Abstract
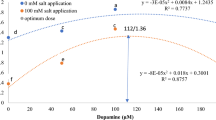
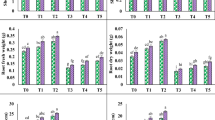
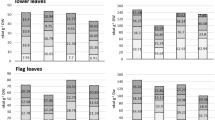
This research was an attempt to study the effects of exogenous cysteine (Cys) on early seedling growth, amylase activity, enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems, reactive oxygen species (ROS), oxidative stress parameters and DNA damage of germinating barley seeds under salt stress (125 mmol l−1 NaCl). Salt stress markedly reduced root elongation and coleoptile growth; these changes could be alleviated by Cys application. Amylase activity exhibited results parallel to early seedling growth. The observed salinity-mediated reduction in amylase activity was markedly impeded by Cys. Isozyme profile confirmed the mitigating effect of Cys on salt-induced amylase inhibition. ROS production was significantly elevated under salt stress. Changes in lipid peroxidation level and DNA damage coincided with high levels of ROS. However, Cys significantly reduced salt-induced ROS production and mitigated oxidative damage to membranes and genetic material. This mitigating effect of Cys was related to low level of ROS as a conclusion its own antioxidant properties rather than its effect on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants. We found that although Cys application resulted in different effects on antioxidant system in root and coleoptiles, it had partial reducing effect as compared to stressed seedlings in both organs (especially roots). These results were supported by the isozymes activity profiles. Despite the partial reduction determined in antioxidant system in Cys-applied seedlings, low ROS levels revealed that Cys decreases the need for activation of antioxidant system by acting as a ROS scavenger. The evidence from this study suggests that Cys alleviates salt-induced growth inhibition and suppresses oxidative damage in germinating barley seeds by modulating cellular redox status due to its own antioxidant property.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Pandey V (2004) Antioxidant enzyme responses to NaCl stress in Cassia angustifoli. Biol Plant 48:555–560
Aghaleh M, Niknam V, Ebrahimzadeh H, Razavi K (2011) Effect of salt stress on physiological and antioxidative responses in two species of Salicornia (S. persica and S. europaea). Acta Physiol Plant 33:1261–1270
Alvarez C, Bermudez MA, Romero LC, Gotor C, Garcıa I (2012) Cysteine homeostasis plays an essential role in plant immunity. New Phytol 193:165–177
Arora N, Bhardwaj R, Sharma P, Arora H (2008) Effects of 28-homobrassinolide on growth, lipid peroxidation and antioxidative enzyme activities in seedlings of Zea mays L. under salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 30(6):833–839
Bannai S (1984) Transport of cystine and cysteine in mammalian-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 779(3):289–306
Bates LS, Woldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–208
Beuchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Isozymes of superoxide dismutase from wheat germ. Biochim Biophys Acta 317:50–64
Bewley JD, Black M (1994) Seeds: physiology of development and germination, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York, p 445
Bozari S, Agar G, Aksakal O, Erturk FA, Yanmis D (2013) Determination of chemical composition and genotoxic effects of essential oil obtained from Nepeta nuda on Zea mays seedlings. Toxicol Ind Health 29(4):339–348
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cakmak T, Dumlupinar R, Erdal S (2010) Chilling resistance of Phaseolus vulgaris and Brassica oleracea under a high-intensity electric field. Z Naturforsch C 65:380–386
Cao Y, Zhang Z, Xue L, Du J, Shang J, Xu F, Yuan S, Lin H (2009) Lack of salicylic acid in Arabidopsis protects plants against moderate salt stress. Z Naturforsch C 64:231–238
de Oliveira-Neto OB, Damasceno AT, de Paiva Campos FA, Gomes-Filho E, Eneas-Filho J, Prisco JT (1998) Effect of NaCl-salinity on the expression of a cotyledonary α-amylase from Vigna unguiculata. Rev Bras Fisiol Veg 10(2):97–100
Dische Z (1962) Color reactions of carbohydrates. Methods Carbohydr Chem 1:475–514
Droux M (2004) Sulfur assimilation and the role of sulfur in plant metabolism: a survey. Photosynth Res 79:331–348
