Abstract
The emergence of online environments has changed the landscape of educational learning. Some students thrive in this learning environment, but others become amotivated and disengaged. Drawing on self-determination theory, we report the findings of a study of 574 undergraduate business students at an Australian higher education institution on their attitude toward online learning, and its impact on their motivation and educational engagement. Data was collected via an e-mail survey and analysed using structural equation modelling and the Hayes’ bootstrapping method. The results of the study were mixed. Attitude to online learning mediated the relationships of both intrinsic motivation to know and extrinsic motivation with engagement, indicating that the design of online learning environments can play a role in enhancing learning experiences. However, attitude to online learning was not found to mediate the intrinsic motivation to accomplish and engagement relationship. A negative mediation effect was partially supported between amotivation and engagement, with study mode found as a moderated mediator to this effect, being stronger and significant for online students as opposed to on-campus students. These results have implications for how students can be engaged online, and the need for educators to design online learning environments that support the learning experience for all students.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
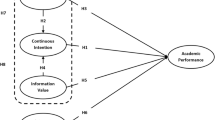
Only affective attitude → att8 loading was less than .50 in magnitude. Given the significance of the loading (t value = 12.569, p < .001), this loading was deemed as tolerable.
Goodness-of-fit statistics for tests of multi-group analysis and invariance tests can be provided. Please contact authors.
References
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: a review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411–423.
Annansingh, F. (2019). Mind the gap: cognitive active learning in virtual learning environment perception of instructors and students. Education and Information Technologies, 24(6), 3669–3688.
Appleton, J. J., Christenson, S. L., & Furlong, M. J. (2008). Student engagement with school: critical conceptual and methodological issues of the construct. Psychology in the Schools, 45(5), 369–386.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2016). IBM SPSS Amos 24 user’s guide. Crawfordville, FL: Amos Development Corporation.
Axelson, R. D., & Flick, A. (2010). Defining student engagement. Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning, 43(1), 38–43.
Bandura, A. (1971). Social learning theory. New York City, NY: General Learning Press.
Bolliger, D. U., & Halupa, C. (2018). Online student perceptions of engagement, transactional distance, and outcomes. Distance Education, 39(3), 299–316.
Booth-Butterfield, S., Mosher, N., & Mollish, D. (1992). Teacher immediacy and student involvement: a dual process analysis. Communication Research Reports, 9, 13–21.
Carini, R., Kuh, G., & Klein, S. (2006). Student engagement and student learning: testing the linkages. Research in Higher Education, 47(1), 1–32.
Chen, K., & Jang, S. (2010). Motivation in online learning: testing a model of self-determination theory. Computers in Human Behavior, 26, 741–752.
Chen, P.-S., Lambert, A., & Guidry, K. (2010). Engaging online learners: the impact of web-based learning technology on college student engagement. Computers & Education, 54(11), 1222–1232.
Cole, M. (2009). Using Wiki technology to support student engagement: lessons from the trenches. Computers & Education, 52(2), 141–146.
Dabbagh, N. (2007). The online learner: characteristics and pedagogical implications. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education, 7(3), 217–226.
Davis, A., Little, P., & Stewart, B. (2008). Developing an infrastructure for online learning. In T. Anderson (Ed.), The theory and practice of online learning (2nd ed., pp. 121–142). Edmonton, AB: AU Press.
Deci, E. L., Vallerand, R. J., Pelletier, L. G., & Ryan, R. M. (1991). Motivation and education: the self-determination perspective. Educational Psychologist, 26(3–4), 325–346.
Demski, J. (2012). This time it’s personal. THE Journal: Technological Horizons in Education, 39(1), 32–36.
Edwards, J. R., & Lambert, L. S. (2007). Methods for integrating moderation and mediation: a general analytical framework using moderated path analysis. Psychological Methods, 12(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.12.1.1
Ellis, R., & Bliuc, A. (2019). Exploring new elements of the student approaches to learning framework: the role of online learning technologies in student learning. Active Learning in Higher Education, 20(1), 11–24.
Farrel, D., Ray, K., Rich, T., Suarez, Z., Christenson, B., & Jennigs, L. (2018). A meta-analysis of approaches to engage social work students online. Journal of Teaching in Social Work, 38(2), 183–197.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Fredricks, J. A., Filsecker, M., & Lawson, M. A. (2016). Student engagement, context, and adjustment: addressing definitional, measurement, and methodological issues. Learning and Instruction, 43, 1–4.
Fried, L., & Konza, D. (2013). Using self-determination theory to investigate student engagement in the classroom. International Journal of Pedagogy and Curriculum, 19(2), 27–40.
