Abstract
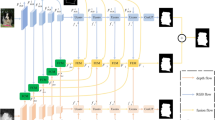
Recently, the pair of RGB images and depth images, which is denoted as RGB-D images, are introduced to improve the performances of salient object detection, because one of the pairs may stand out at least in one modality. However, most existing methods still suffer from dilemma. Firstly, the edges of predicted salient object are blurry. Secondly, how to integrate RGB images and depth images effectively still needs be explored. Thirdly, the quality of depth images have a strong impact on the performance of salient object detection so that the selection of depth images is worthy of exploring. To address above problems, we propose an edge-inspired depth quality evaluation network, which evaluates the quality of the depth images based on the edge information. More specifically, the depth quality evaluation module includes two parts: the depth decider and the depth aggregator. The former judges the quality of the depth images while the latter produces the weighted depth features. Then, the edge detection module is proposed to predict edges of salient object and produce edge features. In addition, features from VGG backbone, edge features and depth features are integrated by multi-modality feature fusion module, which is composed of a series of hybrid dilated convolutions. Moreover, the integrated features are fused by three-feature interactive module and double-feature interactive module to predict the final salient map. Our experiments on four RGB-D datasets demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms previous high-performance RGB-D salient object detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The author will open source the data free of charge if needed.
References
Wang, L., Lu, L., Wang, Y., et al.: Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE (2017)
Li, Q., Yue, Z., Jie, Y.: Saliency based image segmentation. 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology. (2011)
Qin, C., Zhang, G., Zhou, Y., et al: Integration of the saliency-based seed extraction and random walks for image segmentation. Neurocomputing. 129:378–391 (2014)
Guo, C.L., Zhang, L.M.: A novel multi resolution spatio-temporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(1), 185–198 (2010)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Girshick, B., McAllester, D.: Ramanan D: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1627–1645 (2010)
Goldberg, C., Chen, T., Zhang, F.L., Shamir, A., Hu, S.M.: Data-driven object manipulation in images. Computer Graphics Forum. 31(2, pt1), 265–274 (2012)
Chia, Y.S., Zhuo, S., Gupta, R.K., et al: Semantic colorization with internet images. Siggraph Asia Conference. ACM. p.156.1–156.7 (2011)
Ren, Z., Gao, S., Chia, L., et al.: Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology. 24(5):769–779 (2014)
Cheng, M.M., Hou, Q., Zhang, S., Rosin, P.L.: Intelligent visual media processing: When graphics meets vision. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 32(1), 110–121 (2017)
Hong, S., You, T., Kwak, S., Han, B.: Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network. International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 597–606 (2015)
Mahadevan, V., Vasconcelos, N.: Saliency based discriminant tracking. Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL (2009)
Huang, H., Zhang, L., et al: Arcimboldo-like collage using internet images. TOG. 30(6):1–1 (2011)
Margolin, R., Zelnik-Manor, L.: Tal A: Saliency for image manipulation. Vis. Comput. 29(5), 381–392 (2013)
Fan, D.P., Wang, W., Cheng, M.M., Shen, J.: Shifting more attention to video salient object detection. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 8554–8564 (2019)
Yan, P., Li, G., Xie, Y., Li, Z., Wang, C., Chen, T., Lin, L.: Semisupervised video salient object detection using pseudo-labels. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 7284–7293 (2019)
Jiang, H., Wang, J., Yuan, Z., Wu, Y., Zheng, N., Li, S.: Salient object detection: A discriminative regional feature integration approach. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 2083–2090 (2013)
Yan, Q., Xu, L., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Hierarchical saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 1155–1162 (2013)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach. IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
LaLonde, R., Bagci, U.: Capsules for object segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.04241 (2018)
Ma, D.,Wu, X.: CapsuleRRT: Relationships-aware regression tracking via capsules. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 10948–10957 (2021)
Zhang, J., Yu, X., Li, A., Song, P., Liu, B., Dai, Y.: Weakly-supervised salient object detection via scribble annotations. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 12546–12555 (2020)
Liu, J. J., Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Feng, J., Jiang, J.: A Simple Pooling-Based Design for Real-Time Salient Object Detection. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA. pp. 3912–3921. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00404.
