Abstract
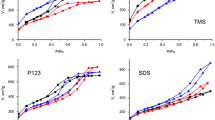
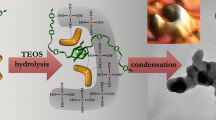
The formation of a mesostructured silicate material of the MCM-41 type is studied. The influence of the replacement of components in a reaction medium is investigated experimentally. Analysis of the results obtained and the data available in the literature suggests that the process under investigation is based on the approximate stoichiometric supramolecular interaction between [Si4O4 + x (OH)9 − x ]−(1 + x) silicate polyanions and C16H33(CH3)3N+ cetyltrimethylammonium cations with the formation of supramolecular aggregates, which condense to a mesostructured organosilicate composite. A further evolution of the product involves hydrolysis of the inner surface and the polymerization of the inorganic component. It is demonstrated that the properties of the product are determined, to a large extent, by the components of the reaction medium, which control the relative reaction rates in the process. The inference is made that an alcohol-ammonia medium is the most optimum for alkaline synthesis. This medium provides good preparation of the initial components for the reaction and the high rate of hydrolysis of pore walls, minimizes the osmotic effects during hydrothermal treatment, and, eventually, favors the formation of a highly structured hydrothermally stable material.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Iler, R.K., Chemistry of Silica, New York: Wiley, 1979.
Kresge, C.T., Leonowicz, M.E., Roth, W.J., et al., Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesized by a Liquid-Crystal Template Mechanism, Nature (London), 1992, vol. 359, pp. 710–712.
Beck, J.S., Vartuli, J.C., Roth, W.J., et al., A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, vol. 114, pp. 10834–10843.
Yanagisawa, T., Shimizu, T., Kuroda, K., and Kato, C., The Preparation of Alkyltrimethylammonium-Kanemite Complexes and Their Conversion to Microporous Materials, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1990, vol. 63, pp. 988–992.
US Patent 2810902 (Du Pont), 1957 (cited according to [1]).
Chiola, V., Ritsko, J.E., and Vanderpool, C.D., Process for Producing Low-Bulk Density Silica, US Patent 3556725, 1971.
Stucky, G.D., Monier, A., Schuth, F., et al., Molecular and Atomic Arrays in Nanoporous Materials Synthesis, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 1994, vol. 240, pp. 187–200.
Zhao, X.S., Lu, G.Q., and Mullar, G.J., Advances in Mesoporous Molecular Sieve MCM-41, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1996, vol. 35, pp. 2075–2090.
Vartuli, J.C., Kresge, C.T., Roth, W.J., et al., Designed Synthesis of Mesoporous Molecular Sieve Systems Using Surfactant Directing Agents, in Advanced Catalysts and Nanostructured Materials: Modern Synthetic Methods, Moser, W., Ed., San Diego: Academic, 1996.
Biz, S. and Occelli, M.L., Synthesis and Characterization of Mesostructured Materials, Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. 40, no.3, pp. 329–407.
Ciesla, U. and Schuth, F., Ordered Mesoporous Materials, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 131–149.
Davis, M.E., Ordered Porous Material for Emerging Applications, Nature (London), 2002, vol. 417, pp. 813–821.
Schuth, F. and Schmidt, W., Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2002, vol. 4, no.5, pp. 269–279.
Corma, A., From Microporous to Mesoporous Molecular Sieve Material and Their Use in Catalysis, Chem. Rev., 1997, vol. 97, pp. 2373–2419.
Hayward, R.C., Alberius-Henning, P., Chmelka, B.F., and Stucky, G.D., The Current Role of Mesostructures in Composite Materials and Device Fabrication, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vols. 44–45, pp. 619–624.
Soler-Illia, G.J. de A.A., Sanchez, C., Lebeau, B., and Patarin, J., Chemical Strategies to Design Textured Materials: From Microporous and Mesoporous Oxides to Nanonetworks and Hierarchical Structures, Chem. Rev., 2002, vol. 102, pp. 4093–4138.
Romannikov, V.N., Fenelonov, V.B., Nosov, A.V., et al., Physicochemical Features of Formation of Silicate Porous Mesophases: I. General Concepts of Mechanism, Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim., 1999, no. 10, pp. 1845–1851.
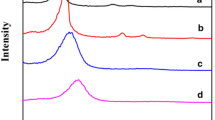
Solovyov, L.A., Kirik, S.D., Shmakov, A.N., and Romannikov, V.N., A Continuous Electron Density Approach in Rietveld Analysis for Structure Investigations of the Mesoporous Silicate Materials, Adv. X-ray Anal., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 110–115.
Jaroniec, M., Kruk, M., Shin, H.J., et al., Comprehensive Characterization of Highly Ordered MCM-41 Silicas Using Nitrogen Adsorption, Thermogravimetry, X-ray Diffraction, and Transmission Electron Microscopy, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vol. 48, pp. 127–134.
McCormick, A.V. and Bell, A.T., The Solution Chemistry of Zeolite Precursors, Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng., 1989, vol. 31, pp. 97–118.
Grun, M., Unger, K.K., Matsumoto, A., and Tsutsumi, K., Novel Pathways for the Preparation of Mesoporous MCM-14 Materials: Control of Porosity and Morphology, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 207–216.
Di Renzo, F., Testa, F., Chen, J.D., et al., Textural Control of Micelle-Templated Mesoporous Silicates: The Effects of Co-Surfactants and Alkalinity, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 28, pp. 437–446.
Schulz-Ekloff, G., Rathousky, J., and Zukal, A., Controlling of Morphology and Characterization of Pore Structure of Ordered Mesoporous Silica, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 273–285.
