Abstract
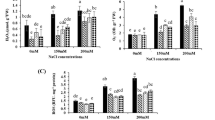
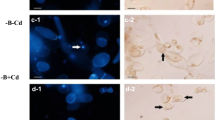
Programmed cell death (PCD) is an active cellular suicide that occurs both in animals and plants throughout development and in response to abiotic or biotic stress. In contrast to plant hypersensitive response-like cell death, little is known about the molecular machinery that regulates the halophyte plant PCD under high salinity stress. Since mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are involved in plant response/tolerance to salt stress, and plant MAPK genes belong to the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) subfamily, we have investigated the role of ERK-like enzymes in high salinity stress-induced cell death in Thellungiella halophila. The data showed that ERK-like enzymes were early (10 min) and transiently activated under 300 mM NaCl stress. Pretreatment with 10 μM U0126, a special MEK/ERK inhibitor, resulted in a small but statistically significant increase of the percentage of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL)-positive nuclei in contrast to salt alone. The effects of U0126 on H2O2 production and cytochrome c (cyt c) release were also investigated. We found that the pretreatment with U0126 accelerated H2O2 production as well as cyt c release, and eventually enhanced cell death. The results suggest that ERK-like enzymes in Thellungiella halophila may act as a positive regulator of salt tolerance, as illustrated by pretreatment with U0126 which enhanced cell death under high salinity stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlfors R, Macioszek V, Rudd J, Brosché M, Schlichting R, Scheel D, Kangasjärvi J (2004) Stress hormone-independent activation and nuclear translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana during ozone exposure. Plant J 40:512–522
Amtmann A, Bohnert HJ, Bressan RA (2005) Abiotic stress and plant genome evolution. Search for new models. Plant Physiol 138:127–130
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983
Ashraf M (1999) Breeding for salinity tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 13:17–42
Balk J, Leaver CJ, McCabe PF (1999) Translocation of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytosol occurs during heat-induced programmed cell death in cucumber plants. FEBS Lett 463:151–154
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bressan RA, Zhang C, Zhang H, Hasegawa PM, Bohnert HJ, Zhu JK (2001) Learning from the Arabidopsis experience: the next gene search paradigm. Plant Physiol 127:1354–1360
Casolo V, Petrussa E, Krajnáková J, Macrì F, Vianello A (2005) Involvement of the mitochondrial K(+)ATP channel in H2O2- or NO-induced programmed death of soybean suspension cell cultures. J Exp Bot 56:997–1006
Chen PY, Lee KT, Chi WC, Hirt H, Chang CC, Huang HJ (2008) Possible involvement of MAP kinase pathways in acquired metal-tolerance induced by heat in plants. Planta 228:499–509
Chinnusamy V, Zhu JK (2003) Plant salt tolerance. In: Hirt H, Shinozaki K (eds) Plant responses to abiotic stress, vol 4. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp 241–270
Chinnusamy V, Schumaker K, Zhu JK (2004) Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signalling in plants. J Exp Bot 55:225–236
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signaling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM (2000) Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256:34–41
de Pinto MC, Francis D, De Gara L (1999) The redox state of the ascorbate-dehydroascorbate pair as a specific sensor of cell division in tobacco BY-2 cells. Protoplasma 209:90–97
de Pinto MC, Paradiso A, Leonetti P, De Gara L (2006) Hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide and cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase at the crossroad between defence and cell death. Plant J 48:784–795
Desikan R, Clarke A, Hancock JT, Neill SJ (1999) H2O2 activates a MAP kinase-like enzyme in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cultures. J Exp Bot 50:1863–1866
Doyle SM, Diamond M, McCabe PF (2010) Chloroplast and reactive oxygen species involvement in apoptotic-like programmed cell death in Arabidopsis suspension cultures. J Exp Bot 61:473–482
Droillard M, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions: involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527:43–50
Horbinski C, Chu CT (2005) Kinase signaling cascades in the mitochondrion: a matter of life or death. Free Radic Biol Med 38:2–11
Huang Y, Li H, Gupta R, Morris PC, Luan S, Kieber JJ (2000) ATMPK4, an Arabidopsis homolog of mitogen-activated protein kinase, is activated in vitro by AtMEK1 through threonine phosphorylation. Plant Physiol 122:1301–1310
