Abstract
The folate content of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) is higher than that of other major crops. Polyglutamylation of folate can enhance its compartmentalization, reduce its transport, increase its affinities with enzymes, and increase the stability of the folate pool in Arabidopsis. The polyglutamylation reaction is catalyzed by folylpolyglutamate synthetases (FPGSs). However, the function of FPGS in foxtail millet remains unclear.
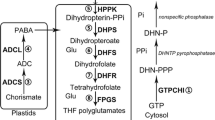
In this study, we identified the Setaria italica FPGS2 (SiFPGS2) gene function in foxtail millet. Phylogenetic tree, protein function domain, and docking analyses results revealed that SiFPGS2 belongs to the FPGS subfamily, possesses the tetrahydrofolypolyglutamate synthetase domain, and can bind tetrahydrofolate (THF) as a substrate. Subcellular localization predicted that SiFPGS2 was localized in the chloroplasts. Cis-acting element prediction analysis indicated the presence of meristem expression motif and root specific motif in the SiFPGS2 promoter. Overexpression of SiFPGS2 in Arabidopsis not only increased the folate content, but also increased the root length. Propidium iodide staining revealed that the increased root length was due to the promotion of cell division in the root apical meristem zone. SiFPGS2 catalyzes the polyglutamylation of THF and leads to an increase in folate content and root length by promoting root apical meristem zone cell division. SiFPGS2 can be used as a candidate gene for the biofortification of folate in Gramineae crops via genetic engineering.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are included in this article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bennetzen JL, Schmutz J, Wang H, Percifield R, Hawkins J, Pontaroli AC, Estep M et al (2012) Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat Biotechnol 30(6):555–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2196
Besson V, Rebeille F, Neuburger M, Douce R, Cossins EA (1993) Effects of tetrahydrofolate polyglutamates on the kinetic parameters of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and glycine decarboxylase from pea leaf mitochondria. Biochem J 292(2):425–430. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2920425
Blancquaert D, Van Daele J, Strobbe S, Kiekens F, Storozhenko S, De Steur H, Gellynck X et al (2015) Improving folate (vitamin B9) stability in biofortified rice through metabolic engineering. Nat Biotechnol 33(10):1076–1078. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3358
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13(8):1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
De Lepeleire J, Strobbe S, Verstraete J, Blancquaert D, Ambach L, Visser RGF, Stove C et al (2018) Folate biofortification of potato by tuber-specific expression of four folate biosynthesis genes. Mol Plant 11(1):175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.12.008
Eckermann C, Eichel J, Schröder J (2000) Plant methionine synthase: new insights into properties and expression. Biol Chem 381(8):695–703. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2000.090
Gorelova V, Ambach L, Rébeillé F, Stove C, Van Der Straeten D (2017) Folates in plants: research advances and progress in crop biofortification. Front Chem 5:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00021
Gregory JF, Quinlivan EP (2002) In vivo kinetics of folate metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 22(22):199–220. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.120701.083554
Hanson AD, Roje S (2001) One-carbon metabolism in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:119–137. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.119
He L, Zhang B, Wang X, Li H, Han Y (2015) Foxtail millet: nutritional and eating quality, and prospects for genetic improvement. Front Agri Sci Eng 2(2):124–133. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FASE-2015054(Chinese)
Hou S, Liu Z, Li Y, Yang M, Hou S, Han Y, Zhao Y et al (2022) Exogenous salicylic acid enhanced resistance of foxtail millet (setaria italica) to sclerospora graminicola. Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00854-5
Hou SY, Man X, Lian B, Ma G, Sun Z, Han L, Yan L et al (2022a) Folate metabolic profiling and expression of folate metabolism-related genes during panicle development in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv). J Sci Food Agric 102(1):268–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11355
Hou SY, Zhang Y, Zhao B, Man X, Ma G, Men Y, Du W et al (2022b) Heterologous expression of SiFBP, a folate-binding protein from foxtail millet, confers increased folate content and altered amino acid profiles with nutritional potential to Arabidopsis. J Agric Food Chem 70(20):6272–6284. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00357
Ishikawa T, Machida C, Yoshioka Y, Kitano H, Machida Y (2003) The GLOBULAR ARREST1 gene, which is involved in the biosynthesis of folates, is essential for embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 33(2):235–244. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01621.x
Jägerstad M, Jastrebova J (2013) Occurrence, stability, and determination of formyl folates in foods. J Agric Food Chem 61(41):9758–9768. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4028427
Man X, Gao H, Yan L, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Han Y, Hou S (2020) Optimization of determination of folic acid in foxtail millet by HPLC. J China Agric Univ 12:11. https://doi.org/10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.12.12 (Chinese)
McNulty H, Ward M, Hoey L, Hughes CF, Pentieva K (2019) Addressing optimal folate and related B-vitamin status through the lifecycle: health impacts and challenges. Proc Nutr Soc 78(3):449–462. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665119000661
