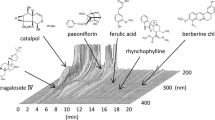
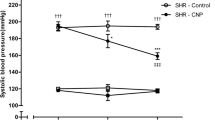
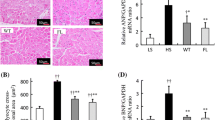
Abstract
The incidence of chronic renal diseases is increasing worldwide, and there is a great need to identify therapies capable of arresting or reducing disease progression. The current treatment of chronic nephropathies is limited to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers, but increasing clinical and experimental evidence suggests that statins could play a therapeutic role. Ultrastructural studies have shown the presence of gap junctions within all the cells of the glomerulus and podocytes have been found to contain primarily connexin-43. The present study aims to observe the beneficial effects of rosuvastatin on structural and ultrastructural renal morphology and on glomerular connexin-43 expression in normotensive rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Rats were randomly allocated into four groups: WKY-C: normotensive animals no receiving rosuvastatin; WKY-ROS: normotensive animals receiving rosuvastatin; SHR-C: hypertensive animals no receiving rosuvastatin; SHR-ROS: hypertensive animals receiving rosuvastatin. Our results show no differences in blood urea, creatinine, uric acid and creatine phosphokinase levels between the groups, however, there was an decreasing of 24-h protein excretion in SHR-ROS. Capsular area in SHR-ROS was decreased, however, there was no alteration in urinary space. By transmission electron microscopy the slit diaphragm and podocyte foot processes were more preserved in SHR-ROS. By scanning electron microscopy the podocyte foot processes were more preserved in SHR-ROS. Increased connexin-43 immunofluorescence was observed in glomeruli of WKY-ROS and SHR-ROS. In conclusion, we hypothesize that renal pleiotropic effect of rosuvastatin can be a therapeutic tool for improving kidney ultrastructure and, consequently, renal function in hypertensive individuals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins RC, Briganti EM, Lewis JB, Hunsicker LG, Braden G, Champion de Crespigny PJ, DeFerrari G, Drury P, Locatelli F, Wiegmann TB, Lewis EJ (2005) Proteinuria reduction and progression to renal failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 45:281–287
Bae EH, Kim IJ, Park JW, Ma SK, Lee JU, Kim SW (2009) Renoprotective effect of rosuvastatin in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Nephrol Dial Transpl 25:1051–1059
Barri YM (2008) Hypertension and kidney disease: a deadly connection. Curr Hypertens Rep 10:39–45
Bidani AK, Griffin KA, Williamson G, Wang X, Loutzenhiser R (2009) Protective importance of the myogenic response in the renal circulation. Hypertension 54:393–398
Chen SH, Chou FF, Ko JY (2010) The use of simvastatin with aromasin in an ovariectomized rat model: effects on the skeletal system. Chang Gung Med J 33:509–514
Ciani L, Patel A, Allen ND, Ffrench-Constant C (2003) Mice lacking the giant protocadherin mFAT1 exhibit renal slit junction abnormalities and a partially penetrant cyclopia and anophthalmia phenotype. Mol Cell Biol 23:3575–3582
Cormack-Aboud FC, Brinkkoetter PT, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ, Durvasula RV (2009) Rosuvastatin protects against podocyte apoptosis in vitro. Nephrol Dial Transpl 24:404–412
Dlugosova K, Okruhlicova L, Mitasikova M, Sotnikova R, Bernatova I, Weismann P, Slezak J, Tribulova N (2009) Modulation of connexin-43 by omega-3 fatty acids in the aorta of old spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 60:63–69
Donoviel DB, Freed DD, Vogel H, Potter DG, Hawkins E, Barrish JP, Mathur BN, Turner CA, Geske R, Montgomery CA, Starbuck M, Brandt M, Gupta A, Ramirez-Solis R, Zambrowicz BP, Powell DR (2001) Proteinuria and perinatal lethality in mice lacking NEPH1, a novel protein with homology to NEPHRIN. Mol Cell Biol 21:4829–4836
Flack JM, Ferdinand KC, Nasser SA, Rossi NF (2010) Hypertension in special populations: chronic kidney disease, organ transplant recipients, pregnancy, autonomic dysfunction, racial and ethnic populations. Cardiol Clin 28:623–638
Gianella A, Nobili E, Abbate M, Zoja C, Gelosa P, Mussoni L, Bellosta S, Canavesi M, Rottoli D, Guerrini U, Brioschi M, Banfi C, Tremoli E, Remuzzi G, Sironi L (2007) Rosuvastatin treatment prevents progressive kidney inflammation and fibrosis in stroke-prone rats. Am J Pathol 170:1165–1177
