Abstract
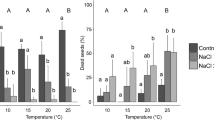
We tested the effects of cold stratification, temperature, light and NaCl on seed germination and germination recovery and of NaCl on radicle growth and radicle elongation recovery of Kalidium caspicum, a small leafy succulent shrub dominant in saline deserts in northwest China. In all conditions of temperature and light/darkness, germination percentages and rates of cold-stratified seeds were significantly higher than those of nonstratified seeds. Germination of a high percentage of both nonstratified and stratified seeds was inhibited by 0.2 M NaCl, and 0.6 M NaCl completely inhibited germination. Nongerminated seeds germinated after they were transferred from NaCl solutions to distilled water. Radicle elongation significantly decreased with increase in salinity, and it was completely inhibited by ≥1.0 M NaCl; radicle elongation recovered in young seedlings pretreated by 10 days of incubation in ≤0.4 M NaCl. Results show that seed germination and early seedling growth of K. caspicum are salt tolerant, and these characteristics help explain why this species can survive and dominate salt habitats, such as those in the Junggar desert in Xinjiang, northwest China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskin C, Baskin J (1998) Seeds: ecology, biogeography, and evolution of dormancy and germination. Academic Press, San Diego
Baskin C, Baskin J (2004a) Germinating seeds of wildflowers, an ecological perspective. Horttechnology 14:467–473
Baskin J, Baskin C (2004b) A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Sci Res 14:1–16
Bewley J, Black M (1982) Physiology and biochemistry of seeds in relation to germination. Volume 2. Viability, dormancy and environmental control. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Côme D (1982) Germination. In: Mazliak P (ed) Croıssance et développement. Physiologie Végétale. II. Hermann, Paris, pp 129–225
Fan Z, Chang Q, Tian C, Yabuki S, Okada A, Liu C (1993) Genesis and characteristics of salt-affected soils in Tarim Basin. In: Proceedings of the Japan–China international symposium on the study of the mechanism of desertification. Science and Technology Agency, Tokyo, pp 219–226
Huang Z, Dong M, Gutterman Y (2004a) Caryopses dormancy, germination and seedling emergence in sand, of Leymus racemosus (Poaceae), a perennial sand dune grass inhabiting the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, China. Aust J Bot 52:519–528
Huang Z, Dong M, Gutterman Y (2004b) Factors influencing seed dormancy and germination in sand, and seedling survival under desiccation, of Psammochloa villosa (Poaceae), inhabiting the moving sand dunes of Ordos, China. Plant Soil 259:231–241
Khan M, Ungar I (1984) Seed polymorphism and germination responses to salinity stress in Atriplex triangularis Willd. Bot Gaz 145:487–494
Kitajima K, Fenner M (2000) Ecology of seedling regeneration. In: Fenner M (ed) Seeds: the ecology of regeneration in plant communities, 2nd edn. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK, pp 331–359
Leadem C (1986) Stratification of Abies amabilis seeds. Can J For Res 16:755–760
Li L, Zhang X (2007) Effect of temperature and salinity on germination of two Kalidium species (Chenopodiaceae). Chin J Appl Environ Biol 13:317–321
Li S (1990) Natural conditions and the establishment basis of Fukang ecosystematic observation and experiment station of Chinese Academy of Science. Arid Zone Res 7:3–4 (in Chinese)
Liu Y (1985) Flora in Desertis Reipublicae Popularum Sinarum, vol 1. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Martin A (1946) The comparative internal morphology of seeds. Am Midl Nat 36:513–660
Philipupillai J, Ungar I (1984) The effect of seed dimorphism on the germination and survival of Salicornia europaea L. populations. Am J Bot 71:542–549
Qu X (2006) Adaptive strategies of the three halophytic species in Xinjiang in their seed germination and early seedling growth stage. M.S. thesis, Laboratory of Quantitative Vegetation Ecology, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Qu X, Huang Z, Baskin J, Baskin C (2007) Effect of temperature, light and salinity on seed germination and radicle growth of the geographically widespread halophyte shrub Halocnemum strobilaceum. Ann Bot. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm047
Shen Y, Guo L, Yan S (2003) Effects of salinity on germination of six salt-tolerant forage species and their recovery from saline conditions. N Z J Agric 46:263–269
Sokal R, Rohlf E (1995) Biometry, 3rd edn. Freeman, San Francisco, CA
Song J, Feng G, Zhang F (2006) Salinity and temperature effects on germination for three salt-resistant euhalophytes, Halostachys caspica, Kalidium foliatum and Halocnemum strobilaceum. Plant Soil 279:201–207
Thanos C, Skordillis A (1987) The effects of light, temperature and osmotic stress on the germination of Pinus halepensis and P. brutia seeds. Seed Sci Technol 15:163–174
Tobe K, Li X, Omasa K (2000) Seed germination and radicle growth of a halophyte, Kalidium caspicum (Chenopodiaceae). Ann Bot 85:391–396
Tobe K, Li X, Omasa K (2002) Effects of sodium, magnesium and calcium salts on seed germination and radicle survival of a halophyte, Kalidium caspicum (Chenopodiaceae). Aust J Bot 50:163–169
Ungar I (1984) Alleviation of seed dormancy in Spergularia marina. Bot Gaz 145:33–36
Ungar I (1995) Seed germination and seed-bank ecology in halophytes. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed development and germination. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 599–628
Ungar I, Binet P (1975) Factors influencing seed dormancy in Spergularia media (L.). C Presl. Aquat Bot 1:45–55
Zeng Y, Cai Z, Ma J, Zhang F, Wang B (2006) Effects of salt and water stress on seed germination of halophytes Kalidium foliatum and Halostachys caspica. Chin J Ecol 25:1014–1018 (in Chinese with English summary)
Zhang L, Hai Y (2002) Plant communities excluded from the book “The Vegetation and its Utilization in Xinjiang”. Arid Land Geogr 25:84–89 (in Chinese with English summary)
Zhao C, Song Y, Wang Y, Jiang P (2004) Analysis on the dynamics of desert-oasis vegetation in the Sangong River Basin. Chin J Appl Ecol 15:249–254 (in Chinese with English summary)
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-431), the National Natural Science Foundation (30570281), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of P.R. China (2005DKA21006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, X., Baskin, J.M., Wang, L. et al. Effects of cold stratification, temperature, light and salinity on seed germination and radicle growth of the desert halophyte shrub, Kalidium caspicum (Chenopodiaceae). Plant Growth Regul 54, 241–248 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-007-9246-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-007-9246-3