Abstract
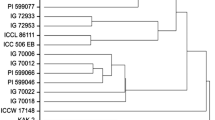
The legume pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübn.), is one of the major constraints to chickpea production, and host plant resistance is an important component for the management of this pest. The levels of resistance in the cultivated chickpea are low to moderate, and therefore, we evaluated 17 accessions of perennial Cicer along with three cultivated chickpea genotypes for resistance to H. armigera. There was a significant reduction in both leaf feeding and larval weights when the larvae were fed on the leaves of Cicer microphyllum Benth. accessions ICC 17146, ICC 17236, ICC 17240, and ICC 17248. Relative resistance index based on leaf feeding, larval survival, and larval weight indicated that C. microphyllum accessions ICC 17146, ICC 17236, ICC 17234, ICC 17240, ICC 17243, and ICC 17248 were highly resistant to H. armigera. Under natural infestation, accessions belonging to C. microphyllum, C. canariense Santos Guerra et Lewis, and C. macracanthum M. Pop suffered a damage rating of <2.0 compared to 4.0 in C. judaicum Boiss. accession ICC 17148 (annual species) and 8.5–9.0 in the cultivated chickpeas (1 = <10% leaf area damaged, and, 9 = >80% leaf area damaged). There was considerable diversity in the accessions belonging to perennial wild species of chickpea, and these can be exploited to increase the levels and diversify the basis of resistance to H. armigera in the cultivated chickpea.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
N.J. Armes D.R. Jadhav K.R. DeSouza (1996) ArticleTitleA survey of insecticide resistance in Helicoverpa armigera in the Indian subcontinent Bull. Entomol. Res. 86 499–514 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmvFSqtLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0007485300039298
K.P.S. Chandel (1984) ArticleTitleA note on occurrence of wild Cicer microphyllum Benth. and its nutrient status Int. Chickpea Newslett. 10 4–5
S.E. Cowgill S.S. Lateef (1996) ArticleTitleIdentification of antibiotic and antixenotic resistance to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in chickpea J. Econ. Entomol. 89 224–229
InstitutionalAuthorNameICRISAT(International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics). (1992) The Medium Term Plan ICRISAT PatancheruA.P. 502 324, India
S. Kaur K.S. Chhabra B.S. Arora (1999) ArticleTitleIncidence of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on wild and cultivated species of chickpea Int. Chickpea Pigeonpea Newslett. 6 18–19
K.R. Kranthi D.R. Jadhav S. Kranthi R.R. Wanjari S.S. Ali D.A. Russel (2002) ArticleTitleInsecticide resistance in five major insect pests of cotton in India Crop Protect. 21 449–460 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XksFyrtbo%3D
G. Ladizinsky A. Adler (1976) ArticleTitleGenetic relationships among the annual species of Cicer L Theor. Appl. Genet. 48 197–203 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00527371
S.S. Lateef (1985) ArticleTitleGram pod borer [Heliothis armigera (Hübn.)] resistance in chickpea Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 14 95–102
Lateef S.S. and Sachan J.N. 1990. Host plant resistance to Helicoverpa armigera (Hübn.) in different agro-economical conditions. In: Chickpea in Ninetees: Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Chickpea, 4–8 Dec 1989. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru, Andhra Pradesh, India, pp. 181–189.
F.J. Muehlbauer (1987) Use of wild species as a source of resistance in cool-season food legume crops K.B. Singh M.C. Saxena (Eds) Breeding for Stress Tolerance in Cool-Season Food Legumes John Wiley and Sons UK
K.M. Olsen J.C. Daly (2000) ArticleTitlePlant–toxin interactions in transgenic Bt cotton and their effect on mortality of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) J. Econ. Entomol. 93 1293–1299 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FhtFSluw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10985045 Occurrence Handle10.1603/0022-0493-93.4.1293
R.P.S. Pundir M.H. Mengesha G.V. Reddy (1993) ArticleTitleMorphology and cytology of Cicer canariensea wild relative of chickpea Euphytica 69 73–75 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00021727
H.C. Sharma (2001) Cotton Bollworm/Legume Pod BorerHelicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera): Biology and Management Crop Protection Compendium. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau International Oxon UK 72
H.C. Sharma K. Mann S.L. Kashyap G. Pampapathy J. Ridsdill-Smith (2002) Identification of Helicoverpa resistance in wild species of chickpeas 12th Australian Plant Breeding Conference Perth Western AustraliaAustralia
H.C. Sharma P.C. Stevenson M.S.J. Simmonds P.W.C. Green (2001) Identification of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) feeding stimulants and the location of their production on the pod-surface of pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) PatancheruAndhra PradeshIndia 85
K.B. Singh R.S. Malhotra M.C. Saxena (1990) ArticleTitleSources for tolerance to cold in Cicer species Crop Sci. 30 1136–1138
K.B. Singh B. Ocampo (1993) ArticleTitleInterspecific hybridization in annual Cicer species J. Genet. Breed. 47 199–204
K.B. Singh B. Ocampo (1997) ArticleTitleExploitation of wild Cicer species for yield improvement in chickpea Theor. Appl. Genet. 95 418–423
K.B. Singh B. Ocampo L.D. Robertson (1998) ArticleTitleDiversity for abiotic and biotic stress resistance in the wild annual Cicer species Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 45 9–17
K.B. Singh S. Weigand M.C. Saxena (1997) ArticleTitleRegistration of ILWC 39 and ILWC 181: Cicer echinospermum germplasm lines with resistance to Callosobruchus chinensis (L.) Crop Sci. 37 634
H.T. Stalker (1980) ArticleTitleUtilization of wild species for crop improvement Adv. Agron. 23 111–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H.C., Bhagwat, M.P., Pampapathy, G. et al. Perennial Wild Relatives of Chickpea as Potential Sources of Resistance to Helicoverpa armigera . Genet Resour Crop Evol 53, 131–138 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-1951-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-1951-4