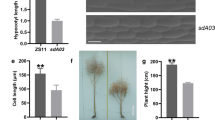
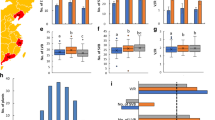
Abstract
A diverse genetic background is essential for genetic analysis and functional genomics research in model plants. In this study, four novel xiaomi-like mutants in different genetic backgrounds, named xiaomi3, xiaomi4, xiaomi5, and xiaomi6, were identified and characterized. These mutants exhibited an extremely early heading phenotype, with heading occurring around 30–40 days after sowing under natural long-day conditions. Significant reductions in plant height, leaf length, leaf width, panicle length, and panicle diameter were observed in the mutants compared to their corresponding wild-types. Notably, these mutants displayed diverse panicle architectures and hull colors, effectively preventing seed mixing between them. Subsequent investigation under controlled short-day and long-day conditions confirmed the significant early heading phenotype of these mutants. Molecular characterization revealed that mutations in the Phytochrome C (SiPHYC) gene, including transposon insertions and a frame shift mutation, were responsible for the extremely early heading phenotype. RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq) analysis identified 19 differentially expressed genes associated with this phenotype. Additionally, genome-wide InDels and SNPs were identified, providing valuable resources for marker-assisted breeding and genetic studies. These findings will contribute to our understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying SiPHYC-mediated photoperiod flowering, and provide valuable resources that will push xiaomi as a C4 model plant.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw sequence data have been deposited in the Beijing Institute of Genomics Data Center (https://bigd.big.ac.cn/) under the BioProject accession PRJCA022856.
References
Bennetzen JL, Schmutz J, Wang H, Percifield R, Hawkins J, Pontaroli AC, Estep M, Feng L, Vaughn JN, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Barry K, Lindquist E, Hellsten U, Deshpande S, Wang X, Wu X, Mitros T, Triplett J, Yang X, Ye C, Mauro-Herrera M, Wang L, Li P, Sharma M, Sharma R, Ronald PC, Panaud O, Kellogg EA, Brutnell TP, Doust AN, Tuskan GA, Rokhsar D, Devos KM (2012) Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat Biotechnol 30:555. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2196
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Cheng J, Tan H, Shan M, Duan M, Ye L, Yang Y, He L, Shen H, Yang Z, Wang X (2022) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the NPF genes provide new insight into low nitrogen tolerance in Setaria. Front Plant Sci 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1043832
Diao XM, Schnable J, Bennetzen JL, Li JY (2014) Initiation of Setaria as a model plant. Front Agr Sci Eng 1(1):16–20. https://doi.org/10.15302/j-fase-2014011
Doi K, Izawa T, Fuse T, Yamanouchi U, Kubo T, Shimatani Z, Yano M, Yoshimura A (2004) Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers short-day promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1. Genes Dev 18(8):926–936. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1189604
Doust AN, Kellogg EA, Devos KM, Bennetzen JL (2009) Foxtail millet: a sequence-driven grass model system. Plant Physiol 149(1):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.129627
He Q, Tang S, Zhi H, Chen J, Zhang J, Liang H, Alam O, Li H, Zhang H, Xing L, Li X, Zhang W, Wang H, Shi J, Du H, Wu H, Wang L, Yang P, Xing L, Yan H, Song Z, Liu J, Wang H, Tian X, Qiao Z, Feng G, Guo R, Zhu W, Ren Y, Hao H, Li M, Zhang A, Guo E, Yan F, Li Q, Liu Y, Tian B, Zhao X, Jia R, Feng B, Zhang J, Wei J, Lai J, Jia G, Purugganan M, Diao X (2023a) A graph-based genome and pan-genome variation of the model plant Setaria. Nat Genet 55(7):1232–1242. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-023-01423-w
He Q, Wang C, He Q, Zhang J, Liang H, Lu Z, Xie K, Tang S, Zhou Y, Liu B, Zhi H, Jia G, Guo G, Du H, Diao X (2023b) A complete reference genome assembly for foxtail millet and Setaria-db, a comprehensive database for Setaria. Mol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2023.12.017
Jia G, Huang X, Zhi H, Zhao Y, Zhao Q, Li W, Chai Y, Yang L, Liu K, Lu H, Zhu C, Lu Y, Zhou C, Fan D, Weng Q, Guo Y, Huang T, Zhang L, Lu T, Feng Q, Hao H, Liu H, Lu P, Zhang N, Li Y, Guo E, Wang S, Wang S, Liu J, Zhang W, Chen G, Zhang B, Li W, Wang Y, Li H, Zhao B, Li J, Diao X, Han B (2013) A haplotype map of genomic variations and genome-wide association studies of agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Nat Genet 45(8):957–961. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2673
Lata C, Gupta S, Prasad M (2013) Foxtail millet: a model crop for genetic and genomic studies in bioenergy grasses. Crit Rev Biotechnol 33(3):328–343. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2012.716809
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25(14):1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, Genome Project Data Processing S (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li B, Du X, Fei Y, Wang F, Xu Y, Li X, Li W, Chen Z, Fan F, Wang J, Tao Y, Jiang Y, Zhu QH, Yang J (2021) Efficient breeding of early-maturing rice cultivar by editing PHYC via CRISPR/Cas9. Rice (N Y) 14(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-021-00527-3
Li X, Gao J, Song J, Guo K, Hou S, Wang X, He Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Tang J, Wang H, Persson S, Huang M, Xu L, Zhong L, Li D, Liu Y, Wu H, Diao X, Chen P, Wang X, Han Y (2022) Multi-omics analyses of 398 foxtail millet accessions reveal genomic regions associated with domestication, metabolite traits, and anti-inflammatory effects. Mol Plant 15(8):1367–1383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2022.07.003
Li X, Hou S, Feng M, Xia R, Li J, Tang S, Han Y, Gao J, Wang X (2023) MDSi: multi-omics database for Setaria italica. BMC Plant Biol 23(1):223. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04238-3
