Abstract
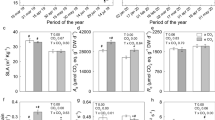
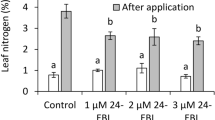
During the whole growth cycle growth, yield and fruit quality of strawberry are often strongly affected by insufficient CO2 and low light in greenhouse production. However, it is still not clear what extent growth, yield and fruit quality of strawberry can be improved by elevated CO2 and supplementary light combination. We measured growth, yield and fruit quality of strawberries under four combinations of two levels of CO2, and two levels of light. Our results showed that yield enhancement throughout the growing season was 23.4% by elevated CO2, 21.46% by LED supplemental light, and 51.3% by their combination. Both elevated CO2 and LED supplemental light significantly increased soluble sugar content, but significantly decreased titratable acidity. LED supplemental light could partly or fully compensate for the negative impacts of elevated CO2 on soluble protein content, total phenol content, total flavonoid content, anthocyanin content, and total antioxidant capacity. Yield under four CO2 and light treatments was positively correlated with soluble sugar content, but negatively correlated with titratable acidity. Taken together, the combination of elevated CO2 and LED supplemental light largely improved both fruit yield and sweetness of strawberry during the autumn through spring in greenhouse. Optimal both CO2 and light is a worthwhile practice for improving strawberry production.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM (1993) Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 90(17), 7915–7922. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.17.7915
Brown CS, Schuerger AC, Sager JC (1995) Growth and photomorphogenesis of pepper plants under red light-emitting-diodes with supplemental blue or far-red lighting. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120(5):808–813. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.120.5.808
Cai C, Yin XY, He SQ, Jiang WY, Si CF, Struik PC, Luo WH, Li G, Xie YT, Xiong Y, Pan GX (2016) Responses of wheat and rice to factorial combinations of ambient and elevated CO2 and temperature in FACE experiments. Glob Change Biol 22(2):856–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13065
Cervantes L, Ariza MT, Gomez-Mora JA, Miranda L, Medina JJ, Soria C, Martinez-Ferri E (2019) Light exposure affects fruit quality in different strawberry cultivars under field conditions. Sci Hort 252:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.03.058
Choi HG, Byoung Yong M, Nam Jun K (2015) Effects of LED light on the production of strawberry during cultivation in a plastic greenhouse and in a growth chamber. Sci Hort 189:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.03.022
Chun OK, Kim DO, Moon HY, Kang HG, Lee CY (2003) Contribution of individual polyphenolics to total antioxidant capacity of plums. J Agric Food Chem 51(25):7240–7245. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0343579
Desjardins Y, Gosselin A, Lamarre M (1990) Growth of transplants and in vitro-cultured clones of asparagus in response to CO2 enrichment and supplemental lighting. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 115(3):364–368. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.115.3.364
Dong JL, Gruda N, Lam SK, Li X, Duan ZQ (2018) Effects of elevated CO2 on nutritional quality of vegetables: a review. Front Plant Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00924
Easlon HM, Bloom AJ (2014) Easy Leaf Area: automated digital image analysis for rapid and accurate measurement of leaf area. Appl Plant Sci 2(7). https://doi.org/10.3732/apps.1400033
Esmaeilizadeh M, Shamsabad MRM, Roosta HR, Dąbrowski P, Rapacz M, Andrzej.Zieliński HM (2021) Manipulation of light spectrum can improve the performance of photosynthetic apparatus of strawberry plants growing under salt and alkalinity stress. PloS one 16(12), e0261585. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261585
Fierro A, Gosselin A, Tremblay N (1994) Supplemental carbon dioxide and light improved tomato and pepper seedling growth and yield. HortScience 29(3):152–154. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.29.3.152
Geiger JW, Davis NM, Blakemore WS, Long CL (2008) A method for determining total nitrogen in Kjeldahl digestion solution using a centrifugal analyser. J Autom Chem 9(2):72–76. https://doi.org/10.1155/S1463924687000166
Goins GD, Yorio NC, Sanwo MM, Brown CS (1997) Photomorphogenesis, photosynthesis, and seed yield of wheat plants grown under red light-emitting diodes (LEDs) with and without supplemental blue lighting. J Exp Bot 48(7):1407–1413. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/48.7.1407
Goudriaan J, H. LH (1994) Modelling potential crop growth processes. Curr Issues Prod Ecol 2:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0750-1
Hidaka K, Dan K, Imamura H, Miyoshi Y, Kitano M (2013) Investigation of supplemental lighting with different light source for high yield of strawberry. IFAC Proc Volumes 46(4):115–119. https://doi.org/10.3182/20130327-3-JP-3017.00028
