kurte M, Fernández-O’ryan C et al (2016) Toll-like receptor 3 pre-conditioning increases the therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. Cytotherapy 18:630–641
Holland AM, Bon-Frauches AC (2021) The enteric nervous system in gastrointestinal disease etiology. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:4713–4733
Hunter MM, Wang A, Parhar KS et al (2010) In vitro-derived alternatively activated macrophages reduce colonic inflammation in mice. Gastroenterology 138:1395–1405
Isidro RA, Appleyard CB (2016) Colonic macrophage polarization in homeostasis, inflammation, and cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 311:G59–73
Li X, Cudaback E, Breyer RM et al (2012) Eicosanoid receptor subtype-mediated opposing regulation of TLR-stimulated expression of astrocyte glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Faseb j 26:3075–3083
Li H, Fan C, Lu H et al (2020) Protective role of berberine on ulcerative colitis through modulating enteric glial cells-intestinal epithelial cells-immune cells interactions. Acta Pharm Sin B 10:447–461
Martini E, Krug SM, Siegmund B, Neurath MF, Becker C (2017) Mend your fences: the epithelial barrier and its relationship with mucosal immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:33–46
Meir M, Kannapin F, Diefenbacher M (2021) Intestinal epithelial barrier maturation by enteric glial cells is GDNF-dependent. Int J Mol Sci 22:1887
Pan LN, Zhu W, Li C et al (2012) Toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C protects against simulated cerebral ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:1246–1253
Pochard C, Coquenlorge S, Jaulin J et al (2016) Defects in 15-HETE production and control of epithelial permeability by human enteric glial cells from patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 150:168–180
Qiu Y, Guo J, Mao R et al (2017) TLR3 preconditioning enhances the therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in TNBS-induced colitis via the TLR3-Jagged-1-Notch-1 pathway. Mucosal Immunol 10:727–742
Rocha SM, Cristovão AC, Campos FL, Fonseca CP, Baltazar G (2012) Astrocyte-derived GDNF is a potent inhibitor of microglial activation. Neurobiol Dis 47:407–415
Savidge TC, Newman P, Pothoulakis C et al (2007) Enteric glia regulate intestinal barrier function and inflammation via release of S-nitrosoglutathione. Gastroenterology 132:1344–1358
Sica A, Mantovani A (2012) Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest 122:787–795
Souza RF, Evangelinellis MM, Mendes CE et al (2020) P2X7 receptor antagonist recovers ileum myenteric neurons after experimental ulcerative colitis. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 11:84–103
Stakenborg M, Abdurahiman S, De Simone V et al (2022) Enteric glial cells favor accumulation of anti-inflammatory macrophages during the resolution of muscularis inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 15:1296–1308
Turco F, Sarnelli G, Cirillo C et al (2014) Enteroglial-derived S100B protein integrates bacteria-induced toll-like receptor signalling in human enteric glial cells. Gut 63:105–115
Vijay-Kumar M, Wu H, Aitken J et al (2007) Activation of toll-like receptor 3 protects against DSS-induced acute colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:856–864
von Boyen GB, Steinkamp M, Geerling I et al (2006) Proinflammatory cytokines induce neurotrophic factor expression in enteric glia: a key to the regulation of epithelial apoptosis in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12:346–354
Walldorf J, Porzner M, Neumann M et al (2022) The selective 5-HT1A agonist SR57746A protects intestinal epithelial cells and enteric glia cells and promotes mucosal recovery in experimental colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 28:423–433
Wang S, Ding Y, Jiang W (2022) CSE/H(2)S ameliorates colitis in mice via protection of enteric glial cells and inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Front Immunol 13:966881
Weisser SB, Brugger HK, Voglmaier NS et al (2011) SHIP-deficient, alternatively activated macrophages protect mice during DSS-induced colitis. J Leukoc Biol 90:483–492
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M et al (2017) Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc 12:1295–1309
Zeng J, Yu H, Gan HT (2021) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice via a macrophage-mediated pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 100:108143
Zhao HW, Yue YH, Han H et al (2017) Effect of toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C on intestinal mucosa and epithelial barrier function in mouse models of acute colitis. World J Gastroenterol 23:999–1009
Funding
This study was supported by the Xing Lin Scholar Scientific Research Fund Project from Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. YYZX2021051) and the Doctoral Special Scientific Research Fund Project from Science & Technology Commission of Chongqing (No. CSTB2022BSXM-JCX0073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed as well as interpreted data, and prepared the manuscript; QQL, XLD and LY performed the experiments; XJY analyzed data and critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, J., Lu, QQ., Du, XL. et al. Toll-like receptor 3 signaling drives enteric glial cells against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J Mol Histol 55, 201–210 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-024-10184-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-024-10184-7