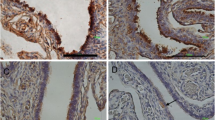
Abstract
Cells of the female reproductive tract are subject to hormonal control via sex steroid genomic receptors expressed at nuclear level. We previously showed that interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) of human myometrium expressed estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER/PR). Our aim, based on these results, was to see if ER and/or PR could be found also in tubal ICLC. Indeed, we present here immunohistochemical evidence that ICLC of human Fallopian tube (isthmic region) have such receptors. Stromal ICLC, as well as ICLC among smooth muscle layers, were identified in tissue sections by their morphological features (e.g. several very long, moniliform, prolongations of cell body) as well as by c-kit positivity, vital staining with methylene blue or silver impregnation. Additional evidence was provided by sequential staining for c-kit and for PR on the same cell, by ‘sandwich method’. In vitro, the 4th passage cell cultures from Fallopian tube muscularis exhibiting ICLC morphology showed the presence of ER-alpha and/or PR-A by immunofluorescence. In conclusion, our data suggest that ICLC could function as steroid sensors, and might be implicated in Fallopian tube motility (via gap junctions or juxta- and/or paracrine mechanisms).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amso NN, Crow J, Shaw RW (1994) Comparative immunohistochemical study of oestrogen and progesterone receptors in the fallopian tube and uterus at different stages of the menstrual cycle and the menopause. Hum Reprod 9:1027–1037
Bigsby RM (2002) Control of growth and differentiation of the endometrium: the role of tissue interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 955:110–117
Brenner RM, Slayden OD (1994) Cyclic changes in the primate oviduct and endometrium. In: Knobil E, Neill JD (eds) The physiology of reproduction, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 541–569
Bussolati G (2005) Of GISTs and EGISTs, ICCs and ICs. Virchows Arch 447:907–908
Christow A, Sun X, Gemzell-Danielsson K (2002) Effect of mifepristone and levonorgestrel on expression of steroid receptors in the human Fallopian tube. Mol Hum Reprod 8:333–340
Ciontea SM, Radu E, Regalia T, Ceafalan L, Cretoiu D, Gherghiceanu M, Braga RI, Malincenco M, Zagrean L, Hinescu ME et al (2005) C-kit immunopositive interstitial cells (Cajal-type) in human myometrium. J Cell Mol Med 9:407–420
Corbo RM, Ulizzi L, Piombo L, Martinez-Labarga C, De Stefano GF, Scacchi R (2007) Estrogen receptor alpha polymorphisms and fertility in populations with different reproductive patterns. Mol Hum Reprod 13:537–540
Cretoiu D, Ciontea SM, Popescu LM, Ceafalan L, Ardeleanu C (2006) Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) as steroid hormone sensors in human myometrium: immunocytochemical approach. J Cell Mol Med 10:789–795
Croxatto HB (2002) Physiology of gamete and embryo transport through the fallopian tube. Reprod Biomed Online 4:160–169
Cunha GR, Cooke PS, Kurita T (2004) Role of stromal-epithelial interactions in hormonal responses. Arch Histol Cytol 67:417–434
Dixon RE, Hwang SJ, Hennig GW, Ramsey KH, Schripsema JH, Sanders KM, Ward SM (2009) Chlamydia infection causes loss of pacemaker cells and inhibits oocyte transport in the mouse oviduct. Biol Reprod 80(4):665–673
Foster R, Solano S, Mahoney J, Fuller A, Oliva E, Seiden MV (2006) Reclassification of a tubal leiomyosarcoma as an eGIST by molecular evaluation of c-KIT. Gynecol Oncol 101:363–366
Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM (2005) Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in human resting mammary gland stroma. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) identification. J Cell Mol Med 9:893–910
Giretti MS, Simoncini T (2008) Rapid regulatory actions of sex steroids on cell movement through the actin cytoskeleton. Steroids 73(9–10):895–900
Hagiwara H, Ohwada N, Aoki T, Suzuki T, Takata K (2008) Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic observations of stromal cells in the human oviduct mucosa. Med Mol Morphol 41(4):221–226
Harhun MI, Pucovsky V, Povstyan OV, Gordienko DV, Bolton TB (2005) Interstitial cells in the vasculature. J Cell Mol Med 9:232–243
Hermoso M, Saez JC, Villalon M (1997) Identification of gap junctions in the oviduct and regulation of connexins during development and by sexual hormones. Eur J Cell Biol 74:1–9
Hinescu ME, Popescu LM (2005) Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in human atrial myocardium. J Cell Mol Med 9:972–975
Hinescu ME, Gherghiceanu M, Mandache E, Ciontea SM, Popescu LM (2006) Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in atrial myocardium: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characterization. J Cell Mol Med 10:243–257
Hinescu ME, Ardeleanu C, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM (2007) Interstitial Cajal-like cells in human gallbladder. J Mol Histol 38:275–284
Hirst GD, Edwards FR (2006) Electrical events underlying organized myogenic contractions of the guinea pig stomach. J Physiol 576:659–665
Huizinga JD, Faussone-Pellegrini MS (2005) About the presence of interstitial cells of Cajal outside the musculature of the gastrointestinal tract. J Cell Mol Med 9:468–473
Hunter RH (2005) The Fallopian tubes in domestic mammals: how vital is their physiological activity? Reprod Nutr Dev 45:281–290