Gefen, D. (2003). Assessing unidimensionality through LISREL: an explanation and an example. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 12(1), 23–47.
Gefen, D., Straub, D. W., & Rigdon, E. E. (2011). An update and extension to SEM guidelines for administrative and social science research. Management Information Systems Quarterly, 35(2), iii-A7.
Gordon, N., Grey, S., & Brayshaw, M. (2015). Motivating and engaging students through technology. In J. Hawkins (Ed.), Student Engagement (pp. 25–43). New York: Nova Science Publishers Inc.
Gourlay, L. (2015). ‘Student engagement’ and the tyranny of participation. Teaching in Higher Education, 20(4), 402–411.
Gray, J., & DiLorento, M. (2016). The effects of student engagement, student satisfaction, and perceived learning in online learning environments. International Journal of Educational Leadership Preparation, 11(1), 98–119.
Hair, J., Jr., Black, W., Babin, B., & Anderson, R. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: aglobal perspective (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Hair, J., Jr., Black, W., Babin, B., & Anderson, R. (2014). Multivariate data analysis (7th edition, Pearson New edition, Pearson New (International). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs, 76(4), 408–420.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: a regression-based approach. New York: Guilford Press.
Henrie, C. R., Halverson, L. R., & Graham, C. R. (2015). Measuring student engagement in technology-mediated learning: a review. Computers & Education, 90, 36–53.
Hsu, H. C. K., Wang, C. V., & Levesque-Bristol, C. (2019). Reexamining the impact of self-determination theory on learning outcomes in the online learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 24(3), 2159–2174.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Kahu, E. R. (2013). Framing student engagement in higher education. Studies in Higher Education, 38(5), 758–773.
Kahu, E. R., & Nelson, K. (2018). Student engagement in the educational interface: understanding the mechanisms of student success. Higher Education Research & Development, 37(1), 58–71.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modelling (2nd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press.
Krause, K., & Coates, H. (2008). Students’ engagement in first-year university. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 33(5), 493–505.
Krause, K., Hartley, R., James, R., & McInnis, C. (2005). The first year experience in Australian universities: findings from a decade of national studies. Canberra: AGPS.
Kuh, G. D., & Hu, S. (2001). The effects of student-faculty interaction in the 1990s. The Review of Higher Education, 24(3), 309–332.
Kuh, G. D., Kinzie, J., Buckley, J. A., Bridges, B. K., & Hayek, J. C. (2007). Piecing together the student success puzzle: research, propositions and recommendations. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Lawlor, J., Marshall, K., & Tangney, B. (2016). Bridge21—exploring the potential to foster intrinsic student motivation through a team-based, technology-mediated learning model. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 25(2), 187–206.
Leach, L. (2016). Enhancing student engagement in one institution. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 40(1), 23–47.
Leach, L., & Zepke, N. (2012). Student engagement in learning: facets of a complex interaction. In I. Solomonides, A. Reid, & P. Petocz (Eds.), Engaging with learning in higher education (pp. 231–255). Faringdon, UK: Libri Publishers.
Lee, W., & Reeve, J. (2012). Teachers’ estimates of their students’ motivation and engagement: being in synch with students. Educational Psychology, 32(6), 727–747.
Liaw, S.-S., Chen, G.-D., & Huang, H.-M. (2008). Users’ attitudes towards web-based collaborative learning systems for knowledge management. Computers & Education, 50, 950–961.
Macfarlane, B., & Tomlinson, M. (2017). Critiques of student engagement. Higher Education Policy, 30(1), 5–21.
MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, P. M., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2011). Construct measurement and validation procedures in MIS and behavioral research: integrating new and existing techniques. MIS Quarterly, 35(2), 293–334.
Marcel, F. (2019). Mobile augmented reality learning objects in higher education. Research in Learning Technology, 27, https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v27.2133
Martin, F., & Bolliger, D. H. (2018). Engagement matters: student perceptions on the importance of engagement strategies in the online learning environment. Online Learning, 22(1), 205–222.
Mehra, V., & Omidian, F. (2011). Examining students’ attitudes towards e-learning: a case from India. Malaysian Journal of Educational Technology, 11(2), 13–18.
Meyer, K. A. (2014). Student engagement in online learning: what works and why. ASHE Higher Education Report, 40(6), 1–114.
Mitchell, I. C., & A. . (2011). A typology of task characteristics and their effects on student engagement. International Journal of Educational Research, 50(5–6), 257–270.
Newbery, G. (2012). The psychology of being engaged and its implications for promoting engagement. In I. Solomonides, A. Reid, & P. Petocz (Eds.), Engaging with learning in higher education (pp. 47–69). Faringdon, UK: Libri.