Huang L, Li B, Li W, Guo H, Zou F (2009) ATP-sensitive potassium channels control glioma cells proliferation by regulating ERK activity. Carcinogenesis 30:737–744
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Morris P, Giraudat J, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K (1998) Isolation of ATMEKK1 (a MAP kinase kinase kinase)-interacting proteins and analysis of a MAP kinase cascade in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 253:532–543
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Yuasa T, Shinozaki K (2000) Various abiotic stresses rapidly activate Arabidopsis MAP kinases ATMPK4 and ATMPK6. Plant J 24:655–665
Inan G, Zhang Q, Li P, Wang Z, Cao Z, Zhang H, Zhang C, Quist TM, Goodwin SM, Zhu J, Shi H, Damsz B, Charbaji T, Gong Q, Ma S, Fredricksen M, Galbraith DW, Jenks MA, Rhodes D, Hasegawa PM, Bohnert HJ, Joly RJ, Bressan RA, Zhu JK (2004) Salt cress: a halophyte and cryophyte Arabidopsis relative model system and its applicability to molecular genetic analyses of growth and development of extremophiles. Plant Physiol 135:1718–1737
Kim M, Ahn JW, Jin UH, Choi D, Paek KH, Pai HS (2003) Activation of the programmed cell death pathway by inhibition of proteasome function in plants. J Biol Chem 278:19406–19415
Kovtun Y, Chiu WL, Tena G, Sheen J (2000) Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2940–2945
Kroj T, Rudd JJ, Nürnberger T, Gäbler Y, Lee J, Scheel D (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinases play an essential role in oxidative burst-independent expression of pathogenesis-related genes in parsley. J Biol Chem 278:2256–2264
Laloi C, Apel K, Danon A (2004) Reactive oxygen signalling: the latest news. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:323–328
Lee J, Klessig DF, Nürnberger T (2001) A harpin binding site in tobacco plasma membranes mediates activation of the pathogenesis-related gene HIN1 independent of extracellular calcium but dependent on mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Plant Cell 13:1079–1093
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon R, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79:583–593
Lew RR, Levina NN, Shabala L, Anderca MI, Shabala SN (2006) Role of a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in ion flux-mediated turgor regulation in fungi. Eukaryot Cell 5:480–487
Li S, Šamaj J, Franklin-Tong VE (2007) A mitogen-activated protein kinase signals to programmed cell death induced by self-incompatibility in Papaver Pollen. Plant Physiol 145:236–245
Lin J, Wang Y, Wang G (2006) Salt stress-induced programmed cell death in tobacco protoplasts is mediated by reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial permeability transition pore status. J Plant Physiol 163:731–739
Liu Y, Ren D, Pike S, Pallardy S, Gassmann W, Zhang S (2007) Chloroplast-generated reactive oxygen species are involved in hypersensitive response-like cell death mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Plant J 51:941–954
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
MAPK Group (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Hirayama T, Hayashida N, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K (1996) A gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is induced simultaneously with genes for a mitogen-activated protein kinase and an S6 ribosomal protein kinase by touch, cold, and water stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:765–769
Mlejnek P, Procházka S (2002) Activation of caspase-like proteases and induction of apoptosis by isopentenyladenosine in tobacco BY-2 cells. Planta 215:158–166
Moon H, Lee B, Choi G, Shin D, Prasad DT, Lee O, Kwak SS, Kim DH, Nam J, Bahk J, Hong JC, Lee SY, Cho MJ, Lim CO, Yun DJ (2003) NDP kinase 2 interacts with two oxidative stress-activated MAPKs to regulate cellular redox state and enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:358–363
Morris PC (2001) MAP kinase signal transduction pathways in plants. New Phytol 151:67–89
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Pedley KF, Martin GB (2005) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:541–547
Petersen M, Brodersen P, Naested H, Andreasson E, Lindhart U, Johansen B, Nielsen HB, Lacy M, Austin MJ, Parker JE, Sharma SB, Klessig DF, Martienssen R, Mattsson O, Jensen AB, Mundy J (2000) Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 negatively regulates systemic acquired resistance. Cell 103:1111–1120
Pitzschke A, Djamei A, Bitton F, Hirt H (2009a) A major role of the MEKK1–MKK1/2–MPK4 pathway in ROS signalling. Mol Plant 2:120–137
Pitzschke A, Schikora A, Hirt H (2009b) MAPK cascade signalling networks in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:421–426
Raman M, Cobb MH (2003) MAP kinase modules: many roads home. Curr Biol 13:R886–R888