Egbichi I, Keyster M, Jacobs A, Klein A, Ludidi N (2013) Modulation of antioxidant enzyme activities and metabolites ratios by nitric oxide in short-term salt stressed soybean root nodules. S Afr J Bot 88:326–333
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammonium chloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620
Erdal S (2012a) Alleviation of salt stress in wheat seedlings by mammalian sex hormones. J Sci Food Agric 92:1411–1416
Erdal S (2012b) Androsterone-induced molecular and physiological changes in maize seedlings in response to chilling stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:1–7
Erdal S (2012c) Exogenous mammalian sex hormones mitigate inhibition in growth by enhancing antioxidant activity and synthesis reactions in germinating maize seeds under salt stress. J Sci Food Agric 92(4):839–843
Erdal S, Demirtas A (2010) Effects of cement flue dust from a cement factory on stress parameters and diversity of aquatic plants. Toxicol Ind Health 26(6):339–343
Erdal S, Dumlupinar R (2010) Progesterone and β-estradiol stimulate seed germination in chickpea by causing important changes in biochemical parameters. Z Naturforsch C 65:239–244
Erdal S, Dumlupinar R, Cakmak T, Genisel M (2009) Mammalian sex hormones influence germination velocity and enzyme activities in germinating maize seeds. Fresenius Environ Bull 19:1458–1465
Erdal S, Genisel M, Turk H, Gorcek Z (2012) Effects of progesterone application on antioxidant enzyme activities and K+/Na+ ratio in bean seeds exposed to salt stress. Toxicol Ind Health 28(10):942–946
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55(396):307–319
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976) The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133:21–25
Genisel M, Turk H, Erdal S (2013) Exogenous progesterone application protects chickpea seedlings against chilling-induced oxidative stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35(1):241–251
Havir EA, McHale NA (1987) Biochemical and development characterization of multiple forms of catalase in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol 84:450–455
Hiroko H, Katsuhiko S, Kohjun S, Shigeyuki N, Kazuo S (2000) Effects of zinc on the reactive oxygen species generating capacity of human neutrophils and on the serum opsonic activity in vitro. Luminescence 15(5):321–327
Hodges DM, Andrews CJ, Johnson DA, Hamilton RI (1996) Antioxidant compound responses to chilling stress in differentially sensitive inbred maize lines. Plant Physiol 98:685–692
Huang J, Redmann RE (1995) Salt tolerance of Hordeum and Brassica species during germination and early seedling growth. Can J Plant Sci 75(4):815–819
Idrees M, Naeem M, Aftab T, Khan MMA, Moinuddin (2010) Salicylic acid mitigates salinity stress by improving antioxidant defence system and enhances vincristine and vinblastine alkaloids production in periwinkle [Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don]. Acta Physiol Plant 33(3):987–999. doi:10.1007/s11738-010-0631-6
Imlay J (2003) Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:395–418
Iriti M, Castorina G, Picchi V, Faoro F, Gomarasca S (2009) Acute exposure of the aquatic macrophyte Callitriche obtusangula to the herbicide oxadiazon: the protective role of N-acetylcysteine. Chemosphere 74:1231–1237
Katsuhara M, Kawasaki T (1996) Salt stress induced nuclear and DNA degradation in meristematic cells of barley roots. Plant Cell Physiol 7(2):169–173
Klein SM, Cohen G, Cederbaum AI (1981) Production of formaldehyde during metabolism of dimethyl sulphoxide by hydroxyl radical generating system. Biochemistry 20:6002–6012
Laemmli DK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during in assembly of the heat of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680
Lee YB, Lee SM (2000) Effect of S-adenosylmethionine on hepatic injury from sequential cold and warm ischemia. Pharmacol Res 23:495–500
Liu G, Quiros C (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Mahmood T, Hameed T, Siddiqui NR, Mumtaz A, Safdar N, Masud T (2010) Effect of environmental changes on phytic acid content of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Pak J Nutr 9(5):447–451
Malanga G, Kozak RG, Puntarlo S (1999) N-Acetylcysteine-dependent protection against UV-B damage in two photosynthetic organism. Plant Sci 141:129–137
