Abstract
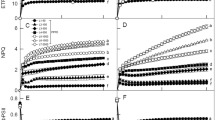
To reveal responses of photosynthetic physiological characteristics in Phoebe bournei seedlings to different light qualities and provide a basis for light environment regulation in seedling cultivation and under-canopy regeneration, we analyzed the photosynthetic physiological characteristics of P. bournei seedlings under five types of light qualities (white, red, blue, green, red: blue = 1:1) with the same photosynthetic photon flux density of 100 ± 5 μmol·m−2·s−1. The results showed that blue light significantly promoted chlorophyll content, Rubisco, RCA and photosynthetic rate (Pn), but water use efficiency (WUE) was reduced by blue light. The red light treatment exhibited the highest initial fluorescence (Fo), but wasn't conducive to the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments and had the lowest maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) and potential photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fo). The seedlings treated by green light showed the lowest Pn, Tr, WUE, rubisco, with the highest Fv/Fm and Fv/Fo. Red-blue light significantly increased WUE, photosynthetic electron transfer rate (ETR), actual photosynthetic efficiency Y(II), and quantum yield of regulated energy dissipation Y(NPQ) in PSII of P. bournei seedlings, with the second highest Pn across treatments. In conclusion, the effects of single light quality on photosynthetic characteristics of P. bournei seedlings exhibited both advantages and disadvantages. The combination of red and blue light, which integrated the advantages of single light quality, enhanced the photosynthetic performance and photoprotective ability of P. bournei seedlings. It promoted the energy conversion and utilization efficiency of PSII, resulting in the best carbon assimilation efficiency. Therefore, red-blue light promoted the growth and development of Phoebe bournei seedlings.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Abbreviations
- Chla :
-
Chlorophyll a
- Chlb :
-
Chlorophyll b
- Ci:
-
Intercellular CO2 concentration
- CK:
-
Control treatment
- ETR:
-
Photosynthetic Electron Transfer Rate
- Fo:
-
Initial fluorescence
- Fm:
-
Maximum fluorescence
- Fv/Fm:
-
Maximum photochemical efficiency
- Fv/Fo:
-
Potential photochemical efficiency
- Gs:
-
Stomatal conductance
- J max :
-
Maximum electron transfer rate
- NPQ:
-
Non-photochemical quenching coefficient
- PARsat :
-
Saturated light intensity
- Pn:
-
Photosynthetic rate
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- qP:
-
Photochemical quenching coefficient
- RCA:
-
Rubisco activase
- Rubisco:
-
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- Tr:
-
Transpiration rate
- WUE:
-
Water use efficiency
- Y(NO):
-
Quantum yield of non-regulated energy dissipation
- Y(NPQ):
-
Quantum yield of regulated energy dissipation
- Y(II):
-
Actual photosynthetic efficiency
- α :
-
Initial slope
References
An J, Wei X, Huo H (2022) Transcriptome analysis reveals the accelerated expression of genes related to photosynthesis and chlorophyll biosynthesis contribution to shade-tolerant in Phoebe bournei. BMC Plant Biol 22:268–281. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03657-y
Carmo-Silva AE, Salvucci ME (2013) The regulatory properties of rubisco activase differ among species and affect photosynthetic induction during light transitions. Plant Physiol 161:1645–1655
Carmo-Silva E, Scales JC, Madgwick PJ, Parry MAJ (2015) Optimizing Rubisco and its regulation for greater resource use efficiency. Plant, Cell Environ 38:1817–1832. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12425
Chang C-L, Chang K-P (2014) The growth response of leaf lettuce at different stages to multiple wavelength-band light-emitting diode lighting. Sci Hortic 179:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.09.013
Dieleman JA, De Visser PHB, Meinen E, Grit JG, Dueck TA (2019) Integrating morphological and physiological responses of tomato plants to light quality to the crop level by 3D modeling. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00839
Fan X-X, Xu Z-G, Liu X-Y, Tang C-M, Wang L-W, Han X-L (2013a) Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci Hortic 153:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.01.017
Fan X, Zang J, Xu Z, Guo S, Jiao X, Liu X, Gao Y (2013b) Effects of different light quality on growth, chlorophyll concentration and chlorophyll biosynthesis precursors of non-heading Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). Acta Physiol Plant 35:2721–2726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1304-z
Fang L, Ma Z, Wang Q, Nian H, Ma Q, Huang Q, Mu Y (2021) Plant growth and photosynthetic characteristics of soybean seedlings under different LED lighting quality conditions. J Plant Growth Regul 40:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10131-2
Folta KM, Maruhnich SA (2007) Green light: a signal to slow down or stop. J Exp Bot 58:3099–3111. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erm130
Fu, L., and Chin, C.M. (1992). China plant red data book.
