Abstract
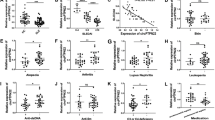
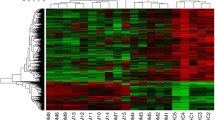
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a systemic autoimmune disease. It’s known that the number of regulatory T (Treg) cells was decreased in DM. Besides, Treg cells were increased after treatment in DM patients. Forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) is specifically expressed in Treg cells and Runt-related transcription factor (RUNX3) could regulate Foxp3 transcription. And our previous experiment showed that Homeobox D gene cluster antisense growth-associated long noncoding RNA (HAGLR) was up-regulated in DM patients. Here, we aimed to explore whether HAGLR regulated the differentiation of Treg cells through RUNX3-mediated transcription of Foxp3, thus affecting the progression of DM. The levels of HAGLR, Foxp3, and RUNX3 were examined by quantitative real-time PCR. The protein levels of Foxp3 and RUNX3 were examined by western blot. The proportions of Treg cells in CD4+ T cells were detected by flow cytometry. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was conducted to observe the histopathological changes of the muscle. RNA pull-down assay was performed to detect the interaction between HAGLR and RUNX3. A dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was conducted to examine the effect of HAGLR on the transcriptional regulation of Foxp3 by RUNX3. HAGLR was up-regulated and Foxp3 was down-regulated in DM patients. Besides, RUNX3 protein levels were decreased in DM patients, while its mRNA levels did not change significantly. The proportion of Treg cells was down-regulated in DM patients. In addition, interference with HAGLR could increase the levels of Foxp3, RUNX3 protein level, and the proportion of Treg cells. Besides, there was an interaction between HAGLR and RUNX3. We also found that knockdown of HAGLR and RUNX3 restored the increased Treg cells induced by HAGLR knockdown alone. In vivo experiments indicated that injection with adv-HAGLR increased Treg cell proportion and attenuated DM development. Interference with HAGLR could increase the protein levels of RUNX3, high levels of RUNX3 further promoted the expression of the Foxp3, thus restoring the number of Treg cells and easing the development of DM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banica L, Besliu A, Pistol G, Stavaru C, Ionescu R, Forsea A, Tanaseanu C, Dumitrache S, Otelea D, Tamsulea I et al (2009) Quantification and molecular characterization of regulatory T cells in connective tissue diseases. Autoimmunity 42(1):41–49
Bellucci M, Agostini F, Masin M, Tartaglia GG (2011) Predicting protein associations with long noncoding RNAs. Nat Methods 8(6):444–445
Bruno L, Mazzarella L, Hoogenkamp M, Hertweck A, Cobb BS, Sauer S, Hadjur S, Leleu M, Naoe Y, Telfer JC et al (2009) Runx proteins regulate Foxp3 expression. J Exp Med 206(11):2329–2337
Chakraborty S, Panda AK, Bose S, Roy D, Kajal K, Guha D, Sa G (2017a) Transcriptional regulation of FOXP3 requires integrated activation of both promoter and CNS regions in tumor-induced CD8(+) Treg cells. Sci Rep 7(1):1628
Chakraborty S, Panda A, Bose S, Roy D, Kajal K, Guha D (2017b) Sa GJSr: transcriptional regulation of FOXP3 requires integrated activation of both promoter and CNS regions in tumor-induced CD8 Treg cells. Sci Rep 7(1):1628
Cirillo D, Agostini F, Klus P, Marchese D, Rodriguez S, Bolognesi B, Tartaglia GG (2013) Neurodegenerative diseases: quantitative predictions of protein-RNA interactions. RNA (New York, NY) 19(2):129–140
Dalakas MC (2015) Inflammatory muscle diseases. N Engl J Med 372(18):1734–1747
Dalakas MC, Hohlfeld R (2003) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet (Lond, Engl) 362(9388):971–982
DeWane M, Waldman R, Lu J (2020) Dermatomyositis: clinical features and pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol 82(2):267–281
Ding JW, Zheng XX, Zhou T, Tong XH, Luo CY, Wang XA (2016) HMGB1Modulates the Treg/Th17 ratio in atherosclerotic patients. J Atheroscler Thromb 23(6):737–745
Feng M, Guo H, Zhang C, Wang Y, Liang Z, Zhao X, Qin Y, Wu Y, Liu G, Gao C et al (2019a) Absolute reduction of regulatory T cells and regulatory effect of short-term and low-dose IL-2 in polymyositis or dermatomyositis. Int Immunopharmacol 77:105912
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4(4):330–336
Guo X, Chen Z, Zhao L, Cheng D, Song W, Zhang X (2019) Long non-coding RNA-HAGLR suppressed tumor growth of lung adenocarcinoma through epigenetically silencing E2F1. Exp Cell Res 382(1):111461
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299(5609):1057–1061
Jablonski R, Bhorade S, Strek M, Dematte J (2020) Recognition and management of myositis-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Chest 158(1):252–263
Jiang T, Huang Y, Liu H, Xu Q, Gong Y, Chen Y, Hu X, Han Z, Gao M (2020) Reduced miR-146a promotes REG3A expression and macrophage migration in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Front Immunol 11:37
Kang J, Zhang HY, Feng GD, Feng DY, Jia HG (2015) Development of an improved animal model of experimental autoimmune myositis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(11):14457–14464
