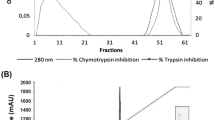
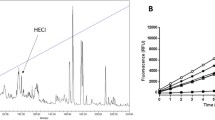
Abstract
The primary structure of the double-headed Bowman-Birk inhibitor (BBI) family and the antitryptic activity were investigated in cultivated and wild Phaseolus species. Two BBI types were identified; the first one inhibits trypsin and chymotrypsin (tc-BBI), the second one elastase and trypsin (et-BBI). Only tc-BBI was found in P. lunatus and P. parvulus, while none of BBI types, identified in this study, was found in P. leptostachyus. The deduced amino acid sequences revealed some polymorphisms within both tc-BBI and et-BBI binding loops that could affect the inhibitory activity. The trypsin inhibitor content showed a high variation with the lowest value recorded in P. lepthostachyus and the highest one observed in P. oligospermus. Southern blot analysis confirmed the absence of both BBI types in P. leptostachyus and suggests that in P. coccineus, P. dumosus and P. costaricensis, the two genes were clustered in a narrow genomic region of 1.3 kbp.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong WB, Wan XS, Kennedy AR, Taylor TH (2003) Development of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor for oral cancer chemoprevention and analysis of Neu immunohistochemical staining intensity with Bowman-Birk inhibitor concentrate treatment. Laryngoscope 113:1687–1702
Birk Y, Gertler A, Khalef S (1963) Heat inactivation of trypsin inhibitor from soybeans. Biochem J 87:281–284
Brauer ABE, Kelly G, Matthews SJ, Leatherbarrow RJ (2002) The H1 NMR solution structure of the antitryptic core peptide of Bowman-Birk inhibitor proteins: a minimal ‘Canonical loop’. J Biomol Struct Dyn 20:59–70
Campos JE, Whitaker JR, Yip TT, Hutchens TW, Blanco-Labra A (2004) Unusual structural characteristics and complete amino acid sequence of a protease inhibitor from Phaseolus acutifolius seeds. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:209–214. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2003.12.002
Carlini CR, Grossi-de-Sa MF (2002) Plant toxic proteins with insecticidal properties. A review on their potentialities as bioinsecticides. Toxicon 40:1515–1539
De Azevedo Pereira R, Valencia-Jiménez A, Picanço Magalhães C et al (2007) Effect of a Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor from Phaseolus coccineus on Hypothenemus hampei gut proteinases in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 55:10714–19719. doi:10.1021/jf072155x
Debouck DG (2000) Biodiversity, ecology and genetic resources of Phaseolus beans—seven answered and unanswered questions. In: Prooc 7th MAFF Int Workshop Genet Resour Part 1 Wild Legumes AFFRC et NIAR, Japan
Delgado-Salinas A, Turley T, Richman A, Lavin M (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of the cultivated and wild species of Phaseolus (Fabaceae). Syst Bot 24:438–460
Delgado-Salinas A, Bibler R, Lavin M (2006) Phylogeny of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae): a recent diversification in an ancient landscape. Syst Bot 31:779–791
Della Gatta C, Piergiovanni AR, Perrino P (1988) An improved method for the determination of trypsin inhibitor level in legumes. Lebensm Wiss Technol 21:315–318
Domoney C, Welham T, Sidebottom C, Firmin JL (1995) Multiple isoforms of Pisum trypsin inhibitors result from modification of two primary gene products. FEBS Letters 360:15–20
Freytag GF, Debouck DG (2002) Taxonomy, distribution, and ecology of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae-Papilionoideae) in North America, Mexico and Central America. SIDA, Botanical Miscellany 23 (1–300)
Galasso I, Piergiovanni AR, Lioi L, Campion B, Bollini R, Sparvoli F (2009) Bowman-Birk inhibitors in common bean. Mol Breeding 23:617–624
Gariani T, McBride JD, Leatherbarrow RJ (1999) The role of the P2′ position of Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor in the inhibition of trypsin. Studies on P2′ variation in cyclic peptides encompassing the reactive site loop. Biochem Biophys Acta 1431:232–237
Jacobsen BK, Knutsen SF, Fraser GE (1998) Does high soy milk intake reduce prostate cancer incidence? The Adventist Health Study (United States). Cancer Causes Control 9:553–557
Kennedy AR, Billings PC, Wan XS, Wan PM (2002) Effects of Bowman-Birk inhibitor on rat colon carcinogesesis. Nutr Cancer 43:174–186