Galvao VC, Fankhauser C (2015) Sensing the light environment in plants: photoreceptors and early signaling steps. Curr Opin Neurobiol 34:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2015.01.013
Gao, J.F.(2006). Experimental Guidance of Plant Physiology. Higher Education Press.
Han P-P, Shen S-G, Wang H-Y, Sun Y, Dai Y-J, Jia S-R (2015) Comparative metabolomic analysis of the effects of light quality on polysaccharide production of cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. Algal Research-Biomass Biofuels Bioproducts 9:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.02.019
Han H, Luo M, Li T, Wei XL (2021) Natural population characteristics, spatial distribution pattern and spatial correlation analysis of Phoebe bournei in Guizhou Province. Acta Ecol Sin 41:5360–5367. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201909201967
Hogewoning SW, Trouwborst G, Maljaars H, Poorter H, van Ieperen W, Harbinson J (2010) Blue light dose-responses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light. J Exp Bot 61:3107–3117. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq132
Hu L, Liao W, Dawuda MM, Yu J, Lv J (2017) Appropriate NH4+: NO3- ratio improves low light tolerance of mini Chinese cabbage seedlings. Bmc Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-0976-8
Hung NK, Trang HTH, Ha CH, Ngoc PB (2022) Effects of blue and red LED lights on rubisco activase gene expression, CO2 fixation efficiency and plant morphology of Gerbera jamesonii. Vietnam J Biotechnol 20:467–477
Inoue S-I, Kinoshita T (2017) Blue light regulation of stomatal opening and the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol 174:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00166
Izzo LG, Mele BH, Vitale L, Vitale E, Arena C (2020) The role of monochromatic red and blue light in tomato early photomorphogenesis and photosynthetic traits. Environm Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104195
Johkan M, Shoji K, Goto F, Hashida S-N, Yoshihara T (2010) Blue light-emitting diode light irradiation of seedlings improves seedling quality and growth after transplanting in red leaf lettuce. HortScience 45:1809–1814
Johkan M, Shoji K, Goto F, Hahida S, Yoshihara T (2012) Effect of green light wavelength and intensity on photomorphogenesis and photosynthesis in Lactuca sativa. Environ Exp Bot 75:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.08.010
Kalaji HM, Schansker G, Brestic M, Bussotti F, Calatayud A, Ferroni L, Goltsev V, Guidi L, Jajoo A, Li P et al (2017) Frequently asked questions about chlorophyll fluorescence, the sequel (vol 132, pg 13, 2017). Photosynth Res 132:67–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-017-0356-0
Kim H-H, Goins GD, Wheeler RM, Sager JC (2004) Green-light supplementation for enhanced lettuce growth under red- and blue-light-emitting diodes. HortScience 39:1617–1622
Kume A, Akitsu T, Nasahara KN (2018) Why is chlorophyll b only used in light-harvesting systems? J Plant Res 131:961–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-018-1052-7
Kuno N, Furuya M (2000) Phytochrome regulation of nuclear gene expression in plants. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1006/scdb.2000.0205
Li H, Tang C, Xu Z (2013) The effects of different light qualities on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) plantlet growth and morphogenesis in vitro. Sci Hortic 150:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.10.009
Li Y, Xin GF, Liu C, Shi QH, Yang FJ, Wei M (2020) Effects of red and blue light on leaf anatomy, CO2 assimilation and the photosynthetic electron transport capacity of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L) seedlings. Bmc Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02523-z
Li J, Yi C, Zhang C, Pan F, Xie C, Zhou W, Zhou C (2021a) Effects of light quality on leaf growth and photosynthetic fluorescence of Brasenia schreberi seedlings. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06082
Li Y, Liu Z, Shi Q, Yang F, Wei M (2021b) Mixed red and blue light promotes tomato seedlings growth by influencing leaf anatomy, photosynthesis, CO2 assimilation and endogenous hormones. Sci Hortic. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110500
Lorimer GH (2003) The carboxylation and oxygenation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate: the primary events in photosynthesis and photorespiration. Annurevplant Physiol 32:349–382. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.32.060181.002025
Lysenko V, Guo Y, Kosolapov A, Usova E, Varduny T, Krasnov V (2020) Polychromatic Fourier-PAM fluorometry and hyperspectral analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence from Phaseolus vulgaris leaves: Effects of green light. Inform Process Agric 7:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2019.09.009
Matthews JSA, Vialet-Chabrand SRM, Lawson T (2017) Diurnal variation in gas exchange: the balance between carbon fixation and water loss. Plant Physiol 174:614–623. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00152
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence–a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.345.659
Meng L, Song W, Liu S, Dong J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Xu Y, Wang S (2015) Light quality regulates lateral root development in tobacco seedlings by shifting auxin distributions. J Plant Growth Regul 34:574–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9491-z
Min, X.U., Liu, J., and Abuduwayiti, A. (2018). Comparative Methods on Chlorophyll Extraction in Plant Physiology Experiment Teaching. Experiment Science and Technology.