Hidaka K, Okamoto A, Araki T, Miyoshi Y, Dan K, Imamura H, Kitano M, Sameshima K, Okimura M (2014) Effect of photoperiod of supplemental lighting with light-emitting diodes on growth and yield of strawberry. Environ Control Biol 52(2):63–74. https://doi.org/10.2525/ecb.52.63
Hidaka K, Dan K, Imamura H, Takayama T, Sameshima K, Okimura M (2015) Variety comparison of effect of supplemental lighting with led on growth and yield in forcing culture of strawberry. Environ Control Biol 53(3):135–143. https://doi.org/10.2525/ecb.53.135
Jin R, Guo S, Xu C, Yang C, Ai W, Tang Y, Qin L (2014) Effects of different carbon dioxide and LED lighting levels on the anti-oxidative capabilities of Gynura bicolor DC. Adv Space Res 53(2):353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.11.019
Johkan M, Shoji K, Goto F, Hashida SN, Yoshihara T (2010) Blue light-emitting diode light irradiation of seedlings improves seedling quality and growth after transplanting in red leaf lettuce. HortScience: a publication of the American Society for Horticultural Science 45(12):414–415. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.45.12.1809
Kaiser E, Ouzounis T, Giday H, Schipper R, Heuvelink E, Marcelis LFM (2019) Adding blue to red supplemental light increases biomass and yield of greenhouse-grown tomatoes, but only to an optimum. Front Plant Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.02002
Körner C (2006) Plant CO2 responses: an issue of definition, time and resource supply. New Phytol 172(3):393–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01886.x
Kumaran A, Karunakaran RJ (2007) Activity-guided isolation and identification of free radical-scavenging components from an aqueous extract of Coleus aromaticus. Food Chem 99(1):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.09.051
Leakey, Andrew D, Ainsworth B, Elizabeth A, Bernacchi, Carl J (2009) Elevated CO2 effects on plant carbon, nitrogen, and water relations: six important lessons from FACE. J Exp Bot 60(10):2859–2876. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp096
Levine LH, Paré P (2009) Antioxidant capacity reduced in scallions grown under elevated CO2 independent of assayed light intensity. Adv Space Res 44(8):887–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2009.06.017
Li X, Dong J, Gruda N, Chu W, Duan Z (2021) Does the short-term fluctuation of mineral element concentrations in the closed hydroponic experimental facilities affect the mineral concentrations in cucumber plants exposed to elevated CO2? Plant Soil 465(1/2):125–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04993-y
Liu Qh, Wu X, Chen Bc M, Jq, Gao J (2014) Effects of low light on agronomic and physiological characteristics of rice including grain yield and quality. Rice Sci 21(005):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60192-4
Long SP, Ainsworth EA, Rogers A, Ort DR (2004) Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide: plants face the future. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55(1):591–628. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant
Long SP, Ainsworth EA, Leakey ADB, Nsberger J, Ort DR (2006) Food for Thought: Lower-Than-Expected crop yield stimulation with rising CO2 concentrations. American Association for the Advancement of Science. 312(5782):1918–1921. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114722
Mamatha H, Srinivasa Rao NK, Laxman RH, Shivashankara KS, Bhatt RM, Pavithra KC (2014) Impact of elevated CO2 on growth, physiology, yield, and quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentumMill) cv. Arka Ashish. Photosynthetica 52(4):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0059-0
Mortensen LM (1994) Effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on growth and yield of eight vegetable species in a cool climate. Sci Hort 58(3):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4238(94)90149-X
Ng A, Mb A, Jtb C (2019) Influence of climate change on protected cultivation: impacts and sustainable adaptation strategies - a review. J Clean Prod 225:481–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.210
Perez-Lopez U, Sgherri C, Miranda-Apodaca J, Micaelli F, Lacuesta M, Mena-Petite A, Quartacci MF, Munoz-Rueda A (2018) Concentration of phenolic compounds is increased in lettuce grown under high light intensity and elevated CO2. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 123:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.12.010
Rapparini F, Neri L, Mihailova G, Petkova S, Georgieva K (2015) Growth irradiance affects the photoprotective mechanisms of the resurrection angiosperm Haberlea rhodopensis Friv. In response to desiccation and rehydration at morphological, physiological and biochemical levels. Environ Experimental Bot 113:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.01.007
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A (1998) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9–10):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Reich M, Van dM AN, Parmar S, Hawkesford MJ, De Kok LJ, Grantz D (2016) Temperature determines size and direction of effects of elevated CO2 and nitrogen form on yield quantity and quality of chinese cabbage. Plant Biol 18:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12396
