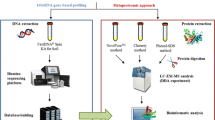
Abstract
Salinity is the major cause of reducing crop yield in wheat, an important staple food crop for food security. Since the rhizosphere microbiome plays an important role in plant growth and development, the present study was conducted to characterize functional metabolic changes in the rhizosphere microbiota of wheat grown under saline and non-saline soils using comparative metaproteomics. In total 1538 and 891 proteins were obtained from wheat rhizosphere from saline and non-saline soils, respectively. The proteins DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta’ (48.43%) followed by Leucine-tRNA ligase (4.45%) and translocase subunit SecA (2.69%) were relatively most abundantly present in salt stressed wheat rhizosphere metaproteome. Induced accumulation of proteins related to proline and spermidine biosynthesis was found in saline wheat rhizosphere. Inositol transporter involved in the osmotic balance and HSP90A, a key player to response regulator in stress were present in saline rhizosphere but were absent in non-saline conditions. Among 1410 proteins unique for saline soil, those linked predominantly with the pathways were sphingolipid, phosphinate and phenazine metabolism. The data is available in ProteomeXchange with the identifier PXD015387. The present study extends knowledge about the rhizosphere community functions utilizing a metaproteomic approach in wheat growing under saline conditions and can help in characterizing key proteins that may lead to physiological adaptations of the plants under saline environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited with the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD015387.
Submission details: Project Name: Metaproteomic datasets of wheat rhizosphere from saline and non-saline soils.
Project accession: PXD015387. Project DOI: Not applicable; Reviewer account details: Username: reviewer12163@ebi.ac.uk Password: 2Y0P1T2L.
References
Aktar F, Islam MS, Milon MA, Islam N, Islam MA (2021) Polyamines: An essentially regulatory modulator of plants to abiotic stress tolerance: a review. Asian J Appl Sci 9(3):195–204
Andronov EE, Petrova SN, Pinaev AG et al (2012) Analysis of the structure of microbial community in soils with different degrees of salinization using T-RFLP and real-time PCR techniques. Eurasian Soil Sci 45:147–56. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229312020044
Bona E, Massa N, Novello G et al (2019) Metaproteomic characterization of the Vitis vinifera rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy204
Cashikar AG, Duennwald M, Lindquist SL (2005) A chaperone pathway in protein disaggregation: HSP26 alteks the nature of protein aggregates to facilitate reactivation by HSP104. J Biol Chem 280(25):23869–75. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M502854200
Chakraborty K, Mondal S, Ray S et al (2020) Tissue tolerance coupled with ionic discrimination can potentially minimize the Energy cost of Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Front Plant Sci 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00265
Darzi Y, Letunic I, Bork P et al (2018) IPath3.0: interactive pathways explorer v3. Nucleic Acids Res 46. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky299
Edwards J, Johnson C, Santos-Medellín C et al (2015) Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1414592112
Glick BR, Gamalero E (2021) Recent developments in the study of plant microbiomes. Microorganisms 9(7):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071533
Gorcek Z, Erdal S (2015) Lipoic acid mitigates oxidative stress and recovers metabolic distortions in salt-stressed wheat seedlings by modulating ion homeostasis, the osmo-regulator level and antioxidant system. J Sci Food Agric. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7020
Gould SB (2018) Membranes and evolution. Curr Biol 28:R381–R385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.086
Hardoim PR, Andreote FD, Reinhold-Hurek B et al (2011) Rice root-associated bacteria: insights into community structures across 10 cultivars. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77(1):154–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01092.x
Huang Y, Yi Z, Jin Y et al (2017) Metatranscriptomics reveals the functions and enzyme profiles of the microbial community in chinese Nong-flavor liquor starter. Front Microbiol 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01747
Imhoff JF (2020) Osmotic adaptation in halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms. In: The biology of halophilic bacteria. CRC Press, p 211–253
Jia X, Zhu Y fang, Hu Y et al (2019) Integrated physiologic, proteomic, and metabolomic analyses of Malus halliana adaptation to saline–alkali stress. Hortic Res. 66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-019-0172-0
Kalhoro NA, Rajpar I, Kalhoro SA, Ali A, Raza S, Ahmed M, Kalhoro FA, Ramzan M, Wahid F (2016) Effect of salts stress on the growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Am J Plant Sci 7(15):2257. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2016.715199
Keiblinger KM, Schneider T, Roschitzki B et al (2012) Effects of stoichiometry and temperature perturbations on beech leaf litter decomposition, enzyme activities and protein expression. Biogeosciences. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-9-4537-2012