Nagarajan R, Gill KS (2018) Evolution of Rubisco activase gene in plants. Plant Mol Biol 96:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-017-0680-y
Naumburg E, Ellsworth DS (2000) Photosynthetic sunfleck utilization potential of understory saplings growing under elevated CO2 in FACE. Oecologia 122:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008844
Nishio JN (2000) Why are higher plants green? Evolution of the higher plant photosynthetic pigment complement. Plant Cell Environ 23:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2000.00563.x
Ohashi-Kaneko K, Matsuda R, Goto E, Fujiwara K, Kurata K (2006) Growth of rice plants under red light with or without supplemental blue light. Soil Sci Plant Nut. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00063.x
OuYang F, Ou Y, Zhu T, Ma J, An S, Zhao J, Wang J, Kong L, Zhang H, Tigabu M (2021) Growth and physiological responses of norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) H. Karst) supplemented with monochromatic red blue and far-red light. Forests. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020164
Paradiso R, Proietti S (2022) Light-quality manipulation to control plant growth and photomorphogenesis in greenhouse horticulture: the state of the art and the opportunities of modern LED systems. J Plant Growth Regul 41:742–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10337-y
Rehman M, Fahad S, Saleem MH, Hafeez M, Rahman MH, Liu F, Deng G (2020) Red light optimized physiological traits and enhanced the growth of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.). Photosynthetica 58:922–931
Riikonen J (2021) Applications of different light spectra in growing forest tree seedlings. Forests. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091194
Sb A, Krekling T, Appelgren M (1995) Light quality affects photosynthesis and leaf anatomy of birch plantlets in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 41:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00051588
Shimizu H, Saito Y, Nakashima H, Miyasaka J, Ohdoi K (2011) Light environment optimization for lettuce growth in plant factory. IFAC Proceed Volumes 44:605–609. https://doi.org/10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.02683
Shuya W, Xin M, Zhongqi T, Yue W, Xuemei X, Guobin Z, Linli H, Zeci L, Jian L, Jihua Y (2022) Red and Blue LED light supplementation in the morning pre-activates the photosynthetic system of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) leaves and promotes plant growth. Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040897
Smith HL, McAusland L, Murchie EH (2017) Don’t ignore the green light: exploring diverse roles in plant processes. J Exp Bot 68:2099–2110. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx098
Snider J, Thibault G, Houry WA (2008) The AAA plus superfamily of functionally diverse proteins. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-4-216
Song Q, Chen S, Wu Y, He Y, Feng J, Yang Z, Lin W, Zheng G, Li Y, Chen H (2020) Comparative transcriptome analyses of gene response to different light conditions of camellia oleifera leaf using illumina and single-molecule real-time-based RNA-sequencing. Forests. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11010091
Sood S, Gupta V, Tripathy BC (2005) Photoregulation of the greening process of wheat seedlings grown in red light*. Plant Mol Biol 59:269–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-8880-2
Su N, Wu Q, Shen Z, Xia K, Cui J (2014) Effects of light quality on the chloroplastic ultrastructure and photosynthetic characteristics of cucumber seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 73:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9883-7
Tanaka R, Tanaka A (2011) Chlorophyll cycle regulates the construction and destruction of the light-harvesting complexes. BBA-Bioenergetics 1807:968–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.01.002
Tanaka A, Ito H, Tanaka R, Tanaka NK, Yoshida K, Okada K (1998) Chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) is involved in chlorophyll b formation from chlorophyll a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12719–12723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.21.12719
Tang X, Liu G, Jiang J, Lei C, Zhang Y, Wang L, Liu X (2020) Effects of growth irradiance on photosynthesis and photorespiration ofPhoebe bourneileaves. Funct Plant Biol 47:1053–1061. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP20062
Tepperman JM, Zhu T, Chang HS, Wang X, Quail PH (2001) Multiple transcription-factor genes are early targets of phytochrome A signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9437–9442. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.161300998