Klunker S, Chong MM, Mantel PY, Palomares O, Bassin C, Ziegler M, Rückert B, Meiler F, Akdis M, Littman DR et al (2009a) Transcription factors RUNX1 and RUNX3 in the induction and suppressive function of Foxp3+ inducible regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 206(12):2701–2715
Klunker S, Chong M, Mantel P, Palomares O, Bassin C, Ziegler M, Rückert B, Meiler F, Akdis M, Littman D et al (2009b) Transcription factors RUNX1 and RUNX3 in the induction and suppressive function of Foxp3+ inducible regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 206(12):2701–2715
Kopp F, Mendell JT (2018) Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 172(3):393–407
Lang B, Armaos A, Tartaglia GG (2019) RNAct: protein-RNA interaction predictions for model organisms with supporting experimental data. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D601–D606
Li Q, Li Q, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhao X, Tan B, Ai J, Zhang Z, Song J, Shan B (2013) Prevalence of Th17 and Treg cells in gastric cancer patients and its correlation with clinical parameters. Oncol Rep 30(3):1215–1222
Li Y, Li Y, Wu J, Miao M, Gao X, Cai W, Shao M, Zhang X, Xu Y, Cong L et al (2020) Predictors of poor outcome of anti-MDA5-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a Chinese cohort with dermatomyositis. J Immunol Res 2020:2024869
Roman MG, Flores LC, Cunningham GM, Cheng C, Dube S, Allen C, Van Remmen H, Bai Y, Saunders TL, Ikeno Y (2020) Thioredoxin overexpression in mitochondria showed minimum effects on aging and age-related diseases in male C57BL/6 mice. APT 2:20–31
Sacks D, Baxter B, Campbell BCV, Carpenter JS, Cognard C, Dippel D, Eesa M, Fischer U, Hausegger K, Hirsch JA et al (2018) Multisociety consensus quality improvement revised consensus statement for endovascular therapy of acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 13(6):612–632
Sadlon T, Brown CY, Bandara V, Hope CM, Schjenken JE, Pederson SM, Breen J, Forrest A, Beyer M, Robertson S et al (2018) Unravelling the molecular basis for regulatory T-cell plasticity and loss of function in disease. Clin Transl Immunol 7(2):e1011
Shimojima Y, Matsuda M, Ishii W, Kishida D, Sekijima YJA (2017) T-cell receptor-mediated characteristic signaling pathway of peripheral blood T cells in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Autoimmunity 50(8):481–490
Sun W, Nie W, Wang Z, Zhang H, Li Y, Fang XJO (2020) Lnc HAGLR promotes colon cancer progression through sponging miR-185–5p and activating CDK4 and CDK6 in vitro and in vivo. Onco Targets Therapy 13:5913–5925
Tjärnlund A, Tang Q, Wick C, Dastmalchi M, Mann H, Tomasová Studýnková J, Chura R, Gullick NJ, Salerno R, Rönnelid J et al (2018a) Abatacept in the treatment of adult dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a randomised, phase IIb treatment delayed-start trial. Ann Rheum Dis 77(1):55–62
Tjärnlund A, Tang Q, Wick C, Dastmalchi M, Mann H, Tomasová Studýnková J, Chura R, Gullick N, Salerno R, Rönnelid J et al (2018b) Abatacept in the treatment of adult dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a randomised, phase IIb treatment delayed-start trial. Ann Rheum Dis 77(1):55–62
Wang L, Yang J, Wang H, Wang W, Liang X (2020) Highly expressed ribosomal protein L34 predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and could be a poential therapy target. APT 2:32–37
Waschbisch A, Schwab N, Ruck T, Stenner MP, Wiendl H (2010) FOXP3+ T regulatory cells in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. J Neuroimmunol 225(1–2):137–142
Williams LM, Rudensky AY (2007) Maintenance of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nat Immunol 8(3):277–284
Wolf D, Hochegger K, Wolf AM, Rumpold HF, Gastl G, Tilg H, Mayer G, Gunsilius E, Rosenkranz AR (2005) CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells inhibit experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(5):1360–1370
Wu L, Xia J, Li D, Kang Y, Fang W, Huang P (1934) Mechanisms of M2 macrophage-derived exosomal long non-coding RNA PVT1 in regulating Th17 cell response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitisa. Front Immunol 2020:11
Xu K, Xu Q, Wu Z, Xu S, Shen J (2018) LncRNA NEAT1 is involved in temozolomide resistance by regulating MGMT in glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Surg Res Commun 1:24–30
Yang C, Shen S, Zheng X, Ye K, Sun Y, Lu Y (2019) Ge HJFjopotFoASfEB: long noncoding RNA HAGLR acts as a microRNA-143–5p sponge to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastatic potential in esophageal cancer by regulating LAMP3. FASEB J 33(9):10490–10504
Zhang Q, Zhou L, Xie H, Zhang H, Gao X (2021) HAGLR aggravates neuropathic pain and promotes inflammatory response and apoptosis of lipopolysaccharide-treated SH-SY5Y cells by sequestering miR-182–5p from ATAT1 and activating NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurochem Int 145:105001
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Public Service and Application Research Foundation, China (Grant No. KY19H090002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, W., Wang, L., Chen, Z. et al. Knockdown of lncRNA HAGLR promotes Treg cell differentiation through increasing the RUNX3 level in dermatomyositis. J Mol Histol 53, 413–421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10051-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10051-9