Ren D, Yang KY, Li GJ, Liu Y, Zhang S (2006) Activation of Ntf4, a tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase, during plant defense response and its involvement in hypersensitive response-like cell death. Plant Physiol 141:1482–1493
Rudd JJ, Keon J, Hammond-Kosack KE (2008) The wheat mitogen-activated protein kinases TaMPK3 and TaMPK6 are differentially regulated at multiple levels during compatible disease interactions with Mycosphaerella graminicola. Plant Physiol 147:802–815
Schwacke R, Hager A (1992) Fungal elicitors induce a transient release of active oxygen species from cultured spruce cells that are dependent on Ca2+ and protein-kinase activity. Planta 187:136–141
Shabala S (2003) Regulation of potassium transport in leaves: from molecular to tissue level. Ann Bot 92:627–634
Shabala S (2009) Salinity and programmed cell death: unravelling mechanisms for ion specific signaling. J Exp Bot 60:709–712
Shabala S, Cuin TA (2008) Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. Physiol Plant 133:651–669
Shabala S, Cuin TA, Prismall L, Nemchinov LG (2007) Expression of animal CED-9 anti-apoptotic gene in tobacco modifies plasma membrane ion fluxes in response to salinity and oxidative stress. Planta 227:189–197
Taji T, Seki M, Satou M, Sakurai T, Kobayashi M, Ishiyama K, Narusaka Y, Narusaka M, Zhu JK, Shinozaki K (2004) Comparative genomics in salt tolerance between Arabidopsis and Arabidopsis-related halophyte salt cress using Arabidopsis microarray. Plant Physiol 135:1697–1709
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Doczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Dangl JL, Hirt H (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Tena G, Asai T, Chiu WL, Sheen J (2001) Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:392–400
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Vacca RA, de Pinto MC, Valenti D, Passarella S, Marra E, De Gara L (2004) Production of reactive oxygen species, alteration of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase, and impairment of mitochondrial metabolism are early events in heat shock-induced programmed cell death in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells. Plant Physiol 134:1100–1112
Vacca RA, Valenti D, Bobba A, Merafina RS, Passarella S, Marra E (2006) Cytochrome c is released in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner and is degraded via caspase-like proteases in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells en route to heat shock-induced cell death. Plant Physiol 141:208–219
Van Breusegem F, Dat JF (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol 141:384–390
Vaux DL, Strasser A (1996) The molecular biology of apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2239–2244
Wang J, Li X, Liu Y, Zhao X (2010) Salt stress induces programmed cell death in Thellungiella halophila suspension-cultured cells. J Plant Physiol 167:1145–1151
Xie Z, Chen Z (2000) Harpin-induced hypersensitive cell death is associated with altered mitochondrial functions in tobacco cells. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:183–190
Yang KY, Liu Y, Zhang S (2001) Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:741–746
Zhang S, Klessig DF (2001) MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling. Trends Plant Sci 6:520–527
Zhang S, Liu Y, Klessig DF (2000) Multiple levels of tobacco WIPK activation during the induction of cell death by fungal elicitins. Plant J 23:339–347
Zhang T, Liu Y, Yang T, Zhang L, Xu S, Xue L, An L (2006) Diverse signals converge at MAPK cascades in plant. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:274–283
Zhao X, Kim Y, Park G, Xu JR (2005) A mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade regulating infection-related morphogenesis in Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 17:1317–1329
Zhu JK (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948
Zhu J, Fu X, Koo YD, Zhu JK, Jenney FE Jr, Adams MWW, Zhu Y, Shi H, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (2007) An enhancer mutant of Arabidopsis salt overly sensitive 3 mediates both ion homeostasis and the oxidative stress response. Mol Cell Biol 27:5214–5224
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 40825001 and 30870425). The authors are grateful to Rui Li from the School of Basic Medical Sciences of Lanzhou University for his help with the TUNEL assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, X., Liu, Y. et al. MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126 enhanced salt stress-induced programmed cell death in Thellungiella halophila suspension-cultured cells. Plant Growth Regul 63, 207–216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9517-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9517-2