Wu, Z., Su, L., Huang, Q.: Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3907–3916 (2019)
Liu, N., Han, J., Yang, M.H.: PiCANet: Pixel-wise contextual attention learning for accurate saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 6438–6451 (2020)
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.H.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3203–3212 (2017)
Qu, L., He, S., Zhang, J., Tian, J., Tang, Y., Yang, Q.: RGBD salient object detection via deep fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(5), 2274–2285 (2017)
Zhang, J., Fan, D.P., Dai, Y., Anwar, S., Saleh, F.S., Zhang, T., Barnes, N.: UC-Net: Uncertainty inspired RGB-D saliency detection via conditional variational autoencoders. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 8582–8591 (2020)
Han, J., Chen, H., Liu, N., Yan, C., Li, X.: CNNs-based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(11), 3171–3183 (2017)
Liang, F., Duan, L., Ma, W., Qiao, Y., Cai, Z., Qing, L.: Stereoscopic saliency model using contrast and depth-guided-background prior. Neurocomputing 275, 2227–2238 (2018)
Zhu, C., Cai, X., Huang, K., Li, T.H., Li, G.: PDNet: Prior-model guided depth-enhanced network for salient object detection. IEEE International conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp. 199–204. (2019)
Chen, H., Li, Y.: Progressively complementary-aware fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3051–3060 (2018)
Zhao, J.X., Cao, Y., Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., Li, X.Y., Zhang, L.: Contrast prior and fluid pyramid integration for RGBD salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3927–3936 (2019)
Wang, T., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Lu, H., Yang, G., Ruan, X., Borji, A: Detect globally, refine locally: A novel approach to saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3127–3135 (2018)
Feng, M., Lu, H., Ding, E.:Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition ,pp. 1623–1632 (2019)
Zhao, J.X., Liu, J.J., Fan, D.P., Cao, Y., Yang, J., Cheng, M.M.: EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. pp. 8779–8788 (2019)
Fan, D.P., Lin, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhu, M., Cheng, M.M.: Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: Models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(5), 2075–2089 (2020)
Wang, N., Gong, X.: Adaptive fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Access 7, 55277–55284 (2019)
Chen, H., Li, Y.: Three-stream attention-aware network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(6), 2825–2835 (2019)
Kun, X., Jichang, G.: A Boundary-Aware Multi-Source Feature Network for Salient Object Detection. Neural Comput Appl. (2023).
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556. (2014)
Er-Sen, L., Shu-Long, Z., Bao-shan, Z., Yong, Z., Chao-gui, X., Li-hua, S.: An adaptive edge-detection method based on the canny operator. Int. Conf. Environ. Sci. Inf. Appl. Technol. 1, 465–469 (2009)
Fu, K., Fan, D.P., Ji, G.P., Zhao, Q.: JL-DCF: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for RGB-D salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3052–3062 (2020)
Li, G., Liu, Z., Ye, L., Wang, Y., Ling, H.: Cross-modal weighting network for RGB-D salient object detection. Proceedings of Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK. Springer International Publishing, Part XVII 16, pp. 665–681 (2020)
Fan, D.P., Zhai, Y., Borji, A., Yang, J., Shao, L.: BBS-Net: RGB-D salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK,, Proceedings. Springer International Publishing Part XII , pp. 275–292.(2020)
Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Pang, Y., Lu, H., Zhang, L.: A single stream network for robust and real-time RGB-D salient object detection. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK Proceedings. Springer International Publishing Part XXII 16, pp. 646–662 (2020)
Guan, W., Wang, T., Qi, J., Zhang, L., Lu, H.: Edge-aware convolution neural network based salient object detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(1), 114–118 (2018)
Xie, S., Tu, Z.: Holistically-nested edge detection. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 1395–1403 (2015)
Yunzhi, Z., Gang, Y., Pingping, Z., Huchuan, L.: Edge-guided feature aggregation network for salient object detection. IEEE SPL 25(12), 1800–1804 (2018)
Luo, Z., Mishra, A., Achkar, A., Eichel, J., Li, S., Jodoin, P.M.: Non-local deep features for salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 6609–6617 (2017)
Zhang, M., Ren,W., Piao, Y., Rong, Z., Lu, H.:Select, supplement and focus for RGB-D saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3472–3481 (2020)
