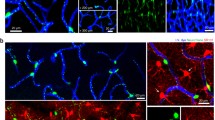
Abstract
The neurovascular structures in the cranial dura mater have been studied with various histological techniques in the past years. In order to obtain a proper approach to reveal the detailed structures, different labeling methods for the cranial vessels and nerve fibers were tested in this study. Firstly, the labeling characteristics of phalloidin, alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and CD31 were compared in rat whole-mount cranial dura mater by using fluorescent immunohistochemistry or histochemistry. Secondly, according to their properties, phalloidin and α-SMA were selected to combine with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) to further demonstrate the cranial neurovascular structure. By these approaches, a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and nerve fibers within the whole-mount rat cranial dura mater was obtained. The results showed that phalloidin, α-SMA, and CD31 were preferably expressed in the wall of cranial vessels, corresponding to the arteriors, venules, and capillaries, respectively. Additionally, CGRP + nerve fibers were clearly demonstrated together with phalloidin + or α-SMA + vessels, forming a delicate neurovascular network in the cranial dura mater. The thick nerve bundles ran closely to the phalloidin + or α-SMA + vessels in parallel pattern, while the thin nerve fibers branched off from the bundles tending to surround the phalloidin + arterioles rather than α-SMA + venules. These findings suggest that phalloidin could be an appropriate biochemical maker to be effectively used together with CGRP for experiments examining the detailed spatial correlation of cranial blood vessels and nerve fibers in a three-dimensional view, which may provide clues for understanding the underlying mechanisms of cranial neurovascular disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon-Martinez L, Yilmaz-Ozcan S, Yemisci M, Schallek J, Kılıç K, Can A, Di Polo A, Dalkara T (2018) Capillary pericytes express α-smooth muscle actin, which requires prevention of filamentous-actin depolymerization for detection. Elife 21:7
Amin FM, Hougaard A, Schytz HW, Asghar MS, Lundholm E, Parvaiz AI, de Koning PJ, Andersen MR, Larsson HB, Fahrenkrug J, Olesen J, Ashina M (2014) Investigation of the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine attacks induced by pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-38. Brain 137:779–794
Andres KH, von Düring M, Muszynski K, Schmidt RF (1987) Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 175:289–301
Armulik A, Genové G, Betsholtz C (2011) Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell 21(2):193–215
Baluk P, Fuxe J, Hashizume H, Romano T, Lashnits E, Butz S, Vestweber D, Corada M, Molendini C, Dejana E, McDonald DM (2007) Functionally specialized junctions between endothelial cells of lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med 204(10):2349–2362
Benarroch EE (2011) CGRP: sensory neuropeptide with multiple neurologic implications. Neurology 77:281–287
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2016) Endothelial PECAM-1 and its function in vascular physiology and atherogenic pathology. Exp Mol Pathol 100(3):409–415
Cooper JA (1987) Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol 105(4):1473–1478
Chazotte B (2010) Labeling cytoskeletal F-actin with rhodamine phalloidin or fluorescein phalloidin for imaging. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 5:pdb.prot4947
Dasgupta K, Jeong J (2019) Developmental biology of the meninges. Genesis 57(5):e23288
Dodick DW (2018) A phase-by-phase review of migraine pathophysiology. Headache 58(Suppl 1):4–16
Dudnakova T, Spraggon L, Slight J, Hastie N (2010) Actin: a novel interaction partner of WT1 influencing its cell dynamic properties. Oncogene 29(7):1085–1092
Eftekhari S, Warfvinge K, Blixt FW, Edvinsson L (2013) Differentiation of nerve fibers storing CGRP and CGRP receptors in the peripheral trigeminovascular system. J Pain 14:1289–1303
Eftekhari S, Salvatore CA, Calamari A, Kane SA, Tajti J, Edvinsson L (2010) Differential distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptor components in the human trigeminal ganglion. Neuroscience 169:683–696
Fricke B, von Düring M, Andres KH (1997) Topography and immunocytochemical characterization of nerve fibers in the leptomeningeal compartments of the rat. A light- and electron-microscopical study. Cell Tissue Res 287:11–22
Goadsby PJ, Holland PR, Martins-Oliveira M, Hoffmann J, Schankin C, Akerman S (2017) Pathophysiology of migraine: a disorder of sensory processing. Physiol Rev 97(2):553–622
Hagan IM (2016) Staining fission yeast filamentous actin with fluorescent phalloidin conjugates. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 6:10
Huber F, Schnauß J, Rönicke S, Rauch P, Müller K, Fütterer C, Käs J (2013) Emergent complexity of the cytoskeleton: from single filaments to tissue. Adv Phys 62(1):1–112
Iyengar S, Ossipov MH, Johnson KW (2017) The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain 158:543–559