Reich PB, Hobbie SE, Lee TD, Pastore MA (2018) Unexpected reversal of C3 versus C4 grass response to elevated CO2 during a 20-year field experiment. Science 360(6386):317–320. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aas9313
Sakai H, Hasegawa T, Kobayashi K (2010) Enhancement of rice canopy carbon gain by elevated CO2 is sensitive to growth stage and leaf nitrogen concentration. New Phytol 170(2):321–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01688.x
Shimomura M, Yoshida H, Fujiuchi N, Ariizumi T, Fukuda N (2020) Continuous blue lighting and elevated carbon dioxide concentration rapidly increase chlorogenic acid content in young lettuce plants. Sci Hort 272(0304–4238):109550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109550
Stutte GW, Edney S, Skerritt T (2009) Photoregulation of bioprotectant content of red leaf lettuce with light-emitting diodes. Hortscience a publication of the American Society for Horticultural Science. 44(1):79–82. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.44.1.79
Sun P, Mantri N, Lou H, Hu Y, Sun D, Zhu Y, Dong T, Lu H (2012) Effects of elevated CO2 and temperature on yield and fruit quality of strawberry (fragaria × ananassa duch) at two levels of nitrogen application. Plos One 7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041000
Tulipani S, Mezzetti B, Capocasa F, Bompadre S, Battino M (2008) Antioxidants, phenolic compounds, and nutritional quality of different strawberry genotypes. J Agricultural Food Chem 56(3):696–704. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0719959
Wang SY, Bunce JA, Maas JL (2003) Elevated carbon dioxide increases contents of antioxidant compounds in field-grown strawberries. J Agricultural Food Chem 51(15):4315–4320. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf021172d
Wang W, Cai C, He J, Gu J, Liu G (2019) Yield, dry matter distribution and photosynthetic characteristics of rice under elevated CO2 and increased temperature conditions. Field Crops Research 248:107605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107605
Wu MC, Hou CY, Jiang CM, Wang YT, Wang CY, Chen HH, Chang HM (2007) A novel approach of LED light radiation improves the antioxidant activity of pea seedlings. Food Chem 101(4):1753–1758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.02.010
Xu F, Cao S, Shi L, Chen W, Su X, Yang Z (2014) Blue light irradiation affects anthocyanin content and enzymes activities involved in postharvest strawberry fruit. J Agric Food Chem 62(20):4778–4783. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf501120u
Yin X (2013) Improving ecophysiological simulation models to predict the impact of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on crop productivity. Ann Botany 112(3):465–475. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct016
Yin X, Schapendonk AHCM, Struik PC (2018) Exploring the optimum nitrogen partitioning to predict the acclimation of C3 leaf photosynthesis to varying growth conditions. J Exp Bot 70(9):2435–2447. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery277
Yoneda A, Yasutake D, Hidaka K, Muztahidin NI, Miyoshi Y, Kitano M, Okayasu T (2020) Effects of supplemental lighting during the period of rapid fruit development on the growth, yield, and energy use efficiency in strawberry plant production. Int Agrophys 34(2):233–239. https://doi.org/10.31545/intagr/117623
Yorio NC, Goins GD, Kagie HR, Wheeler RM, Sager JC (2001) Improving spinach, radish, and lettuce growth under red light-emitting diodes (LEDs) with blue light supplementation. HortScience 36(2):380–383. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.36.2.380
Zhang Y, Seeram NP, Lee R, Feng L, Heber D (2008) Isolation and identification of strawberry phenolics with antioxidant and human cancer cell antiproliferative properties. J Agricultural Food Chem 56(3):670–675. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf071989c
Zheng Y, Wang SY, Wang CY, Zheng W (2007) Changes in strawberry phenolics, anthocyanins, and antioxidant capacity in response to high oxygen treatments. LWT - Food Science and Technology 40(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.08.013
Zivcak M, Brestic M, Kalaji HM, Govindjee (2014) Photosynthetic responses of sun- and shade-grown barley leaves to high light: is the lower PSII connectivity in shade leaves associated with protection against excess of light? Photosynth Res 119(3):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-014-9969-8
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, China (No.2020B020201006), the program of Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (No.BE2018402), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31971508), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP22005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Baris Uzilday.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Cai, C., Shen, M. et al. Responses of growth, yield and fruit quality of strawberry to elevated CO2, LED supplemental light, and their combination in autumn through spring greenhouse production. Plant Growth Regul 102, 351–365 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01065-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01065-2