Abstract
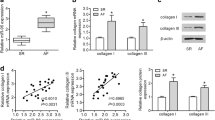
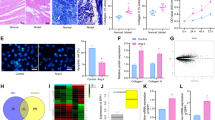
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been shown to be associated with cardiac fibrosis. Atrial fibrosis is an important pathophysiological event in the progression of atrial fibrillation (AF). Although a novel circRNA calmodulin binding transcription activator 1 (circCAMTA1) has been reported to be related with the development of AF, the detailed molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. In this study, we found that circCAMTA1 was upregulated in atrial muscle tissues of AF patients and angiotensin-II (Ang-II)-treated human atrial fibroblasts (HAFs). Moreover, circCAMTA1 expression was positively correlated with the expression of collagen (I and III) and α-SMA in atrial muscle tissues of AF patients. In vitro experiments, knockdown of circCAMTA1 significantly suppressed Ang-II-induced HAFs proliferation and reduced the expression of atrial fibrosis-associated genes, but overexpression of circCAMTA1 exhibited opposite results. In vivo experiments, circCAMTA1 knockdown ameliorated Ang-II-induced atrial fibrosis by reducing AF incidence, AF duration, and collagen synthesis. Functionally, circCAMTA1 facilitated Ang-II-induced atrial fibrosis in vitro and in vivo via downregulating the inhibitory effect of miR-214-3p on transforming growth factor β receptor 1 (TGFBR1) expression. In conclusions, circCAMTA1 knockdown alleviated atrial fibrosis through downregulating TGFBR1 expression intermediated by miR-214-3p in AF, suggesting circCAMTA1/miR-214-3p/TGFBR1 axis may be a novel therapeutic target for AF treatment in clinic.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babapoor-Farrokhran S, Tarighati Rasekhi R, Gill D et al (2021) How transforming growth factor contributes to atrial fibrillation? Life Sci 266:118823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118823
Bai M, Pan CL, Jiang GX et al (2020) CircRNA 010567 improves myocardial infarction rats through inhibiting TGF-β1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(1):369–375. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202001_19935
Bayoumi AS, Aonuma T, Teoh JP et al (2018) Circular noncoding RNAs as potential therapies and circulating biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39(7):1100–1109. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.196
Blomström-Lundqvist C, Gizurarson S, Schwieler J et al (2019) Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic medication on quality of life in patients with Atrial Fibrillation: the CAPTAF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 321(11):1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.0335
Cao F, Li Z, Ding WM et al (2019) LncRNA PVT1 regulates atrial fibrosis via miR-128-3p-SP1-TGF-β1-Smad axis in atrial fibrillation. Mol Med 25(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-019-0074-5
Cheng D, Xu Q, Liu Y et al (2021) Long noncoding RNA-SNHG20 promotes silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by miR-490-3p/TGFBR1 axis. Toxicology 451:152683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2021.152683
Cheng R, Dang R, Zhou Y et al (2017) MicroRNA-98 inhibits TGF-β1-induced differentiation and collagen production of cardiac fibroblasts by targeting TGFBR1. Hum Cell 30(3):192–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0163-0
Denby L, Ramdas V, Lu R et al (2014) MicroRNA-214 antagonism protects against renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(1):65–80. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2013010072
Dong H, Dong S, Zhang L et al (2016) MicroRNA-214 exerts a cardio-protective effect by inhibition of fibrosis. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 299(10):1348–1357. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23396
Dzeshka MS, Lip GY, Snezhitskiy V et al (2015) Cardiac fibrosis in patients with Atrial Fibrillation: mechanisms and clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol 66(8):943–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1313
Echahidi N, Pibarot P, O’Hara G et al (2008) Mechanisms, prevention, and treatment of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 51(8):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.043
Gao Y, Liu Y, Fu Y et al (2021) The potential regulatory role of hsa_circ_0004104 in the persistency of atrial fibrillation by promoting cardiac fibrosis via TGF-β pathway. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 21(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-021-01847-4
Hohendanner F, Messroghli D, Bode D et al (2018) Atrial remodelling in heart failure: recent developments and relevance for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail 5(2):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12260
Hu HJ, Zhang C, Tang ZH et al (2019) Regulating the Warburg effect on metabolic stress and myocardial fibrosis remodeling and atrial intracardiac waveform activity induced by atrial fibrillation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(3):653–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.055
Hu M, Wei X, Li M et al (2019) Circular RNA expression profiles of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatic heart disease. Anatol J Cardiol 21(1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2018.35902
Jalife J, Kaur K (2015) Atrial remodeling, fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc Med 25(6):475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2014.12.015
Jiang S, Guo C, Zhang W et al (2019) The Integrative Regulatory Network of circRNA, microRNA, and mRNA in Atrial Fibrillation. Front Genet 10:526. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00526
Kiyosawa N, Watanabe K, Morishima Y et al (2020) Exploratory analysis of circulating miRNA signatures in Atrial Fibrillation Patients determining potential biomarkers to support decision-making in anticoagulation and catheter ablation. Int J Mol Sci 21(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072444
Kugler S, Duray G, Préda I (2018) [Novel mechanisms in the initiation and maintenance of atrial fibrillation: tailored individual treatment]. Orv Hetil 159(28):1135–1145. https://doi.org/10.1556/650.2018.31087
Liao W, Liang P, Liu B et al (2020) MicroRNA-140-5p mediates renal fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway by directly targeting TGFBR1. Front Physiol 11:1093. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.01093
Marrouche NF, Wilber D, Hindricks G et al (2014) Association of atrial tissue fibrosis identified by delayed enhancement MRI and atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: the DECAAF study. JAMA 311(5):498–506. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3