Jacobs B, Dussor G (2016) Neurovascular contributions to migraine: moving beyond vasodilation. Neuroscience 338:130–144
Jansen I, Uddman R, Ekman R, Olesen J, Ottosson A, Edvinsson L (1992) Distribution and effects of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, and calcitonin gene-related peptide in human middle meningeal arteries: comparison with cerebral and temporal arteries. Peptides 13:527–536
Kekere V, Alsayouri K (2020) Anatomy, head and neck, dura mater. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL)
Kornfield TE, Newman EA (2014) Regulation of blood flow in the retinal trilaminar vascular network. J Neurosci 34(34):11504–11513
Kur J, Newman EA, Chan-Ling T (2012) Cellular and physiological mechanisms underlying blood flow regulation in the retina and choroid in health and disease. Prog Retin Eye Res 31(5):377–406
Lennerz JK, Rühle V, Ceppa EP, Neuhuber WL, Bunnett NW, Grady EF, Messlinger K (2008) Calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR), receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in the rat trigeminovascular system: differences between peripheral and central CGRP receptor distribution. J Comp Neurol 507:1277–1299
Liu Y, Broman J, Edvinsson L (2008) Central projections of the sensory innervation of the rat middle meningeal artery. Brain Res 1208:103–110
Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T (2007) Regionally varying F-actin network in the apical cytoplasm of ependymocytes. Neurosci Res 57:522–530
Li YC, Bai WZ, Sakai K, Hashikawa T (2009) Fluorescence and electron microscopic localization of F-actin in the ependymocytes. J Histochem Cytochem 57:741–751
MacGregor Sharp M, Criswell TP, Dobson H, Finucane C, Verma A, Carare RO (2019) Solving an old dogma: is it an arteriole or a venule? Front Aging Neurosci 11:289
Messlinger K, Hanesch U, Baumgärtel M, Trost B, Schmidt RF (1993) Innervation of the dura mater encephali of cat and rat: ultrastructure and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like and substance P-like immunoreactivity. Anat Embryol (Berl) 188:219–237
Messlinger K, Fischer MJ, Lennerz JK (2011) Neuropeptide effects in the trigeminal system: pathophysiology and clinical relevance in migraine. Keio J Med 60:82–89
Pankov R, Endo Y, Even-Ram S, Araki M, Clark K, Cukierman E, Matsumoto K, Yamada KM (2005) A Rac switch regulates random versus directionally persistent cell migration. J Cell Biol 170:793–802
Russell FA, King R, Smillie SJ, Kodji X, Brain SD (2014) Calcitonin gene-related peptide: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 94:1099–1142
Shimizu T, Toriumi H, Sato H, Shibata M, Nagata E, Gotoh K, Suzuki N (2007) Distribution and origin of TRPV1 receptor-containing nerve fibers in the dura mater of rat. Brain Res 1173:84–91
Skalli O, Pelte MF, Peclet MC, Gabbiani G, Gugliotta P, Bussolati G, Ravazzola M, Orci L (1989) Alpha-smooth muscle actin, a differentiation marker of smooth muscle cells, is present in microfilamentous bundles of pericytes. J Histochem Cytochem 37(3):315–321
Smillie SJ, Brain SD (2011) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and its role in hypertension. Neuropeptides 45(2):93–104
Strassman AM, Weissner W, Williams M, Ali S, Levy D (2004) Axon diameters and intradural trajectories of the dural innervation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 473:364–376
Thavarajah R, Mudimbaimannar VK, Elizabeth J, Rao UK, Ranganathan K (2012) Chemical and physical basics of routine formaldehyde fixation. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 16:400–405
Uddman RL, Edvinsson R, Ekman T, Kingman T, McCulloch J (1985) Innervation of the feline cerebral vasculature by nerve fibers containing calcitonin gene-related peptide: trigeminal origin and co-existence with substance P. Neurosci Lett 62:131–136
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Nourshargh S (2007) PECAM-1: a multi-functional molecule in inflammation and vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(12):2514–2523
Wulf E, Deboben A, Bautz FA, Faulstich H, Wieland T (1979) Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4498–4502
Funding
This study was supported by the project of National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2019YFC1709103; No. 2018YFC1707804), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81774211; 81774432; 81801561).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work presented here was carried out in collaboration between all authors. JW, DX, JC, CS, HW, SW, WB, SW, JZ and BZ carried out the experiments and analysed the data. JW and WB designed the study and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript accepted for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xu, D., Cui, J. et al. A new approach for examining the neurovascular structure with phalloidin and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat cranial dura mater. J Mol Hist 51, 541–548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09903-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09903-7