Meyer AJ, Hell R (2005) Glutathione homeostasis and redox-regulation by sulfhydryl groups. Photosynth Res 86:435–457
Mullineaux PM, Rausch T (2005) Glutathione, photosynthesis and the redox regulation of stress-responsive gene expression. Photosynth Res 86:459–474
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25(2):239–250
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nasri N, Kaddour R, Rabhi M, Plassard C, Lachaal M (2011) Effect of salinity on germination, phytase activity and phytate content in lettuce seedling. Acta Physiol Plant 33(3):935–942
Nelson WS, Prodohl PA, Avise JC (1996) Development and application of long-PCR for the assay of full-length animal mitochondria DNA. Mol Ecol 5:807–810
Rausch T, Wachter A (2005) Sulfur metabolism: a versatile platform for launching defence operations. Trends Plant Sci 10:503–509
Ruiz JM, Blumwald E (2002) Salinity-induced glutathione synthesis in Brassica napus. Planta 214:965–969
Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Agarwal S, Meen RC (2005) Differences in antioxidant activity in response to salinity stress in tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes. Biol Plant 49:85–91
Shah K, Nahakpam S (2012) Heat exposure alters the expression of SOD, POD, APX and CAT isozymes and mitigates low cadmium toxicity in seedlings of sensitive and tolerant rice cultivars. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:106–113
Shereen A, Ansari R, Raza S, Mumtaz S, Khan MA (2011) Salinity induced metabolic changes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds during germination. Pak J Bot 43(3):1659–1661
Smith P, Krohn R, Hermanson G, Mallia A, Gartner F, Provenzano M, Fujimoto E, Goeke N, Olson B, Klenk D (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Stanca AM, Crosatti C, Grossi M, Lacerenza NG, Rizza F, Cattivelli L (1996) Molecular adaptation of barley to cold and drought conditions. Euphytica 92(1–2):215–219
Sumithra K, Jutur PP, Carmel BD, Reddy AR (2006) Salinity-induced changes in two cultivars of Vigna radiata: responses of antioxidative and proline metabolism. Plant Growth Regul 50:11–22
Swaileh KM, Hussein R, Ezzughayyar A (2008) Evaluating wastewater-induced plant genotoxicity using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. Environ Toxicol 23:117–122
Turk H, Erdal S, Genisel M, Atici O, Demir Y, Yanmis D (2014) The regulatory effect of melatonin on physiological, biochemical and molecular parameters in cold-stressed wheat seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. doi:10.1007/s10725-014-9905-0
Valencia A, Bustillo AE, Ossa GA, Chrispeels MJ (2000) Alpha-amylases of the coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) and their inhibition by two plant amylase inhibitors. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30(3):207–213
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Werker E, Lerner HR, Weimberg R, Poljakoff-Mayber A (1983) Structural changes occurring in nuclei of barley root cells in response to a combined effect of salinity and ageing. Am J Bot 70:222–225
Wirtz M, Droux M (2005) Synthesis of the sulfur amino acids: cysteine and methionine. Photosynth Res 86:345–362
Woodbury W, Spencer A, Stahman M (1971) An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal Biochem 44(1):301–305
Wu T, Hsu Y, Lee T (2009) Effects of cadmium on the regulation of antioxidant enzyme activity, gene expression, and antioxidant defenses in the marine macroalga Ulva fasciata. Bot Stud 50:25–34
Yee Y, Tam NFY, Wong YS, Lu CY (2002) Growth and physiological responses of two mangrove species (Bruguira gymnorrhiza and Kandelia candel) to waterlogging. Environ Exp Bot 49:209–221
Zagorchev L, Seal CE, Kranner I, Odjakova M (2013) A central role for thiols in plant tolerance to abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 14:7405–7432
Zhu J (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Derya Yanmis for her help in determination of RAPD profile.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Genisel, M., Erdal, S. & Kizilkaya, M. The mitigating effect of cysteine on growth inhibition in salt-stressed barley seeds is related to its own reducing capacity rather than its effects on antioxidant system. Plant Growth Regul 75, 187–197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9943-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9943-7