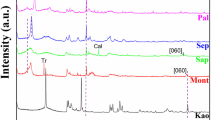
Clinoptilolitic zeolite based on the native zeolite of Nakhchivan was synthesized, and the influence of the conditions of synthesis for the crystallization process (temperature, concentration of the thermal solution and mineralizer) was studied. The starting material was zeolite tuff from the Nakhchivan Kyukyuchaiskoe deposit. The optimal conditions of synthesis afforded the production of clinoptilolite with 100% crystallinity. Other structural types of zeolites or their associations can be obtained by changing the optimal conditions of synthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 September 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00390-0
References
M. Grce and K. Pavelic, “Antiviral properties of clinoptilolite,” Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 79(1 – 3), 165 – 169 (2005).
C. Baerlocher, L. B. McCusker, and D. H. Olson, Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007).
N. Lihareva, L. Dimova, O. Petrov, and Y. Tzvetanova, “Investigation of Zn sorption by natural clinoptilolite and mordenite,” Bulgar. Chem. Commun., 3(41), 266 – 271 (2009).
V. Jha and S. Hayashi, “Modification on natural clinoptilolite zeolite for its NH4+ retention capacity,” J. Hazardous Mater., 169(1 – 3), 29 – 35 (2009).
E. V. Klimova, “Zeolites as a means for purifying water from radionuclides (purification of drinking water),” Ekolog. Bezopas. APK, Ref. Zh., No. 2, 302 (2011).
A. Zendelska, M. Golomeova, S. Jakupi, and K. Lisichkov, “Characterization and application of clinoptilolite for removal of heavy metal ions from water resources,” Geologica Macedonica, 32(1), 21 – 32 (2018).
R. V. Nekrasov, A. A. Zelenchenkova, M. G. Chabaev, and S. Tulunay, “Use of native clinoptilolite in horse feed,” Ukrainian J. Ecology, 7(4), 5 – 11 (2017).
S. E. Bachman, M. L. Galyean, G. S. Smith, et al., “Early aspects of locoweed toxicosis and evaluation of a mineral supplement or clinoptilolite as dietary treatments,” J. Animal Sci., 70(10), 3125 – 3132 (1992).
A. N. Uyumaz, L. S. Ozyegin, N. Buyukakyuz, et al., “Evaluation of tcp loaded clinoptilolite use as graft material on Rabbit Tibia,” Key Eng. Mater., 493 – 494, 175 – 180 (2011).
H. Derakhshankhah, S. Jafari, S. Sarvari, et al., “Biomedical applications of zeolitic nanoparticles, with an emphasis on medical interventions,” Int. J. Nanomedicine, 15, 363 – 386 (2020).
P. Ambrozova, J. Kynicky, T. Urubek, and V. Nguyen, “Synthesis and modification of clinoptilolite,” Molecules, 22, 1107 – 1119 (2017).
J.-S. Yuan, L. Shi, and H.-R. Han, “Synthesis of clinoptilolite,” Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 23(6), 994 – 998 (2007).
C. D. Williams, “Synthesis of pure clinoptilolite without the use of seed crystals,” Chem. Commun., No. 21, 2113 – 2114 (1997).
S. Yang, A. Vlessidis, and N. Evmiridis, “Influence of gel composition and crystallization conditions on the conventional synthesis of zeolites,” Industr. Eng. Chem. Res., 36(5), 1622 – 1631 (1997).
M. A. Camblor, A. Mifsud, and J. Pérez-Pariente, “Influence of the synthesis conditions on the crystallization of zeolite beta,” Zeolites, 11(8), 792 – 797 (1991).
S. Srilai,W. Tanwongwal, K. Onpecth, et al., “Influence of crystallization time for synthesis of zeolite A and zeolite X from natural kaolin,” Key Eng. Mater., 824, 231 – 235 (2019).
R. M. Mohamed, O. A. Fouad, A. A. Ismail, and I. A. Ibrahim, “Influence of crystallization times on the synthesis of nanosized ZSM-5,” Mater. Lett., 59(27), 3441 – 3444 (2005).
D. E. Anderson, S. Balapangu, and K. T. Elvis, “Investigating the influence of temperature on the kaolinite-base synthesis of zeolite and urease immobilization for the potential fabrication of electrochemical urea biosensors,” Sensors (Basel), 17(8), 1831 – 1846 (2017).
A. S. Barbosa, L. A. Lima, B. V. Sousa, et al., “Influence of crystallization time on structural and morphological characteristics the precursor of zeolite MCM-22,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 660 – 661, 567 – 572 (2010).
S. L. Shima, R. Zainab, and T. Sugeng, “Effect of different templates on the synthesis of mesoporous sodalite,” J. Chemistry, 27, 613 – 618 (2015).
M. M. J. Treacy and J. B. Higgins, Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, Elsevier, New York (2001).
H. Bekkum, E. M. Flanigen, P. A. Jacobs, and J. C. Jansen, Introduction to Zeolite Science and Practice, Elsevier, New York (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 4, pp. 43 – 48, April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamedova, G.A. Influence of Synthesis Conditions on Clinoptilolitic Zeolite Crystallization. Glass Ceram 78, 168–171 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00370-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00370-4