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of Fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Luo W, Tang Y, Li S, Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhang R, Diao X, Yu J (2023) The m6A reader SiYTH1 enhances drought tolerance by affecting the messenger RNA stability of genes related to stomatal closure and reactive oxygen species scavenging in Setaria italica. J Integr Plant Biol 65(12):2569–2586. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13575
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20(9):1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Meinke DW, Cherry JM, Dean C, Rounsley SD, Koornneef M (1998) Arabidopsis thaliana: a model plant for genome analysis. Science 282(5389):662–682. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5389.662
Monte E, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Zhang Y, Li X, Young J, Austin-Phillips S, Quail PH (2003) Isolation and characterization of phyC mutants in Arabidopsis reveals complex crosstalk between phytochrome signaling pathways. Plant Cell 15(9):1962–1980. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.012971
Peng R, Zhang B (2021) Foxtail millet: a new model for C4 plants. Trends Plant Sci 26(3):199–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.12.003
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdottir H, Winckler W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G, Mesirov JP (2011) Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol 29(1):24–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1754
Sage RF (2004) The evolution of C4 photosynthesis. New Phytol 161(2):341–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.00974.x
Stefanov MA, Rashkov GD, Apostolova EL (2022) Assessment of the photosynthetic apparatus functions by chlorophyll fluorescence and P700 absorbance in C3 and C4 plants under physiological conditions and under salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 23(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073768
Sun K, Huang M, Zong W, Xiao D, Lei C, Luo Y, Song Y, Li S, Hao Y, Luo W, Xu B, Guo X, Wei G, Chen L, Liu YG, Guo J (2022) Hd1, Ghd7, and DTH8 synergistically determine the rice heading date and yield-related agronomic traits. J Genet Genomics 49 (5):437–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2022.02.018
Takano M, Inagaki N, Xie X, Yuzurihara N, Hihara F, Ishizuka T, Yano M, Nishimura M, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Shinomura T (2005) Distinct and cooperative functions of phytochromes A, B, and C in the control of deetiolation and flowering in rice. Plant Cell 17(12):3311–3325. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.035899
Tang S, Zhao Z, Liu X, Sui Y, Zhang D, Zhi H, Gao Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhao M, Li D, Wang K, He Q, Zhang R, Zhang W, Jia G, Tang W, Ye X, Wu C, Diao X (2023) An E2-E3 pair contributes to seed size control in grain crops. Nat Commun 14(1):3091. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38812-y
Wang H, Jia G, Zhang N, Zhi H, Xing L, Zhang H, Sui Y, Tang S, Li M, Zhang H, Feng B, Wu C, Diao X (2022) Domestication-associated PHYTOCHROME C is a flowering time repressor and a key factor determining Setaria as a short-day plant. New Phytol 236(5):1809–1823. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18493
Yang X, Wan Z, Perry L, Lu H, Wang Q, Zhao C, Li J, Xie F, Yu J, Cui T, Wang T, Li M, Ge Q (2012) Early millet use in northern China. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(10):3726–3730. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1115430109
Yang ZR, Zhang HS, Li XK, Shen HM, Gao JH, Hou SY, Zhang B, Mayes S, Bennett M, Ma JX, Wu CY, Sui Y, Han YH, Wang XC (2020) A mini foxtail millet with an Arabidopsis-like life cycle as a C4 model system. Nat Plants 6(9):1167–1178. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-020-0747-7
Zhang G, Liu X, Quan Z, Cheng S, Xu X, Pan S, Xie M, Zeng P, Yue Z, Wang W, Tao Y, Bian C, Han C, Xia Q, Peng X, Cao R, Yang X, Zhan D, Hu J, Zhang Y, Li H, Li H, Li N, Wang J, Wang C, Wang R, Guo T, Cai Y, Liu C, Xiang H, Shi Q, Huang P, Chen Q, Li Y, Wang J, Zhao Z, Wang J (2012) Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides insights into grass evolution and biofuel potential. Nat Biotechnol 30:549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2195
Zhu X, Shan L, Wang Y, Quick WP (2010) C4 rice – an ideal arena for systems biology research. J Integr Plant Biol 52(8):762–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00983.x
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3400300, 2022YFC3400301), Shanxi Province Science and Technology Major Special Project (202101140601027), the Central Government Guides the Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project (YDZJSX2021B010), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123423, 20210302123385), Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Shanxi Province (2023KY319) and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-06-14.5-B8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingchun Wang designed the experiments, coordinated the study, performed map-based cloning of the XIAOMI4 gene and wrote the manuscript. Meng Shan, Mengmeng Duan, Huimin Shen, Yujing Wang and Zhirong Yang characterized the xiaomi allele phenotype. Yiru Zhang and Xingchun Wang identified the xiaomi3 mutant. Yuanhuai Han identified the xiaomi4 mutant. Kai Zhao identified the xiaomi5 and xiaomi6 mutants. Xukai Li analyzed genome resequencing data and identified the InDels and SNPs.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The manuscript has been seen and approved by all authors, and has not been submitted to anywhere else for consideration.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Ben Zhang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, M., Duan, M., Shen, H. et al. Identification and characterization of four novel xiaomi alleles to facilitate foxtail millet as a C4 model plant. Plant Growth Regul (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-024-01134-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-024-01134-0