Yu, J., Shi, J.-L., Wang, L.-Z., et al., Preparation of High Thermal Stability MCM-41 in the Low Surfactant/Silicon Molar Ratio Synthesis System, Mater. Lett., 2001, vol. 48, pp. 112–116.
Kruk, M., Jaroniec, M., and Sayari, A., Influence of Hydrothermal Restructuring Conditions on Structural Properties of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 217–229.
Kawi, S. and Shen, S.-C., Effects of Structural and Non-Structural Al Species on the Stability of MCM-41 Materials in Boiling Water, Mater. Lett., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 108–112.
Kim, W.J., Yoo, J.C., and Hayhurst, D.T., Synthesis of Hydrothermally Stable MCM-41 with Initial Adjustment of pH and Direct Addition of NaF, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2000, vol. 39, pp. 177–186.
Kisler, J.M., Gee, M.L., Stevens, G.W., and O’Connor, A.J., Comparative Study of Silylation Methods to Improve the Stability of Silicate MCM-41 in Aqueous Solutions, Chem. Mater., 2003, vol. 15, pp. 619–624.
Mokaya, R., Influence of Alumination Pathway on the Steam Stability of Al-Grafted MCM-41, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 2003, vol. 146, pp. 435–438.
Kim, W.J., Yoo, J.C., and Hayhurst, D.T., Synthesis of MCM-48 via Phase Transformation with Direct Addition of NaF and Enhancement of Hydrothermal Stability by Post-Treatment in NaF Solution, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 125–137.
Kim, J.M., Jun, S., and Ryoo, R., Improvement of Hydrothermal Stability of Mesoporous Silica Using Salts: Reinvestigation for Time-Dependent Effects, J.Phys. Chem. B, 1999, vol. 103, pp. 6200–6205.
Lin, H.-P. and Mou, C.-Y., Salt Effect in Post-Synthesis Hydrothermal Treatment of MCM-41, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2002, vol. 55, pp. 69–80.
Oye, G., Sjoblom, J., and Stocker, M., Synthesis and Characterization of Siliceous and Aluminum-Containing Mesoporous Materials from Different Surfactant Solutions, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 171–180.
Zhao, X.S. and Lu, G.Q., Modification of MCM-41 by Surface Silylation with Trimethylchlorosilane and Adsorption Study, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, vol. 102, pp. 1556–1561.
Lee, J.S., Joo, S.H., and Ryoo, R., Synthesis of Mesoporous Silicas of Controlled Pore Wall Thickness and Their Replication to Ordered Nanoporous Carbons with Various Pore Diameters, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, vol. 124, no.7, pp. 1156–1157.
Solovyov, L.A., Kirik, S.D., Shmakov, A.N., and Romannikov, V.N., X-ray Structural Modeling of Mesoporous Mesophase Material, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vols. 44–45, pp. 17–23.
Fenelonov, V.B., Derevyankin, A.Yu., Kirik, S.D., et al., Comparative Textural Study of Highly Ordered Silicate and Aluminosilicate Mesoporous Mesophase Materials Having Different Pore Sizes, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vols. 44–45, pp. 33–40.
Tolbert, S.H., Landry, C.C., Stucky, G.D., et al., Phase Transitions in Mesostructured Silica/Surfactant Composites: Surfactant Packing and Role of Charge Density Matching, Chem. Mater., 2001, vol. 13, pp. 2247–2256.
Kleitz, F., Schmidt, W., and Schuth, F., Evolution of Mesoporous Materials during the Calcination Process: Structural and Chemical Behavior, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vols. 44–45, pp. 95–109.
Gallis, K.W. and Landry, C.C., Synthesis of MCM-48 by a Phase Transformation Process, Chem. Mater., 1997, vol. 9, pp. 2035–2046.
Xu, J., Luan, Z.H., He, H.Y., et al., A Reliable Synthesis of Cubic Mesoporous MCM-48 Molecular Sieve, Chem. Mater., 1998, vol. 10, pp. 3690–3698.
Pevzner, S. and Regev, O., The In Situ Phase Transitions Occurring during Bicontinuous Cubic Phase Formation, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, vol. 38, pp. 413–421.
Romannikov, V.N., Fenelonov, V.B., and Derevyankin, A.Yu., Physicochemical Features of Formation of Silicate Porous Mesophases: II. The Effect of Size of Molecules of Surfactant Cations, Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim., 1999, no. 10, pp. 1852–1856.
Kodenev, E.G., Shmakov, A.N., Derevyankin, A.Yu., et al., Physicochemical Features of Formation of Silicate Porous Mesophases: III. Conditions of Formation and Properties of Mesoporous Silica, Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim., 2000, no. 10, pp. 1685–1691.
Zhao, X.S., Lu, G.Q., Whittaker, A.K., et al., Comprehensive Study of Surface Chemistry of MCM-41 Using Si-29 CP/MAS NMR, FTIR, Pyridine-TPD, and TGA, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1997, vol. 101, pp. 6525–6531.
Solovyov, L.A., Belousov, O.V.., Shmakov, A.N., et al., X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Mesostructured Materials by Continuous Density Function Technique, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 2003, vol. 146, pp. 299–302.
Solovyov, L.A., Zaikovskii, V.I., Shmakov, A.N., et al., Framework Characterization of Mesostructured Carbon CMK-1 by X-ray Powder Diffraction and Electron Microscopy, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, vol. 106, pp. 12 198–12 202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2005 by Fizika i Khimiya Stekla, Kirik, Belousov, Parfenov, Vershinina.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirik, S.D., Belousov, O.V., Parfenov, V.A. et al. System Approach to Analysis of the Role of the Synthesis Components and Stability of the MCM-41 Mesostructured Silicate Material. Glass Phys Chem 31, 439–451 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10720-005-0081-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10720-005-0081-1