Abstract
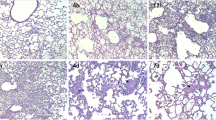
Aspiration is a devastating complication during decontamination procedure in poisoning patients. We have investigated whether S-methylisothiourea protects different pulmonary aspiration gastrointestinal decontamination agent-induced lung injury in rats. Forty-two male Sprague–Dawley rats were assigned to one of six groups (n = 7): normal saline, activated charcoal, polyethylene glycol, normal saline + S-methylisothiourea treated activated charcoal + S-methylisothiourea treated and polyethylene glycol + S-methylisothiourea treated. Normal saline, activated aharcoal and polyethylene glycol were instilled into the lungs. The rats received S-methylisothiourea i.p twice daily for 7 days. Serum surfactant protein D, oxidative stress products and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the lung were investigated. The aspiration of activated charcoal significantly increased all histopathological scores (P < 0.01). Only peribronchial inflammatory cell infiltration, alveolar edema, and alveolar histiocytes were increased in the polyethylene glycol groups as compared to the normal saline group (P < 0.05). Pulmonary aspiration increased serum malondialdehyde (P < 0.001), and surfactant protein D (P < 0.05) levels and decreased serum superoxide dismutase levels (P < 0.05). S-methylisothiourea treatment decreased all histopathological scores in the activated charcoal treated S-methylisothiourea group (P < 0.01) and only decreased alveolar edema and alveolar histiocytes in the polyethylene glycol-treated S-methylisothiourea group (P < 0.05). S-methylisothiourea treatment reduced elevated oxidative factors, inducible nitric oxide synthase activity and serum surfactant protein D levels. Our findings showed that S-methylisothiourea may be a protective drug against Activated Charcoal and Polyethylene Glycol-induced lung injury.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argent A, Hatherill M, Reynolds L, Purves L (2002) Fulminant pulmonary oedema after administration of a balanced electrolyte polyethylene glycol solution. Arch Dis Child 86(3):209
Arnold T, Willis B, Xiao F, Conrad S, Carden D (1999) Aspiration of activated charcoal elicits an increase in lung microvascular permeability. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37(1):9–16
Arnold TC, Zhang S, Xiao F, Conrad SA, Carden DL (2003) Pressure-controlled ventilation attenuates lung microvascular ınjury in a rat model of activated charcoal aspiration. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 41(2):119–124
Bhatia M, Moochhala S (2004) Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Pathol 202(2):145–156
Bond GR (2002) The role of activated charcoal and gastric emptying in gastrointestinal decontamination: a state-of-the-art review. Ann Emerg Med 39:273–286
Bridges JP, Davis HW, Damodarasamy M, Kuroki Y, Howles G, Hui DY et al (2000) Pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D are potent endogenous inhibitors of lipid peroxidation and oxidative cellular injury. J Biol Chem 275:38848–38855
Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR, Green JL, Rumack BH, Giffin SL (2010) 2009 Annual report of the American association of poison control centers’ national poison data system. Clin Toxicol 48:979–1178
Donoso A, Linares M, Leo′n J, Rojas G, Valverde C, Ramı′rez M et al (2003) Activated charcoal laryngitis in an ıntubated patient. Pediatr Emerg Care 19(6):420–421
Dorrington CL, Johnson DW, Brant R (2003) Multiple dose activated charcoal complication study group. The frequency of complications associated with the use of multiple-dose activated charcoal. Ann Emerg Med 41(3):370–377
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 86:421–431
Elliott CG, Colby TV, Kelly TM, Hicks HG (1989) Charcoal lung: bronchiolitis obliterans after aspiration of activated charcoal. Chest 96(3):672–674
Enkhbaatar P, Wang J, Saunders F, Lange M, Hamahata A, Rehberg S et al (2011) Mechanistic aspects of inducible nitric oxide synthase-induced lung injury in burn trauma. Burns 37(4):638–645
Golej J, Boigner H, Burda G, Hermon M, Trittenwein G (2001) Severe respiratory failure following charcoal application in a toddler. Resuscitation 49(3):315–318
Greene KE, King TE Jr, Kuroki Y, Bucher-Bartelson B, Hunninghake GW, Newman LS et al (2002) Serum surfactant proteins-A and -D as biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 19:439–446
Guzel A, Basaran UN, Aksu B, Kanter M, Yalcin O, Aktas C et al (2008) Protective effects of S-methylisothiourea sulfate on different aspiration materials-induced lung injury in rats. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72(8):1241–1250
Guzel A, Kanter M, Aksu B, Basaran UN, Yalcin O, Guzel A et al (2009) Preventive effects of curcumin on different aspiration material-induced lung injury in rats. Pediatr Surg Int 25:83–92
Harris CR, Filandrinos D (1993) Accidental administration of activated charcoal into the lung: aspiration by proxy. Ann Emerg Med 22(9):1470–1473