Keiblinger KM, Fuchs S, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S et al (2016) Soil and leaf litter metaproteomics-A brief guideline from sampling to understanding. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/iw180
Knief C, Delmotte N, Chaffron S et al (2012) Metaproteogenomic analysis of microbial communities in the phyllosphere and rhizosphere of rice. ISME J. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.192
Kojo S (2004) Vitamin C: basic Metabolism and its function as an index of oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 11(8):1041–64. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867043455567
Kokoeva MV, Storch KF, Klein C et al (2002) A novel mode of sensory transduction in archaea: binding protein-mediated chemotaxis towards osmoprotectants and amino acids. EMBO J 21(10):2312–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.10.2312
Kuzyakov Y, Razavi BS (2019) Rhizosphere size and shape: temporal dynamics and spatial stationarity. Soil Biol Biochem 135:343–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.05.011
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lee BN, Kroken S, Chou DYT et al (2005) Functional analysis of all nonribosomal peptide synthetases in Cochliobolus heterostrophus reveals a factor, NPS6, involved in virulence and resistance to oxidative stress. Eukaryot Cell. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.4.3.545-555
Liang X, Zhang L, Natarajan SK, Becker DF (2013) Proline mechanisms of stress survival. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(9):998–1011. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5074
Lin W, Wu L, Lin S et al (2013) Metaproteomic analysis of ratoon sugarcane rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-135
Liu M, Chen J, Guo Z et al (2017) Differential responses of polyamines and antioxidants to drought in a centipedegrass mutant in comparison to its wild type plants. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00792
Lu T, Ke M, Peijnenburg WJGM et al (2018) Investigation of Rhizospheric Microbial Communities in Wheat, Barley, and two Rice varieties at the Seedling Stage. J Agric Food Chem 66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b06155
Maiale S, Sánchez DH, Guirado A, Vidal A, Ruiz OA (2004) Spermine accumulation under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 161(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-01167
Malviya N, Yadav AK, Yandigeri MS, Arora DK (2011) Diversity of culturable streptomycetes from wheat cropping system of fertile regions of Indo-Gangetic Plains, India. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(7):1593–1602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0612-3
Mandal AK, Sethi M, Yaduvanshi NPS, Yadav RK, Bundela DS, Chaudhari SK, Chinchmalatpure A, Sharma DK (2013) Salt affected soils of Nain experimental farm: site characteristics, reclaimability and potential use. Tech Bull CSSRI/Karnal/2013/03:34
Mao C, Obeid LM (2008) Ceramidases: regulators of cellular responses mediated by ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1781(9):424–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.06.002
Meena A, Rao KS (2021) Assessment of soil microbial and enzyme activity in the rhizosphere zone under different land use/cover of a semiarid region, India. Ecol Process 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00288-3
Mendes R, Garbeva P, Raaijmakers JM (2013) The rhizosphere microbiome: significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12028
Mokrani S, Nabti EH, Cruz C (2020) Current advances in plant growth promoting bacteria alleviating salt stress for sustainable agriculture. Appl Sci 10(20):7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207025
Moran MA, Belas R, Schell MA et al (2007) Ecological genomics of marine Roseobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(14):4559–69. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02580-06
Moretti M, Minerdi D, Gehrig P et al (2012) A bacterial-fungal metaproteomic analysis enlightens an intriguing multicomponent interaction in the rhizosphere of Lactuca sativa. J Proteome Res 11(4):2061–2077. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr201204v
Morris RM, Nunn BL, Frazar C et al (2010) Comparative metaproteomics reveals ocean-scale shifts in microbial nutrient utilization and energy transduction. ISME J 4(5):673–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.4
Manoharachary C, Mukerji KG (2006) Rhizosphere biology–an overview. In: Microbial activity in the rhizoshere. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, p 1–15.
Mukhtar S, Mehnaz S, Mirza MS, Malik KA (2019) Isolation and characterization of bacteria associated with the rhizosphere of halophytes (Salsola stocksii and Atriplex amnicola) for production of hydrolytic enzymes. Braz J Microbiol 50(1):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00044-y
Narsing Rao MP, Dong ZY, Xiao M, Li WJ (2019) Effect of salt stress on plants and role of microbes in promoting plant growth under salt stress. In: Microorganisms in saline environments: strategies and functions. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, p 423–35.
