Abstract
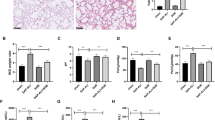
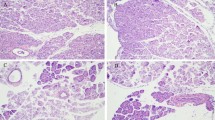
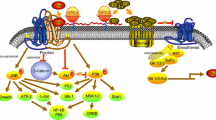
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) associated acute lung injury (ALI) accounts for about 70% mortality of SAP patients. However, there are no precise biomarkers for the disease currently. Herein, we evaluated the potential of gamma-enolase (ENO2), against its universal isoform alpha-enolase (ENO1), as a marker of SAP–ALI in a rat model. Firstly, 16 male Sprague–Dawley rats were randomly divided into two groups, Sham (n = 8) and SAP–ALI (n = 8), for pancreatitis induction. Ultra-structure examination by electron microscopy and HE staining were used for lung injury assessment. Lung tissue expressions of alpha-enolase and gamma-enolase were evaluated by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. In a prospective validation experiment, 28 rats were used: sham (n = 8), SAP–ALI at 3 h (3 h, n = 10), and SAP–ALI at 24 h (24 h, n = 10). Lung tissue damage, tissue expression and circulating alpha-enolase and gamma-enolase levels were evaluated. Elevated serum levels of α-amylase and TNF-α were observed in SAP rats but not in sham-operated rats. Histological examination of pancreatic and lung tissues indicated marked damage in SAP rats. While alpha-enolase was universally expressed, gamma-enolase was expressed only in damaged lung tissues. Gamma-enolase was detected in lung tissues, BALF, and serum as early as 3 h post-surgery when physical pathological damage was not apparent. Unlike alpha-enolase, secreted and/or circulating gamma-enolase level progressively increased, especially in serum, as lung damage progressed. Thus, gamma-enolase may signal and correlate lung tissue damage well before obvious physical pathological tissue damage and might be a candidate diagnostic and/or prognostic marker.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E, Carmody A, Shenkar R, Arcaroli J (2000) Neutrophils as early immunologic effectors in hemorrhage- or endotoxemia induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L1137–L1145
Acosta JM, Ledesma CL (1974) Gallstone migration as a cause of acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 290:484–487
Allen FJ, Van Velden DJ, Heyns CF (1995) Are neuroendocrine cells of practical value as an independent prognostic parameter in prostate cancer? Br J Urol 75:751–754
Bhargava M, Becker TL, Vilken KJ, Jagtap PD, Dey S, Steinbach MS, Wu B, Kumar V, Bitterman PB, Ingbar DH, Wendt CH (2014) Proteomic profile in acute respiratory distress syndrome differentiates survivors from non-survivors. PLoS ONE 9:e109713. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109713
Blondonnet R, Constantin J-M, Sapin V, Jabaudon M (2016) A pathophysiologic approach to biomarkers in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3501373
Collazos J, Esteban C, Fernandez A, Genolla J (1994) Measurement of the serum tumor marker neuron-specific enolase in patients with benign pulmonary diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 150:143–145
Dervenis C, Johnson CD, Bassi C, Bradley E, Imrie CW, McMahon MJ, Modlin I (1999) Diagnosis, objective assessment of severity, and management of acute pancreatitis: Santorini consensus conference. Int J Pancreatol 25:195–210
Díaz-Ramos A, Roig-Borrellas A, García-Melero A, López-Alemany R (2012) α-Enolase, a multifunctional protein: its role on pathophysiological situations. J Biomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/156795
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J, Zeller R (2008) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4986
Flexner S (1906) The constituents of the bile causing pancreatitis and the effect of colloids upon its action. J Exp Med 8:167–177
Fremont RD, Koyama T, Calfee CS, Wu W, Dossett LA, Bossert FR, Mitchell D, Wickersham N, Bernard GR, Matthay MA, May AK, Ware LB (2010) Acute lung injury in patients with traumatic injuries: utility of a panel of biomarkers for diagnosis and pathogenesis. J Trauma 68:1121–1127
Guice KS, Oldham KT, Johnson KJ, Kunkel RG, Morganroth ML, Ward PA (1988) Pancreatitis-induced acute lung injury: an ARDS model. Ann Surg 208:71–77
Haimoto H, Takahashi Y, Koshikawa T, Nagura H, Kato K (1985) Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-enolase in normal human tissues other than nervous and neuroendocrine tissues. Lab Invest 52:257–263
Hao X, Sun B, Hu L et al (2004) Differential gene and protein expression in primary breast malignancies and their lymph node metastases as revealed by combined cDNA microarray and tissue microarray analysis. Cancer 100:1110–1122
Isgrò MA, Bottoni P, Scatena R (2015) Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol 867:125–143
Kasprzak A, Zabel M, Biczysko W (2007) Selected markers (chromogranin A, neuron-specific enolase, synaptophysin, protein gene product 9.5) in diagnosis and prognosis of neuroendocrine pulmonary tumours. Pol J Pathol 58:23–33
Kondoh H, Lleonart ME, Bernard D, Gil J (2007) Protection from oxidative stress by enhanced glycolysis; a possible mechanism of cellular immortalization. Histol Histopathol 22:85–90
Konrad FM, Reutershan J (2012) CXCR2 in acute lung injury. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/740987
