Abstract
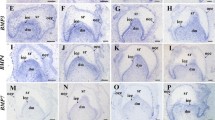
We previously performed cDNA subtraction between the mouse mandibles at embryonic day 10.5 (E10.5) in the pre-initiation stage of the odontogenesis and E12.0 in the late initiation stage to investigate the key regulator genes in odontogenesis. Ribosomal protein L21 (Rpl21) is one of differentially expressed genes in the E12.0 mandible. This study examined the precise expression pattern of Rpl21 mRNA in the mouse mandibular first molar by in situ hybridization. Rpl21 mRNA was expressed in the presumptive dental epithelium and the underlying mesenchyme at E10.5, and in the thickened dental epithelium at E12.0. Strong in situ signals were observed in the epithelial bud at E14.0, and in the enamel organ at E15.0. However, either no (E14.0) or only a weak (E15.0) in situ signal was found in the primary enamel knot at these gestational days. Rpl21 was strongly expressed in the inner enamel epithelium, cervical loop and dental lamina from E16.0 to E18.0. In addition, Rpl21 mRNA was also demonstrated in various developing cranio-facial organs. These results suggest that Rpl21 participates in the synthesis of various polypeptides which might be related to the initiation and the development of such tooth germ, and also in the synthesis of enamel components in the presecretory stage of the ameloblast. Rpl21 for protein synthesis might also be related to the morphogenesis of the developing cranio-facial organs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Matsuo K, Yamaza H, Wada H, Honda J, Ming X, Sakai H (2005) Possible functional involvement of thymosin beta 4 in developing tooth germ of mouse lower first molar. Histochem Cell Biol 124:207–213. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0040-x
Anderson SJ, Lauritsen JP, Hartman MG, Foushee AM, Lefebvre JM, Shinton SA, Gerhardt B, Hardy RR, Oravecz T, Wiest DL (2007) Ablation of ribosomal protein L22 selectively impairs alphabeta T cell development by activation of a p53-dependent checkpoint. Immunity 26:759–772. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.04.012
Beringer M, Rodnina MV (2007) Importance of tRNA interactions with 23S rRNA for peptide bond formation on the ribosome: studies with substrate analogs. Biol Chem 388:687–691. doi:10.1515/BC.2007.077
Caldarola S, De Stefano MC, Amaldi F, Loreni F (2009) Synthesis and function of ribosomal proteins–fading models and new perspectives. FEBS J 276:3199–3210. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07036.x
D’Souza RN (2007) Development of the tooth and its supporting tissues. In: Nanci A (ed) Ten Cate’s oral histology: development, structure, and function, 7th edn. Mosby Elsevier, St. Louis, pp 79–107
Deutsch D, Palmon A, Dafni L, Catalano-Sherman J, Young MF, Fisher LW (1995) The enamelin (tuftelin) gene. Int J Dev Biol 39:135–143
Fincham AG, Moradian-Oldak J, Simmer JP (1999) The structural biology of the developing dental enamel matrix. J Struct Biol 126:270–299. doi:10.1006/jsbi.1999.4130
Fukae M, Tanabe T, Murakami C, Dohi N, Uchida T, Shimizu M (1996) Primary structure of the porcine 89-kDa enamelin. Adv Dent Res 10:111–118
Gritli-Linde A, Bei M, Maas R, Zhang XM, Linde A, McMahon AP (2002) Shh signaling within the dental epithelium is necessary for cell proliferation, growth and polarization. Development 129:5323–5337
Honda JY, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Yamaz H, Xie M, Takahashi K, Enoki N, Nagata K, Nakashima A, Sakai H (2008) Glycolytic enzyme Pgk1 is strongly expressed in the developing tooth germ of the mouse lower first molar. Histol Histopathol 23:423–432
Jernvall J, Kettunen P, Karavanova I, Martin LB, Thesleff I (1994) Evidence for the role of the enamel knot as a control center in mammalian tooth cusp formation: non-dividing cells express growth stimulating Fgf-4 gene. Int J Dev Biol 38:463–469
Jernvall J, Aberg T, Kettunen P, Keranen S, Thesleff I (1998) The life history of an embryonic signaling center: BMP-4 induces p21 and is associated with apoptosis in the mouse tooth enamel knot. Development 125:161–169