Hanner F, Sorensen CM, Holstein-Rathlou NH, Peti-Peterdi J (2010) Connexins and the kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R1143–R1155
Hedenmalm K, Alvan G, Ohagen P, Dahl ML (2010) Muscle toxicity with statins. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 19:223–231
Krzesinski JM, Cohen EP (2007) Hypertension and the kidney. Acta Clin Belg 62:5–14
Loch D, Levick S, Hoey A, Brown L (2006) Rosuvastatin attenuates hypertension-induced cardiovascular remodeling without affecting blood pressure in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47:396–404
Neto-Ferreira R, Novaes Rocha V, da Silva Torres T, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, de Carvalho JJ (2011). Beneficial effects of rosuvastatin on aortic adverse remodeling in nitric oxide-deficient rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63(5):473–478
Nicholls SJ, Tuzcu EM, Sipahi I, Grasso AW, Schoenhagen P, Hu T, Wolski K, Crowe T, Desai MY, Hazen SL, Kapadia SR, Nissen SE (2007) Statins, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and regression of coronary atherosclerosis. JAMA 297:499–508
Ofstad J, Iversen BM (2005) Glomerular and tubular damage in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F665–F672
Ossani GP, Castiglia NI, Martino MF, Fariña SL, Uceda AM, Monsserrat AJ (2009) Morphometry of the glomerular tuft during normal postnatal growth in female rats. Effects of age, location of glomeruli and methods of obtaining and processing the renal tissue. Scand J Lab Anim Sci 36:265–269
Palmer BF, Fenves AZ (2010) Optimizing blood pressure control in patients with chronic kidney disease. Proc Bayl Univ Med Cent 23:239–245
Pfefferkorn JA (2011) Novel 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 21:187–203
Putaala H, Soininen R, Kilpeläinen P, Wartiovaara J, Tryggvason K (2001) The murine nephrin gene is specifically expressed in kidney, brain and pancreas: inactivation of the gene leads to massive proteinuria and neonatal death. Hum Mol Genet 10:1–8
Ren Y, D’Ambrosio MA, Liu R, Pagano PJ, Garvin JL, Carretero AO (2010) Enhanced myogenic response in the afferent arteriole of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H1769–H1775
Renke M, Tylicki L, Rutkowski P, Neuwelt A, Larczyński W, Ziętkiewicz M, Aleksandrowicz E, Lysiak-Szydłowska W, Rutkowski B (2010) Atorvastatin improves tubular status in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease—placebo controlled, randomized, cross-over study. Acta Biochim Pol 57:547–552
Roselli S, Heidet L, Sich M, Henger A, Kretzler M, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2004) Early glomerular filtration defect and severe renal disease in podocin-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 24:550–560
Strippoli GF, Navaneethan SD, Johnson DW, Perkovic V, Pellegrini F, Nicolucci A, Craig JC (2008) Effects of statins in patients with chronic kidney disease: meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Bmj 336:645–651
Suh JW, Choi DJ, Chang HJ, Cho YS, Youn TJ, Chae IH, Kim KI, Kim CH, Kim HS, Oh BH, Park YB (2010) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor improves endothelial dysfunction in spontaneous hypertensive rats via down-regulation of caveolin-1 and activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Korean Med Sci 25:16–23
Tryggvason K, Patrakka J, Wartiovaara J (2006) Hereditary proteinuria syndromes and mechanisms of proteinuria. N Engl J Med 354:1387–1401
Verhulst A, Sayer R, De Broe ME, D’Haese PC, Brown CD (2008) Human proximal tubular epithelium actively secretes but does not retain rosuvastatin. Mol Pharmacol 74:1084–1091
Yaoita E, Yao J, Yoshida Y, Morioka T, Nameta M, Takata T, Kamiie J, Fujinaka H, Oite T, Yamamoto T (2002) Up-Regulation of Connexin43 in Glomerular Podocytes in response to Injury. Am J Path 161:1597–1606
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de nível Superior (Capes) and Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (UERJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Érica Peres de Barros and Angélica Beatriz Garcia-Pinto contributed equally for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Barros, É.P., Garcia-Pinto, A.B., Machado, P.Y. et al. Rosuvastatin beneficially alters the glomerular structure of kidneys from spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). J Mol Hist 42, 323–331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9336-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9336-4