Mehrshahi P, Gonzalez-Jorge S, Akhtar TA, Ward JL, Santoyo-Castelazo A, Marcus SE, Lara-Núñez A et al (2010) Functional analysis of folate polyglutamylation and its essential role in plant metabolism and development. Plant J 64(2):267–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04336.x
Orsomando G, De La Garza RD, Green BJ, Peng M, Rea PA, Ryan TJ, Gregory JF et al (2005) Plant gamma-glutamyl hydrolases and folate polyglutamates: characterization, compartmentation, and co-occurrence in vacuoles. J Biol Chem 280(32):28877–28884. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M504306200
Ravanel S, Cherest H, Jabrin S, Grunwald D, Surdin-Kerjan Y, Douce R, Rébeillé F (2001) Tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis in plants: molecular and functional characterization of dihydrofolate synthetase and three isoforms of folylpolyglutamate synthetase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(26):15360–15365. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.261585098
Sachdev N, Goomer S, Singh LR (2021) Foxtail millet: a potential crop to meet future demand scenario for alternative sustainable protein. J Sci Food Agric 101(3):831–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10716
Sangshetti JN, Joshi SS, Patil RH, Moloney MG, Shinde DB (2017) Mur ligase inhibitors as anti-bacterials: a comprehensive review. Curr Pharm Des 23(21):3164–3196. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612823666170214115048
Scott J, Rebeille F, Fletcher J (2000) Folic acid and folates: the feasibility for nutritional enhancement in plant foods. J Sci Food Agric 80(7):795–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(20000515)
Shao L, Wang L (2014) Analysis of folic acid contents in main grain crops, fruits and vegetables. Food Sci 35(24):290–294. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201424056(Chinese)
Shao L, Wang L, Bai W, Liu Y (2014) Evaluation and analysis of folic acid content in millet from different ecological regions in Shanxi Province. Sci Agric Sin 47(07):1265–1272 (Chinese)
Srivastava AC, Ramos-Parra PA, Bedair M, Robledo-Hernández AL, Tang Y, Sumner LW, de la Díaz RI et al (2011a) The folylpolyglutamate synthetase plastidial isoform is required for postembryonic root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155(3):1237–1251. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.168278
Srivastava AC, Tang Y, De La Garza RI, Blancaflor EB (2011b) The plastidial folylpolyglutamate synthetase and root apical meristem maintenance. Plant Signal Behav 6(5):751–754. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.5.15403
Strobbe S, Van Der Straeten D (2017) Folate biofortification in food crops. Curr Opin Biotechnol 44:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.12.003
Wan X, Han LD, Yang M, Zhang HY, Zhang CY, Hu P (2019) Simultaneous extraction and determination of mono-/polyglutamyl folates using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its applications in starchy crops. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(13):2891–2904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01742-0
Wang L, Kong D, Lv Q, Niu G, Han T, Zhao X, Meng S et al (2017) Tetrahydrofolate Modulates floral transition through epigenetic silencing. Plant Physiol 174(2):1274–1284. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01750
Yang Z, Zhang H, Li X, Shen H, Gao J, Hou S, Zhang B et al (2020) A mini foxtail millet with an Arabidopsis-like life cycle as a C4 model system. Nat Plants 6(9):1167–1178. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-020-0747-7
Yu J, Qiu H, Liu X, Wang M, Gao Y, Chory J, Tao Y (2015) Characterization of tub4(P287L), a beta-tubulin mutant, revealed new aspects of microtubule regulation in shade. J Integr Plant Biol 57(9):757–769. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12363
Zhang G, Liu X, Quan Z, Cheng S, Xu X, Pan S, Xie M et al (2012) Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides insights into grass evolution and biofuel potential. Nat Biotechnol 30(6):549–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2195
Zhang Y, Wen C, Liu S, Zheng L, Shen B, Tao Y (2016) Shade avoidance 6 encodes an Arabidopsis flap endonuclease required for maintenance of genome integrity and development. Nucleic Acids Res 44(3):1271–1284. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1474
Acknowledgements
We thank Lida Han at the Laboratory of Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, for measuring the folate content.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number [32100316]), Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number [U21A20216]), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (Grant number [20210302123397]), National Key Research and Development Project (Grant number [2018YFD1000700/2018YFD1000706]), and Youth Fund Project on Application of Basic Research Project of Shanxi Province (Grant number [201901D211363]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yijuan Zhang and Siyu Hou designed the study and prepared the manuscript. Chongmei Zhang, Xiaxia Man, Lida Han, and Xuemei Ren performed the experiments. Yihan Men, Xueyin Li, and Yang Yang analyzed the data. Yuanhuai Han and Zhaoxia Sun supervised the study and modified the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declarations
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Ben Zhang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Man, X. et al. Functional characterization of the SiFPGS2 gene of foxtail millet in folate accumulation and root development. Plant Growth Regul 99, 137–147 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00904-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00904-y