Hunter RH, Cicinelli E, Einer-Jensen N (2007) Peritoneal fluid as an unrecognised vector between female reproductive tissues. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 86:260–265
Hutchings G, Williams O, Cretoiu D, Ciontea SM (2009) Myometrial interstitial cells and the coordination of myometrial contractility. J Cell Mol Med. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00894.x
Kurita T, Lee KJ, Cooke PS, Lydon JP, Cunha GR (2000) Paracrine regulation of epithelial progesterone receptor and lactoferrin by progesterone in the mouse uterus. Biol Reprod 62:831–838
Lang RJ, Klemm MF (2005) Interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells in the upper urinary tract. J Cell Mol Med 9:542–556
Lindblom B, Hamberger L, Ljung B (1980) Contractile patterns of isolated oviductal smooth muscle under different hormonal conditions. Fertil Steril 33:283–287
Lyons RA, Saridogan E, Djahanbakhch O (2006) The effect of ovarian follicular fluid and peritoneal fluid on Fallopian tube ciliary beat frequency. Hum Reprod 21:52–56
Mastroianni L (1999) The fallopian tube and reproductive health. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 12:121–126
McCloskey KD, Gurney AM (2002) Kit positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 168:832–836
Min KW, Leabu M (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) and gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): facts, speculations, and myths. J Cell Mol Med 10:995–1013
Mote PA, Johnston JF, Manninen T, Tuohimaa P, Clarke CL (2001) Detection of progesterone receptor forms A and B by immunohistochemical analysis. J Clin Pathol 54:624–663
Okada A, Ohta Y, Inoue S, Hiroi H, Muramatsu M, Iguchi T (2003) Expression of estrogen, progesterone and androgen receptors in the oviduct of developing, cycling and pre-implantation rats. J Mol Endocrinol 30:301–315
Popescu LM, Andrei F, Hinescu ME (2005a) Snapshots of mammary gland interstitial cells: methylene-blue vital staining and c-kit immunopositivity. J Cell Mol Med 9:476–477
Popescu LM, Ciontea SM, Cretoiu D, Hinescu ME, Radu E, Ionescu N, Ceausu M, Gherghiceanu M, Braga RI, Vasilescu F et al (2005b) Novel type of interstitial cell (Cajal-like) in human fallopian tube. J Cell Mol Med 9:479–523
Popescu LM, Hinescu ME, Ionescu N, Ciontea SM, Cretoiu D, Ardelean C (2005c) Interstitial cells of Cajal in pancreas. J Cell Mol Med 9:169–190
Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Hinescu ME, Cretoiu D, Ceafalan L, Regalia T, Popescu AC, Ardeleanu C, Mandache E (2006a) Insights into the interstitium of ventricular myocardium: interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC). J Cell Mol Med 10:429–458
Popescu LM, Vidulescu C, Curici A, Caravia L, Simionescu AA, Ciontea SM, Simion S (2006b) Imatinib inhibits spontaneous rhythmic contractions of human uterus and intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 546:177–181
Popescu LM, Ciontea SM, Cretoiu D (2007) Interstitial Cajal-like cells in human uterus and Fallopian tube. Ann NY Acad Sci 1101:139–165
Radu E, Regalia T, Ceafalan L, Andrei F, Cretoiu D, Popescu LM (2005) Cajal-type cells from human mammary gland stroma: phenotype characteristics in cell culture. J Cell Mol Med 9:748–752
Sanders KM, Koh SD, Ward SM (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Physiol 68:307–343
Sergeant GP, Thornbury KD, McHale NG, Hollywood MA (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal in the urethra. J Cell Mol Med 10:280–291
Shafik A, El-Sibai O, Shafik I, Shafik AA (2005a) Immunohistochemical identification of the pacemaker Cajal cells in the normal human vagina. Arch Gynecol Obstet 272:13–16
Shafik A, Shafik I, El-Sibai O (2005b) Identification of c-kit-positive cells in the human prostate: the interstitial cells of Cajal. Arch Androl 51:345–351
Shafik A, Shafik I, Shafik AA, El-Sibai O (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal in erectile dysfunction. Arch Androl 52:255–262
Shafik A, Shafik I, El-Sibai O, Shafik AA (2007) Interstitial cells of Cajal in Tunica Albuginea of the testicles. Androl Update 1:9–15
Talo A, Hodgson BJ (1978) Electrical slow waves in oviductal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig, mouse and the immature baboon. Experientia 34:198–200
Thyberg J, Nilsson J, Palmberg L, Sjölund M (1985) Adult human arterial smooth muscle cells in primary culture. Modulation from contractile to synthetic phenotype. Cell Tissue Res 239:69–74
Villalón M, Hermoso M, Budinich M, Aguilera J, Sáez JC (1997) Regulation of smooth muscle activity and gap junction by sexual hormones in the oviduct. In: Latorre R, Sáez JC (eds) Ion channels to cell-to-cell conversations. Plenum Press, New York, pp 459–468
Wånggren K, Stavreus-Evers A, Olsson C, Andersson E, Gemzell-Danielsson K (2008) Regulation of muscular contractions in the human Fallopian tube through prostaglandins and progestagens. Hum Reprod 23(10):2359–2368
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank professor Carmen Ardeleanu, ‘Victor Babeş’ National Institute of Pathology and Dr. Emil Toescu, University of Birmingham, for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cretoiu, S.M., Cretoiu, D., Suciu, L. et al. Interstitial Cajal-like cells of human Fallopian tube express estrogen and progesterone receptors. J Mol Hist 40, 387–394 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-009-9252-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-009-9252-z