Hasan AG, Brown WR (2011) Colonic cleansing for colonoscopy: a risk to be taken seriously. Gastrointest Endosc 73(3):616–618
Hill J, Heslop C, Man SF, Frohlich J, Connett JE, Anthonisen NR et al (2011) Circulating surfactant protein-D and the risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Eur Heart J 32(15):1918–1925
Hur GY, Lee SY, Shim JJ, In KH, Kang KH, Yoo SH (2008) Aspiration pneumonia due to polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution (Golytely) treated by bronchoalveolar lavage. Respirology 13:152–154
Kim K, Li Y, Jin G, Chong W, Liu B, Lu J, et al. (2011) Effect of valproic acid on acute lung injury in a rodent model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion. Resuscitation Aug 6. (Epub ahead of print)
Kinder BW, Brown KK, McCormack FX, Ix JH, Kervitsky A, Schwarz MI et al (2009) Serum surfactant protein-A is a strong predictor of early mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 135(6):1557–1563
Klein E, Weigel J, Buford MC, Holian A, Wells SM (2010) Asymmetric dimethylarginine potentiates lung inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 299:L816–L825
Kuroki Y, Takahashi H, Chiba H, Akino T (1998) Surfactant proteins A and D: disease markers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1408:334–345
Marczin N, Royston D (2001) Nitric oxide as mediator, marker and modulator of microvascular damage in ARDS. Br J Anaesth 87(2):179–183
Marschall HU, Bartels F (1998) Life-threatening complications of nasogastric administration of polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solutions (GoLytely) for bowel cleansing. Gastrointest Endosc 47:408–410
Moll J, Kerns W II, Tomaszewski C, Rose R (1999) Incidence of aspiration pneumonia in intubated patients receiving activated charcoal. J Emerg Med 17:279–283
Narsinghani U, Chadha M, Farrar HC, Anand KS (2001) Life-threatening respiratory failure following accidental infusion of polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution into the lung. Clin Toxicol 39:105–107
Numata M, Suzuki S, Miyazawa N, Miyashita A, Nagashima Y, Inoue S et al (1998) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury in dogs. J Immunol 160(6):3031–3037
Paap CM, Ehrlich R (1993) Acute pulmonary edema after polyethylene glycol intestinal lavage in a child. Ann Pharmacoth 27:1044–1047
Radioo DM, Rocke DA, Brock-Utne JG, Marszalek A, Engelbrecht HE (1990) Critical volume for pulmonary acid aspiration: reappraisal in a primate model. Br J Anaesth 65:248
Raghavendran K, Nemzek J, Napolitano LM, Knight PR (2011) Aspiration-induced lung injury. Crit Care Med 39:818–826
Rodgers GC, Condurache T, Reed MD, Bestic M, Gal P (2007) Poisonings. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 18th edn. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 339–357
Seder DB, Christman RA, Quinn MO, Knauft ME (2006) A 45-year-old man with a lung mass and history of charcoal aspiration. Respir Care 51(11):1251–1254
Shohrati M, Ghanei M, Shamspour N, Jafari M (2008) Activity and function in lung injuries due to sulphur mustard. Biomarkers 13:728–733
Smith SW (2010) Drugs and pharmaceuticals: management of intoxication and antidotes. EXS 100:397–460
Takıl A, Umuroglu T, Gogus YF, Eti Z, Yildizeli B, Ahiskali R (2003) Histopathologic effects of lipid content of enteral solutions after pulmonary aspiration in rats. Nutrition 19:666–669
Tasaka S, Amaya F, Hashimoto S, Ishızaka A (2008) Roles of oxidants and redox signaling in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(4):739–753
Tenenbein M (1988) Whole bowel irrigation as a gastrointestinal decontamination procedure after acute poisoning. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp 3:77–84
Visscher DW, Myers JL (2006) Bronchiolitis: the pathologist’s perspective. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:41–47
Wang CC, Choy CS, Liu YH, Cheah KP, Li JS, Wang JT et al (2010) Protective effect of dried safflower petal aqueous extract and its main constituent, carthamus yellow, against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Sci Food Agric 91:218–225
Ware LB, Koyama T, Billheimer DD, Wu W, Bernard GR, Thompson BT et al (2010) NHLBI ARDS Clinical trials network. Prognostic and pathogenetic value of combining clinical and biochemical indices in patients with acute lung injury. Chest 137(2):288–296
Wong A, Briars GL (2002) Acute pulmonary oedema complicating polyethylene glycol intestinal lavage. Arch Dis Child 87:537–538
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflict of interest in all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güzel, A., Güzel, A., Günaydin, M. et al. The role of iNOS inhibitors on lung injury induced by gastrointestinal decontamination agents aspiration. J Mol Hist 43, 351–360 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9397-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9397-z