Ng, K.-Y., Ang, S., & Chan, K.-Y. (2008). Personality and leader effectiveness: A moderated mediation model of leadership self-efficacy, job demands, and job autonomy. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(4), 733–743.
Ong, C.-S., & Lai, J.-Y. (2006). Gender differences in perceptions and relationships among dominants of e-learning acceptance. Computers in Human Behavior, 22, 816–829.
Plante, T. G. (2020). Top 10 tips for good Zoom hygiene and etiquette in education. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/do-the-right-thing/202003/top-10-tips-good-zoom-hygiene-and-etiquette-in-education. Accessed 28 July 2020.
Plewa, C., Galán-Muros, V., & Davey, T. (2015). Engaging business in curriculum design and delivery: a higher education institution perspective. Higher Education, 70(1), 35–53.
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185–227.
Purnomo, A., Kurniawan, B., & Aristin, N. (2019). Motivation to learn independently through blended learning, Advances in Social Science. Education and Humanities Research (ASSEHR), 330, 261–264.
Quin, D. (2016). Longitudinal and contextual associations between teacher–student relationships and student engagement: a systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 87(2), 345–387.
Radianti J., Majchrzak, T. A., Fromm, J., & Wohlgenannt, I. (2020). A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Computers & Education, 147, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103778
Reeve, J. (2012). A self-determination theory perspective on student engagement. In S. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 149–172). New York, NY: Springer.
Reschly, A., & Christenson, S. (2012). Jingle, jangle, and conceptual haziness: evolution and future directions of the engagement construct. In S. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 3–20). New York, NY: Springer.
Robinson, C. C., & Hullinger, H. (2008). New benchmarks in higher education: student engagement in online learning. Journal of Education for Business, 84(2), 101–108.
Rovai, A., Ponton, M., Wighting, M., & Baker, J. (2007). A comparative analysis of student motivation in traditional classroom and e-learning courses. International Journal on ELearning, 6(3), 413.
Ryan, R., & Deci, E. (2000). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25(1), 54–67.
Ryan, R., & Deci, E. (2009). Promoting self-determined school engagement: motivation, learning, and well-being. In K. R. Wentzel & A. Wigfield (Eds.), Handbook of motivation at school (pp. 171–196). New York, NY.: Routledge.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E.L. (2020). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 61, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2020.101860
Sailer, M., & Sailer, M. (2020). Gamification of in-class activities in flipped classroom lectures. British Journal of Educational Technology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12948
Sanders, L. D., Daly, A. P., & Fitzgerald, K. (2016). Predicting retention, understanding attrition: a prospective study of foundation year students. Widening Participation and Lifelong Learning, 18(2), 50–83.
Sims, R. R., & Sims, S. J. (Eds.). (1995). The importance of learning styles: understanding the implications for learning, course design, and education. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press.
Skinner, E., Furrer, C., Marchand, G., & Kindermann, T. (2008). Engagement and disaffection in the classroom: part of a larger motivational dynamic? Journal of Educational Psychology, 100(4), 765–781.
Stevens, T., & Switzer, C. (2006). Differences between online and traditional students: a study of motivational orientation, self efficacy, and attitudes. Turkish Journal of Distance Education, 7(2), 90–100.
Sun, J., & Rueda, R. (2012). Situational interest, computer self-efficacy and self-regulation: their impact on student engagement in distance education. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(2), 191–204.
Tanner, K. D. (2013). Structure matters: twenty-one teaching strategies to promote student engagement and cultivate classroom equity. CBE – Life Sciences Education, 12, 322–331.
Trowler, V., & Trowler, P. (2010). Student engagement evidence summary. UK: University of Lancaster.
Vallerand, R. J., Pelletier, L. G., Blais, M. R., Briere, N. M., Senecal, C., & Vallieres, E. F. (1992). The Academic Motivation Scale: a measure of intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivation in education. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 52(4), 1003–1017.
Wengrowicz, N., Swart, W., Paul, R., Macleod, K., Dori, D., & Dori, Y. J. (2018). Students’ collaborative learning attitudes and their satisfaction with online collaborative case-based courses. American Journal of Distance Education, 32(4), 283–300.
Wlodkowski, R. J., & Ginsberg, M. B. (1995). Diversity and motivation: culturally responsive teaching. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Wong, L., & Fong, M. (2014). Student attitudes to traditional and online methods of delivery. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 13, 1–13.
Yatz, Y. J. (2002). Attitudes affecting college students’ preferences for distance learning. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 18, 2–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrer, J., Ringer, A., Saville, K. et al. Students’ motivation and engagement in higher education: the importance of attitude to online learning. High Educ 83, 317–338 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00657-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00657-5