Naz I, Mirza MS, Bano A (2014) Molecular characterization of rhizosphere bacterial communities associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars at flowering stage. J Anim Plant Sci 24(4):1123–1134
Penn K, Jensen PR (2012) Comparative genomics reveals evidence of marine adaptation in Salinispora species. BMC Genomics 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-86
Pérez-López U, Robredo A, Lacuesta M et al (2009) The oxidative stress caused by salinity in two barley cultivars is mitigated by elevated CO2. Physiol Plant 135(1):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01174.x
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, Van-Der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(11):789–799
Płaza G, Jałowiecki Ł, Głowacka D, Hubeny J, Harnisz M, Korzeniewska E (2021) Insights into the microbial diversity and structure in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant with particular regard to Archaea. PLoS ONE 16(4):e0250514. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250514
Prabha R, Singh DP, Gupta S et al (2019) Rhizosphere metagenomics of Paspalum scrobiculatum l. (kodo millet) reveals rhizobiome multifunctionalities. Microorganisms 7(12):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120608
Praeg N, Illmer P (2020) Microbial community composition in the rhizosphere of Larix decidua under different light regimes with additional focus on methane cycling microorganisms. Sci Rep 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79143-y
Rahman SJ, Charles TC, Kaur P (2016) Metagenomic approaches to identify novel organisms from the soil environment in a classroom setting. J Microbiol Biol Educ 17(3):423. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v17i3.1115
Ramadas S, Kumar TMK, Singh GP (2019) Wheat production in India: Trends and Prospects. IntechOpen Chap. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.86314
Rascovan N, Carbonetto B, Perrig D et al (2016) Integrated analysis of root microbiomes of soybean and wheat from agricultural fields. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28084
Renu, Gupta SK, Rai AK et al (2019) Metaproteomic data of maize rhizosphere for deciphering functional diversity. Data Br. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104574
Rubiano-Labrador C, Bland C, Miotello G et al (2014) Proteogenomic insights into salt tolerance by a halotolerant alpha-proteobacterium isolated from an andean saline spring. J Proteom 97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2013.05.020
Rubiano-Labrador C, Bland C, Miotello G et al (2015) Salt stress induced changes in the exoproteome of the halotolerant bacterium Tistlia consotensis deciphered by proteogenomics. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135065
Sahu PK, Singh DP, Prabha R et al (2019) Connecting microbial capabilities with the soil and plant health: options for agricultural sustainability. Ecol Indic 105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.084
Shakya M, Lo CC, Chain PSG (2019) Advances and challenges in metatranscriptomic analysis. Front Genet 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00904
Singh DP, Prabha R, Gupta VK et al (2018) Metatranscriptome analysis deciphers multifunctional genes and enzymes linked with the degradation of aromatic compounds and pesticides in the wheat rhizosphere. Front Microbiol 9:1331. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01331
Srivastava R, Srivastava AK, Ramteke PW, Gupta VK, Srivastava AK (2020) Metagenome dataset of wheat rhizosphere from Ghazipur region of Eastern Uttar Pradesh. Data Brief 28:105094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.105094
Suzuki T, Miyauchi K (2010) Discovery and characterization of tRNA ile lysidine synthetase (TilS). FEBS Lett 21:584:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.11.085
Tahir M, Mirza MS, Hameed S et al (2015) Cultivation-based and molecular assessment of bacterial diversity in the rhizosheath of wheat under different crop rotations. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130030
Takami H, Takaki Y, Uchiyama I (2002) Genome sequence of Oceanobacillus iheyensis isolated from the Iheya Ridge and its unexpected adaptive capabilities to extreme environments. Nucleic Acids Res 30(18):3927–35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf526
Tartaglia M, Bastida F, Sciarrillo R, Guarino C (2020) Soil metaproteomics for the study of the relationships between microorganisms and plants: a review of extraction protocols and ecological insights. Int J Mol Sci 21:8455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228455
Tu Q, He Z, Zhou J (2014) Strain/species identification in metagenomes using genome-specific markers. Nucleic Acids Res 42. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku138
Turner TR, James EK, Poole PS (2013) The plant microbiome. Genome Biol 14:209. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-209
Velázquez-Sepúlveda I, Orozco-Mosqueda M, Prieto-Barajas CM, Santoyo G (2012) Bacterial diversity associated with the rhizosphere of wheat plants (Triticum aestivum): toward a metagenomic analysis.Phyton. Int J Exp Bot 81:81–87. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2012.81.081
Wang HB, Zhang ZX, Li H, He HB, Fang CX, Zhang AJ, Li QS, Chen RS, Guo XK, Lin HF, Wu LK (2011) Characterization of metaproteomics in crop rhizospheric soil. J Proteome Res 4(3):932–940. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr100981r
Watt M, Silk WK, Passioura JB (2006) Rates of root and organism growth, soil conditions, and temporal and spatial development of the rhizosphere. Ann Botany 97(5):839–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl028
Wilmes P, Bond PL (2004) The application of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and downstream analyses to a mixed community of prokaryotic microorganisms. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00687.x
Wu L, Kellogg L, Devol AH et al (2008) Microarray-based characterization of microbial community functional structure and heterogeneity in marine sediments from the Gulf of Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02751-07
Wu L, Wang H, Zhang Z et al (2011) Comparative metaproteomic analysis on consecutively Rehmannia glutinosa-monocultured rhizosphere soil. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020611
Zhang Y, Li T, Wu H et al (2019) Effect of different fertilization practices on soil microbial community in a wheat-maize rotation system. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11154088
Zschiedrich CP, Keidel V, Szurmant H (2016) Molecular mechanisms of two-component signal transduction. J Mol Biol 25(19):3752–3775
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by ICAR funded Network Project of the Center of Agricultural Bioinformatics (CABin) at ICAR-National Bureau of Agriculturally Important Microorganisms (NBAIM), Mau, and is work of Sub-Project “Metatranscriptomics and metaproteomics analysis of wheat rhizosphere”. The authors are thankful to the CABin, ICAR-IASRI project from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Government of India for financial support. The authors are grateful to the Director, ICAR-NBAIM, Mau for providing the necessary support to carry out the project and Dr Murugan Kumar, Scientist, ICAR-NBAIM for help in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Hong-Xia Zhang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Renu, Sarim, K.M., Gupta, S.K. et al. A comparative analysis of rhizospheric metaproteome of wheat grown in saline and non-saline soils identifies proteins linked with characteristic functions. Plant Growth Regul 101, 415–426 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01027-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01027-8