Cong, R., Lei, J., Zhang, C., Huang, Q., Cao, X., Hou, C.: Saliency detection for stereoscopic images based on depth confidence analysis and multiple cues fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(6), 819–823 (2016)
Mittal, A., Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, C.: No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(12), 4695–4708 (2012)
Wang, X., Li, S., Chen, C., Hao, A., Qin, H.: Depth quality-aware selective saliency fusion for RGB-D image salient object detection. Neurocomputing 432, 44–56 (2021)
Chen, C., Wei, J., Peng, C., Qin, H.: Depth-quality-aware salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2350–2363 (2021)
Zhang, W., Ji, G.P., Wang, Z., Fu, K., Zhao, Q.: Depth quality-inspired feature manipulation for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. Proceedings of the 29th ACM international conference on multimedia. pp. 731–740(2021)
Chen, Z., Xu, Q., Cong, R., Huang, Q.: Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell. 34(07), 10599–10606 (2020)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV) . pp. 565–571 (2016)
Chen, X., Zheng, A., Li, J., Lu, F.: Look, perceive and segment: Finding the salient objects in images via two-stream fixation-semantic cnns. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 1050–1058 (2017)
Tao, D., Cheng, J., Song, M., Lin, X.: Manifold ranking-based matrix factorization for saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(6), 1122–1134 (2015)
Wang, A., Wang, M.: RGB-D salient object detection via minimum barrier distance transform and saliency fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(5), 663–667 (2017)
Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., Liu, Y., Li, T., Borji, A.: Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision., pp. 4548–4557 (2017)
Fan, D.P., Gong, C., Cao, Y., Ren, B., Cheng, M.M., Borji, A.: Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.10421 (2018)
Chen, H., Li, Y., Su, D.: Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-D salient object detection. Pattern Recognition, 86, pp.376–385(2019)
Piao, Y., Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., Lu, H.: Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on Computer Vision , pp. 7254–7263(2019)
Liu, N., Zhang, N., Han, J.: Learning selective self-mutual attention for RGB-D saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 13756–13765 (2020)
Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., Piao, Y., Lu, H.:Accurate RGB-D salient object detection via collaborative learning. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, Proceedings, Part XVIII 16, pp. 52–69. Springer International Publishing (2020)
Li, C., Cong, R., Piao, Y., Xu, Q., Loy, C.C.: RGB-D salient object detection with cross-modality modulation and selection. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, Proceedings, Part VIII 16 , pp. 225–241. Springer International Publishing (2020)
Piao, Y., Rong, Z., Zhang, M., Ren, W., Lu, H.: A2dele: Adaptive and attentive depth distiller for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 9060–9069 (2020)
Chen, S., Fu, Y.: Progressively guided alternate refinement network for RGB-D salient object detection. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, Proceedings, Part VIII 16 ,pp. 520–538.Springer International Publishing (2020)
Yoosefdoost, I., Basirifard, M.: Álvarez-García J: Reservoir Operation Management with New Multi-Objective (MOEPO) and Metaheuristic (EPO) Algorithms. Water 14, 2329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152329
Sheikhpour, R., Berahmand, K., Forouzandeh, S.: Hessian-based semi-supervised feature selection using generalized uncorrelated constraint. Knowl.-Based Syst. 269, 110521 (2023)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the people who contributed to this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China. (No.62171315).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
First of all, Jichang Guo and Kun Xu find the idea of evaluating the quality of depth images by using the edge information and design the whole architecture, together. In addition, Kun Xu writes the main manuscript text and accomplishes the network by using pytorch. Finally, Jichang Guo review and revise papers and experimental results. The Kun Xu is a PhD candidate and the Jichang Guo is a professor and the doctoral supervisor for Kun Xu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors have strictly adhered to ethical standards and are dedicated to scientific research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Guo, J. A Novel Edge-Inspired Depth Quality Evaluation Network for RGB-D Salient Object Detection. J Grid Computing 21, 38 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09674-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09674-x