Terashima I, Ooeda H, Fujita T, Oguchi R (2016) Light environment within a leaf. II. Progress in the past one-third century. J Plant Res 129:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0808-1
Vicente R, Morcuende R, Babiano J (2011) Differences in Rubisco and chlorophyll content among tissues and growth stages in two tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) varieties. Agron Res 9:501–507
Wang H, Gu M, Cui J, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu J (2009) Effects of light quality on CO2 assimilation, chlorophyll-fluorescence quenching, expression of Calvin cycle genes and carbohydrate accumulation in Cucumis sativus. J Photochem Photobiol B-Biology 96:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.03.010
Wang XY, Xu XM, Cui J (2015) The importance of blue light for leaf area expansion, development of photosynthetic apparatus, and chloroplast ultrastructure of Cucumis sativus grown under weak light. Photosynthetica 53:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0083-8
Wang H, Wu F, Li M, Zhu X, Shi C, Shao C, Ding G (2022) Structure and chlorophyll fluorescence of heteroblastic foliage affect first-year growth in Pinus massoniana Lamb. seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 170:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.12.006
Wei H, Hauer RJ, Chen G, Chen X, He X (2020) Growth, nutrient assimilation, and carbohydrate metabolism in korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) seedlings in response to light spectra. Forests. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11010044
Weller JL, Perrotta G, Schreuder ME, van Tuinen A, Koornneef M, Giuliano G, Kendrick RE (2001) Genetic dissection of blue-light sensing in tomato using mutants deficient in cryptochrome 1 and phytochromes A, B1 and B2. The Plant J 25:427–440. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00978.x
Xu Y, Yang M, Cheng F, Liu S, Liang Y (2020) Effects of LED photoperiods and light qualities on in vitro growth and chlorophyll fluorescence ofCunninghamia lanceolata. Bmc Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02480-7
XUKai, GUOYan-ping, ZHANGShang-long, ZHANGLiang-cheng, and ZHANGLing-xiao, (2004) Effect of light quality on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in strawberry leaves. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 38:369–375
Yang X, Xu H, Shao L, Li T, Wang Y, Wang R (2018) Response of photosynthetic capacity of tomato leaves to different LED light wavelength. Environ Exp Bot 150:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.03.013
Ye ZP (2010) A review on modeling of responses of photosynthesis to light and CO2 China. J Plant Ecol 34(06):727–740
Yoshida H, Mizuta D, Fukuda N, Hikosaka S, Goto E (2016) Effects of varying light quality from single-peak blue and red light-emitting diodes during nursery period on flowering, photosynthesis, growth, and fruit yield of everbearing strawberry. Plant Biotechnol 33:267–276. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.16.0216a
Yu WW, Liu Y, Song LL, Jacobs DF, Du XH, Ying YQ, Shao QS, Wu JS (2017) Effect of differential light quality on morphology, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzyme activity in Camptotheca acuminata seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 36:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9625-y
Zhang H, Tu Y, Kang J, Song W, Zheng L (2021) Blue light dosage affects photosynthesis, chlorophyll, and antioxidant properties of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Photosynthetica 59:547–556
Zheng, W.J. (1983). Sylva Sinica. Vol. 1.
Funding
This work was supported in full by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870613) and Guizhou Province High-level Innovative Talents Training Plan Project (2016) 5661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. WXL and JNQ designed the experiment, JNQ, NRX and CXY coordinated the experiment. NRX performed statistical analysis and formulated the manuscript. NRX, SSC and WXL revised and improved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Robert Sharwood.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, R., Wei, X., Jin, N. et al. Response of photosynthetic pigments, gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters to light quality in Phoebe bournei seedlings. Plant Growth Regul (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-024-01131-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-024-01131-3