Abstract
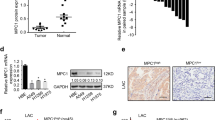
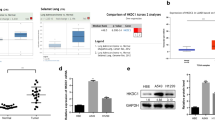
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common histological subtype of lung cancer, and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. G6PD has been reported to enhance the progression of various tumors by regulating the intracellular redox state and mediating nucleic acid synthesis. However, the biological role and molecular mechanism of G6PD in LUAD remain largely unknown. In this study, we found that G6PD was significantly upregulated in LUAD specimens and cell lines, and that the high levels of G6PD expression were closely associated with a poor prognosis for LUAD patients. Moreover, we found that G6PD significantly promoted the proliferation and migration of LUAD cells in vitro, and overexpression of G6PD also play a role of facilitating tumorigenesis in in vivo experiments. Mechanistically, the STAT3 signaling pathway was significantly activated by G6PD-mediated LUAD progression. Overall, our results suggest that G6PD could serve as a novel prognostic marker and therapeutic target for treating LUAD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amara I, Timoumi R, Annabi E, Salem I, Abid-Essefi S (2020) Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate inhibits glutathione regeneration and dehydrogenases of the pentose phosphate pathway on human colon carcinoma cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 25:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-01060-5
Barajas J, Reyes R, Guerrero M, Jacob S, Motiwala T, Ghoshal K (2018) The role of miR-122 in the dysregulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) expression in hepatocellular cancer. Sci Rep 8:9105. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27358-5
Cheng A, Chiu D, See L, Liao C, Chen I, Chang J (2001) Poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal cancer patients with low glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase activity. Jpn J Cancer Res: Gann 92:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2001.tb01132.x
Detterbeck F, Boffa D, Kim A, Tanoue L (2017) The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest 151:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.010
Drabovich A, Pavlou M, Dimitromanolakis A, Diamandis E (2012) Quantitative analysis of energy metabolic pathways in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by selected reaction monitoring assay. Mol Cell Proteom 11:422–434. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M111.015214
Hu H et al (2014) Changes in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression results in altered behavior of HBV-associated liver cancer cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 307:G611-622. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00160.2014
Hu T et al (2016) miR-1 inhibits progression of high-risk papillomavirus-associated human cervical cancer by targeting G6PD. Oncotarget 7:86103–86116. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13344
Huang M, Page C, Reynolds R, Lin J (2000) Constitutive activation of stat 3 oncogene product in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Gynec Oncol 79:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.2000.5931
Huang T et al (2019) Antrodia cinnamomea induces anti-tumor activity by inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway in lung cancer cells. Sci Rep 9:5145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41653-9
Jiang P, Du W, Wang X, Mancuso A, Gao X, Wu M, Yang X (2011) p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nature Cell Biol 13:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2172
Kim D, Chan K, Sano S, Digiovanni J (2007) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) in epithelial carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog 46:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.20342
Kong J et al (2021) ICAM-1 activates platelets and promotes endothelial permeability through VE-cadherin after insufficient radiofrequency ablation. Adv Sci (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 8:2002228. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202002228
Nagashio R et al (2019) Prognostic significance of G6PD expression and localization in lung adenocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1867:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.05.005
Rao K et al (1997) Hepatic hyperplasia and cancer in rats: metabolic alterations associated with cell growth. Gastroenterology 113:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70101-x
Rao X et al (2015) O-GlcNAcylation of G6PD promotes the pentose phosphate pathway and tumor growth. Nature Commun 6:8468. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9468
Riganti C, Gazzano E, Polimeni M, Aldieri E, Ghigo D (2012) The pentose phosphate pathway: an antioxidant defense and a crossroad in tumor cell fate. Free Radic Biol Med 53:421–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.006
Shi Y et al (2016) Prognostic and predictive values of CDK1 and MAD2L1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7:85235–85243. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13252
Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. Cancer J Clin 69:7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Wang G, Li Y, Yang Z, Xu W, Yang Y, Tan X (2018) ROS mediated EGFR/MEK/ERK/HIF-1α loop regulates glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500:873–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.177
Yang L et al (2018) Regulation of AMPK-related glycolipid metabolism imbalances redox homeostasis and inhibits anchorage independent growth in human breast cancer cells. Redox Biol 17:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.04.016
Yu F, Wu W, Liang M, Huang Y, Chen C (2020) Prognostic significance of Rab27A and Rab27B expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Manag Res 12:6353–6361. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s258940
Zappa C, Mousa S (2016) Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5:288–300. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2016.06.07
Funding
This work was supported by the Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (grant number: 2018Y9017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chun Chen conceived and designed the study. Weidong Wu performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Fengqiang Yu and Nanding Yu performed the experiments and analyzed data. Yong Zhu helped with manuscript revision. Weihan Wu and Pengqiang Gao collected patients’ clinical data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare having no conflict of interest relevant to this research.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Fujian Medical University Union Hospital (Fuzhou, China).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Yu, F., Yu, N. et al. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase promotes the proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the STAT3 signaling pathway. J Mol Histol 53, 215–225 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10045-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10045-7