Kim JY, Cha YG, Cho SW, Kim EJ, Lee MJ, Lee JM, Cai J, Ohshima H, Jung HS (2006) Inhibition of apoptosis in early tooth development alters tooth shape and size. J Dent Res 85:530–535
Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Wada H, Matsuo K, Nonaka K, Honda J, Koyano K, Sakai H (2006) Type II/III Runx2/Cbfa1 is required for tooth germ development. Bone 38:836–844. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2005.10.026
Krebsbach PH, Lee SK, Matsuki Y, Kozak CA, Yamada KM, Yamada Y (1996) Full-length sequence, localization, and chromosomal mapping of ameloblastin. A novel tooth-specific gene. J Biol Chem 271:4431–4435
MacDougall M, DuPont BR, Simmons D, Reus B, Krebsbach P, Karrman C, Holmgren G, Leach RJ, Forsman K (1997) Ameloblastin gene (AMBN) maps within the critical region for autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta at chromosome 4q21. Genomics 41:115–118. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4643
Miletich I, Sharpe PT (2003) Normal and abnormal dental development. Hum Mol Genet 12 Spec No 1, R69–R73
Mina M (2001) Regulation of mandibular growth and morphogenesis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 12:276–300
Ofir-Rosenfeld Y, Boggs K, Michael D, Kastan MB, Oren M (2008) Mdm2 regulates p53 mRNA translation through inhibitory interactions with ribosomal protein L26. Mol Cell 32:180–189. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.031
Shigemura N, Kiyoshima T, Kobayashi I, Matsuo K, Yamaza H, Akamine A, Sakai H (1999) The distribution of BrdU- and TUNEL-positive cells during odontogenesis in mouse lower first molars. Histochem J 31:367–377
Smith CE (1998) Cellular and chemical events during enamel maturation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 9:128–161
Takagi M, Absalon MJ, McLure KG, Kastan MB (2005) Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin. Cell 123:49–63. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.034
Thesleff I (2006) The genetic basis of tooth development and dental defects. Am J Med Genet A 140:2530–2535. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31360
Wada H, Kobayashi I, Yamaza H, Matsuo K, Kiyoshima T, Akhtar M, Sakai T, Koyano K, Sakai H (2002) In situ expression of heat shock proteins, Hsc73, Hsj2 and Hsp86 in the developing tooth germ of mouse lower first molar. Histochem J 34:105–109
Wood DE, Newcomb EW (2000) Cleavage of Bax enhances its cell death function. Exp Cell Res 256:375–382. doi:10.1006/excr.2000.4859
Xie M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Yamaza H, Honda J, Takahashi K, Enoki N, Akamine A, Sakai H (2007) Functional implication of nucleolin in the mouse first molar development. J Biol Chem 282:23275–23283. doi:10.1074/jbc.M610779200
Yamaza H, Matsuo K, Kiyoshima T, Shigemura N, Kobayashi I, Wada H, Akamime A, Sakai H (2001a) Detection of differentially expressed genes in the early developmental stage of the mouse mandible. Int J Dev Biol 45:675–680
Yamaza H, Matsuo K, Kobayashi I, Wada H, Kiyoshima T, Akhtar M, Ishibashi Y, Sakai T, Akamine A, Sakai H (2001b) Expression of Set-alpha during morphogenesis of mouse lower first molar. Histochem J 33:437–441
Zeichner-David M, Diekwisch T, Fincham A, Lau E, MacDougall M, Moradian-Oldak J, Simmer J, Snead M, Slavkin HC (1995) Control of ameloblast differentiation. Int J Dev Biol 39:69–92
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge support by a Grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (20390466 to H.S. and 21592331 to I.K.). The authors thank to Dr. K. Matsuo for his discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ming Xie, Ieyoshi Kobayashi and Tamotsu Kiyoshima contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Kobayashi, I., Kiyoshima, T. et al. In situ expression of ribosomal protein L21 in developing tooth germ of the mouse lower first molar. J Mol Hist 40, 361–367 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-009-9249-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-009-9249-7