Ni H, Li W, Zhuge Y et al (2019) Inhibition of circHIPK3 prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by sponging miR-29b-3p. Int J Cardiol 292:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.04.006
Palano F, Adduci C, Cosentino P et al (2020) Assessing Atrial Fibrillation Substrates by P Wave Analysis: a Comprehensive Review. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 27(5):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-020-00390-1
Qi Y, Wu H, Mai C et al (2020) LncRNA-MIAT-Mediated mir-214-3p silencing is responsible for IL-17 production and Cardiac Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:243. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00243
Ruan ZB, Wang F, Bao TT et al (2020) Genome-wide analysis of circular RNA expression profiles in patients with atrial fibrillation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 13(8):1933–1950
Shirazi-Tehrani E, Firouzabadi N, Tamaddon G et al (2020) Carvedilol alters circulating MiR-1 and MiR-214 in Heart failure. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 13:375–383. https://doi.org/10.2147/pgpm.s263740
Song Y, Wei CAI, Wang J (2021) Upregulation of mir-143-3p attenuates oxidative stress-mediated cell ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes with atrial fibrillation by degrading glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1. BIOCELL 45:733–744. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2021.013236
Sonnenschein K, Wilczek AL, de Gonzalo-Calvo D et al (2019) Serum circular RNAs act as blood-based biomarkers for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep 9(1):20350. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56617-2
Tan Z, Jiang X, Zhou W et al (2021) Taohong siwu decoction attenuates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting fibrosis proliferation and collagen deposition via TGFBR1 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 270:113838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.113838
Tang CM, Zhang M, Huang L et al (2017) CircRNA_000203 enhances the expression of fibrosis-associated genes by derepressing targets of miR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in cardiac fibroblasts. Sci Rep 7:40342. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40342
Teng Y, Ding M, Wang X et al (2020) LncRNA RMRP accelerates hypoxia-induced injury by targeting mir-214-5p in H9c2 cells. J Pharmacol Sci 142(2):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2019.07.014
Van Gelder IC, Rienstra M, Crijns HJ et al (2016) Rate control in atrial fibrillation. Lancet 388(10046):818–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31258-2
Wang Y, Cai H, Li H et al (2018) Atrial overexpression of microRNA-27b attenuates angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis and fibrillation by targeting ALK5. Hum Cell 31(3):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-018-0208-z
Xiao J, Zhang Y, Tang Y et al (2021) Hsa-miR-4443 inhibits myocardial fibroblast proliferation by targeting THBS1 to regulate TGF-β1/α-SMA/collagen signaling in atrial fibrillation. Braz J Med Biol Res 54(4):e10692. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431x202010692
Yang K, Shi J, Hu Z et al (2019) The deficiency of mir-214-3p exacerbates cardiac fibrosis via miR-214-3p/NLRC5 axis. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(17):1845–1856. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20190203
Yang X, Dan X, Men R et al (2017) MiR-142-3p blocks TGF-β-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells through targeting TGFβRI. Life Sci 187:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.017
Yousefi F, Soltani BM (2021) Circular RNAs as potential theranostics in the cardiac fibrosis. Heart Fail Rev 26(1):195–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09908-9
Yu RB, Li K, Wang G et al (2019) MiR-23 enhances cardiac fibroblast proliferation and suppresses fibroblast apoptosis via targeting TGF-β1 in atrial fibrillation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(10):4419–4424. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201905_17950
Zhang C, Huo ST, Wu Z et al (2020) Rapid Development of Targeting circRNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.022
Zhang H, Liu L, Hu J et al (2015) MicroRNA Regulatory Network revealing the mechanism of inflammation in Atrial Fibrillation. Med Sci Monit 21:3505–3513. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.895982
Zhang PP, Sun J, Li W (2020) Genome-wide profiling reveals atrial fibrillation-related circular RNAs in atrial appendages. Gene 728:144286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.144286
Zhang XL, An BF, Zhang GC (2019) MiR-27 alleviates myocardial cell damage induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation via targeting TGFBR1 and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 35(10):607–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12092
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J (2018) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for Human Diseases. EBioMedicine 34:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036
Zhao X, Wang K, Liao Y et al (2015) MicroRNA-101a inhibits cardiac fibrosis induced by hypoxia via targeting TGFβRI on cardiac fibroblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(1):213–226. https://doi.org/10.1159/000369689
Zhou B, Yu JW (2017) A novel identified circular RNA, circRNA_010567, promotes myocardial fibrosis via suppressing miR-141 by targeting TGF-β1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487(4):769–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.044
Zhu L, Li N, Sun L et al (2021) Non-coding RNAs: the key detectors and regulators in cardiovascular disease. Genomics 113(1 Pt 2):1233–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.10.024
Zhu Y, Pan W, Yang T et al (2019) Upregulation of circular RNA CircNFIB attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis by sponging miR-433. Front Genet 10:564. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00564
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZ conceived and designed the study and wrote the manuscript. LZ, QL, and WZ conducted the experiments. WML provided experimental advice and revised the manuscript. WY, HYZ, and YHK provided experimental advice. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Lou, Q., Zhang, W. et al. CircCAMTA1 facilitates atrial fibrosis by regulating the miR-214-3p/TGFBR1 axis in atrial fibrillation. J Mol Histol 54, 55–65 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-022-10110-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-022-10110-9