Lamerz R (1998) NSE (neuron-specific enolase) γ-enolase. In: Thomas L (ed) Clinical laboratory diagnostics: use and assessment of clinical laboratory results, 1st edn. TH-Books Verlagsgesellschaft, Frankfurt, pp 979–981
Leiherer A, Stoemmer K, Muendlein A, Saely CH, Kinz E, Brandtner EM, Fraunberger P, Drexel H (2016) Quercetin impacts expression of metabolism and obesity-associated genes in SGBS adipocytes. Nutrients 8:E282. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050282
Liu G, Zhang J, Chen H, Wang C, Qiu Y, Liu Y, Wan J, Guo H (2014) Effects and mechanisms of alveolar type II epithelial cell apoptosis in severe pancreatitis-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med 7:565–572
Luan Z-G, Zhang J, Yin X-H, Ma X-C, Guo R-X (2013) Ethyl pyruvate significantly inhibits tumour necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and high mobility group box 1 releasing and attenuates sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury. Clin Exp Immunol 172:417–426
Mair J (1997) Progress in myocardial damage detection: new biochemical markers for clinicians. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 34:1–66
Nakatsuka S, Nishiu M, Tomita Y, Miwa H, Takakuwa T, Iuchl K, Yamamoto S, Aozasa K (2002) Enhanced expression of neuron-specific enolase (NSE) in pyothorax-associated lymphoma (PAL). Jpn J Cancer Res 93:411–416
Niklinski J, Furman M (1995) Clinical tumour markers in lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev 4:129–138
Renzulli P, Jakob SM, Täuber M, Candinas D, Gloor B (2005) Severe acute pancreatitis: case-oriented discussion of interdisciplinary management. Pancreatology 5:145–156
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ, Hudson LD (2005) Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 353:1685–1693
Samuel I, Yuan Z, Meyerholz DK, Twait E, Willard DE, Kempurai D (2010) A novel model of severe gallstone pancreatitis: murine pancreatic duct ligation results in systemic inflammation and substantial mortality. Pancreatology 10:536–544
Schmechel D, Marangos PJ, Brightman M (1978) Neuron-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature 276:834–836
Soh MA, Garrett SH, Somji S, Dunlevy JR, Zhou XD, Sens MA, Bethula CS, Allen C, Sens DA (2011) Arsenic, cadmium and neuron specific enolase (gamma-enolase, γ-enolase) expression in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int 11:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2867-11-41
Stelzl T, von Bose MJ, Hogl B, Fuchs HH, Flugel KA (1995) A comparison of the prognostic value of neuron-specific enolase serum levels and somatosensory evoked potentials in 13 reanimated patients. Eur J Emerg Med 2:24–27
Suresh MR (2005) Cancer markers. In: Wild D (ed) The immunoassay handbook, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 664–694
Takashima M, Kuramitsu Y, Yokoyama Y, Iizuka N, Fujimoto M, Nishisaka T, Okita K, Oka M, Nakamura K (2005) Overexpression of alpha enolase in hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: association with tumor progression as determined by proteomic analysis. Proteomics 5:1686–1692
Tang M, Tian Y, Li D, Lv J, Li Q, Kuang C, Hu P, Wang Y, Wang J, Su K, Wei L (2014) TNF-α mediated increase of HIF-1α inhibits VASP expression, which reduces alveolar-capillary barrier function during acute lung injury (ALI). PLoS ONE 9:e102967
Tiainen M, Roine RO, Pettila V, Takkunen O (2003) Serum neuron-specific enolase and S-100B protein in cardiac arrest patients treated with hypothermia. Stroke 34:2881–2886
Vizin T, Kos J (2015) Gamma-enolase: a well-known tumour marker, with a less-known role in cancer. Radiol Oncol 49:217–226
Xu H, Ye X, Steinberg H, Liu SF (2010) Selective blockade of endothelial NF-kappaB pathway differentially affects systemic inflammation and multiple organ dysfunction and injury in septic mice. J Pathol 220:490–498
Yan T, Skaftnesmo KO, Leiss L, Sleire L, Wang J, Li X, Enger P (2011) Neuronal markers are expressed in human gliomas and NSE knockdown sensitizes glioblastoma cells to radiotherapy and temozolomide. BMC Cancer 11:524. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-524
Zhang JW, Zhang GX, Chen HL, Liu GL, Owusu L, Wang YX, Wang GY, Xu CM (2015) Therapeutic effect of Qingyi decoction in severe acute pancreatitis-induced intestinal barrier injury. World J Gastroenterol 21:3537–3546
Acknowledgements
Support for this study was by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573751) to HC. However, the funding body had no influence on the study design, data interpretation, or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LO and HC conceived and designed the experiment; CX, GL, JZ, ZT, ZS and LO carried out the animal model and sample collections; LO, CX, ZT, JZ and ZS carried out validation experiments; HC secured funding for the study, and with LO drafted the manuscript; All authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest concerning this publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owusu, L., Xu, C., Chen, H. et al. Gamma-enolase predicts lung damage in severe acute pancreatitis-induced acute lung injury. J Mol Hist 49, 347–356 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9774-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9774-3