Laskowski M, Kato I (1980) Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem 49:593–626
Lioi L, Galasso I, Lanave C, Daminati MG, Bollini R, Sparvoli F (2007) Evolutionary analysis of the APA genes in the Phaseolus genus: wild beans as source of lectin-related resistance factors? Theor App Genet 115:959–970. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0622-1
McBride JD, Freeman HNM, Leatherbarrow RJ (1999) Selection of human elastase inhibitors from a conformationally constrained combinatorial peptide library. Eur J Biochem 266:403–412
Mello MO, Tanaka AS, Silva-Filho MC (2003) Molecular evolution of Bowman-Birk type proteinase inhibitors in flowering plants. Mol Phylog Evol 27:103–112. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00373-1
Meyers BC, Kaushik S, Nandety RS (2005) Evolving disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:129–134
Molsov VV, Valueva TA (2005) Proteinase inhibitors and their function in plants: a review. Appl Biochem Microbiol 41:227–246
Morrison SC, Savage GP, Morton JD, Russell AC (2007) Identification and stability of trypsin inhibitor isoforms in pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars grown in New Zealand. Food Chem 100:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.062
Odani S, Ikenaka T (1973) Studies on soybean trypsin inhibitors. 8. Disulfide bridges in soybean Bowman-Birk inhibitors. J Biochem (Tokio) 74:697–715
Odani S, Ono T (1980) Chemical substitution of the reactive site leucine residue in soybean Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor with others amino acids. J Biochem 88:1555–1558
Piergiovanni AR, Galasso I (2004) Polymorphism of trypsin and chymotrypsin binding loops in Bowman-Birk inhibitors from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 166:1525–1531. doi:10.1002/jsfa.1404
Piergiovanni AR, Pignone D (2003) Effect of year-to-year variation and genotype on trypsin inhibitor level in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds. J Sci Food Agric 83:473–476. doi:10.1016/J.plantsci.2004.02.005
Prakash B, Selvaraj S, Murthy MR, Sreerama YN, Rao DR, Gowda LR (1996) Analysis of amino acid sequences of plant Bowman-Birk protease inhibitors. J Mol Evol 42:560–569
Rui-Feng Q, Zhan-Wu S, Cheng-Wu C (2005) Structural features and molecular evolution of Bowman-Birk protease inhibitors and their potential application. Acta Biochim Biophys Sinica 37:283–292. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00048.x
Ryan CA (1990) Protease inhibitors in plants: genes for improving defences against insects and pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 28:425–449
Scarafoni A, Consonni A, Galbusera V, Negri A, Tedeschi G, Rasmussen P, Magni C, Duranti M (2008) Identification and characterization of a Bowman-Birk inhibitor active towards trypsin but not chymotrypsin in Lupinus albus seeds. Phytochem 69:1820–1825. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.03.023
Schechter J, Berger A (1967) On the size of the active site proteases I Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:157–162
Ware JH, Wan XS, Newberne P, Kennedy AR (1999) Bowman-Birk inhibitor concentrate reduces colon inflammation in mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 44:986–990
Wilson KA, Laskowski MS (1975) The partial amino acid sequence of trypsin inhibitor II from garden bean, Phaseolus vulgaris, with location of the trypsin and elastase-reactive sites. J Biol Chem 250:4261–4267
Wu C, Whitaker JR (1990) Purification and partial characterisation of four trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitors from red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris var. Linden). J Agric Food Chem 38:1523–1529
Acknowledgments
Research partially supported by Ministry of Agriculture Food and Forestry Policies with funds released by C.I.P.E (Resolution 17/2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lioi, L., Galasso, I., Daminati, M.G. et al. Inhibitory properties and binding loop polymorphism in Bowman-Birk inhibitors from Phaseolus species. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57, 533–542 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9491-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9491-6