Abstract
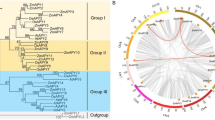
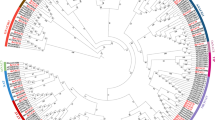
Xylanase inhibitor proteins (XIP) are widely distributed in the plant kingdom, and also exist in rice. However, a systematic bioinformatics analysis of this gene family in rice (OsXIP) has not been conducted to date. In this study, we identified 32 members of the OsXIP gene family and analyzed their physicochemical properties, chromosomal localization, gene structure, protein structure, expression profiles, and interaction networks. Our results indicated that OsXIP genes exhibit an uneven distribution across eight rice chromosomes. These genes generally feature a low number of introns or are intronless, all family members, except for OsXIP20, contain two highly conserved motifs, namely Motif 8 and Motif 9. In addition, it is worth noting that the promoter regions of OsXIP gene family members feature a widespread presence of abscisic acid response elements (ABRE) and gibberellin response elements (GARE-motif and TATC-box). Quantitative Real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis unveiled that the expression of OsXIP genes exhibited higher levels in leaves and roots, with considerable variation in the expression of each gene in these tissues both prior to and following treatments with abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellin (GA3). Protein interaction studies and microRNA (miRNA) target prediction showed that OsXIP engages with key elements within the hormone-responsive and drought signaling pathways. The qRT-PCR suggested osa-miR2927 as a potential key regulator in the rice responding to drought stress, functioning as tissue-specific and temporally regulation. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further analysis of the functions within the OsXIP gene family.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Achkar NP, Cambiagno DA, Manavella PA (2016) miRNA biogenesis: a dynamic pathway. Trends Plant Sci 21:1034–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TPLANTS.2016.09.003
Andrew W, Martino B, Stefan B et al (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46: W296–W303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CELL.2009.01.002
Basit A, Liu J, Rahim K et al (2018) Thermophilic xylanases: from bench to bottle. Crit Rev Biotech-Nol 38:989–1002. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2018.1425662
Baumgarten A, Cannon S, Spangler R, May G (2003) Genome-level evolution of resistance genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 165:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/GENETICS/165.1.309
Beaugrand J, Gebruers K, Ververken C et al (2006) Antibodies against wheat xylanase inhibitors as tools for the selective identification of their homologues in other cereals. J Cereal Sci 44:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCS.2006.02.003
Beliën T, Van Campenhout S, Van Acker M et al (2007) Mutational analysis of endoxylanases XylA and XylB from the phytopathogen fusarium graminearum reveals comprehensive insights into Their inhibitor insensitivity. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4602–4608. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00442-07
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V et al (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A et al (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Chen VB, Davis IW, Richardson DC (2009) KING (Kinemage, Next Generation): a versatile interactive molecular and scientific visualization program. Protein Sci 18: 2403–2409. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.250
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y et al (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLP.2020.06.009
Chunxiao HOU (2014) Functions and expression patterns of rice xylanase inhibitory proteins. Biologia Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0787-2
Damian S, Rebecca K, Mikaela K et al (2023) The STRING database in 2023: protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res 51: D638–D646. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1000
DeLano W L (2002) Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr 40:82–92. https://legacy.ccp4.ac.uk/newsletters/newsletter40/11_pymol.html
Durand A, Hughes R, Roussel A et al (2005) Emergence of a subfamily of xylanase inhibitors within glycoside hydrolase family 18. FEBS J 272:1745–1755. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1742-4658.2005.04606.X
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PCBI.1002195
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR (2011) HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W29–W37. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKR367
Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2009) Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in plants. New Phytol 183:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-8137.2009.02923.X
Gao F, Li J, Zhang J et al (2022) Genome-wide identification of the ZIP gene family in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and expression analysis under different element stress. PLoS One 17:e0274319. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0274319
Goesaert H, Elliott G, Kroon PA et al (2004) Occurrence of proteinaceous endoxylanase inhibitors in cereals. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Proteins and Proteomics 1696:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBAPAP.2003.08.015
Goesaert H, Gebruers K, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2005) Purification and characterization of a XIP-type endoxylanase inhibitor from rice (Oryza sativa). J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 20:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360400002080
Guo H, Zhang Y, Wang Z et al (2019) Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in the asteranae. Plants 8:393. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS8100393
Gusakov AV (2010) Proteinaceous inhibitors of microbial xylanases. Biochem (Moscow) 75:1185–1199. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297910100019/METRICS
Helen M, John W, Zukang F et al (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Hou CX, Zhan YH, Jiang DA, Weng XY (2014) Functional characterization of a new pathogen induced xylanase inhibitor (RIXI) from rice. Eur J Plant Pathol 138:405–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10658-013-0342-0
Houb EB (2001) The arms race is ancient history in Arabidopsis, the wildflower. Nature Reviews Genetics 2:516–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/35080508
Hu L, Wang P, Hao Z et al (2021) Gibberellin oxidase gene family in L. Chinense: genome-wide identification and gene expression analysis. Int J Mol Sci 22:7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137167
Ishida K, Noutoshi Y (2022) The function of the plant cell wall in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Physiol Biochem 1:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.10.015
Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D et al (2010) Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nature Genetics 42:541–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.591
Juge N, Delcour J (2006) Proteinaceous Xylanase inhibitors: structure, function and evolution. Curr Enzym Inhib 2:29–35. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340806775473562
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14:587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kumar S, Singh N, Sinha M et al (2010) Crystal structure determination and inhibition studies of a novel xylanase and α-amylase inhibitor protein (XAIP) from Scadoxus multiflorus. FEBS J 277:2868–2882. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07703.x
Lei P, Wei X, Gao R et al (2021) Genome-wide identification of PYL gene family in wheat: Evolution, expression and 3D structure analysis. Genomics 113:854–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YGENO.2020.12.017
Li MY, Jiao YT, Wang YT et al (2020) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated VvPR4b editing decreases downy mildew resistance in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Hortic Res 7:149. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41438-020-00371-4
Liu H, Lyu HM, Zhu K et al (2021) The emergence and evolution of intron-poor and intronless genes in intron-rich plant gene families. Plant J 105:1072–1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/TPJ.15088
Liu M, Li J, Rehman AU et al (2022a) Sensitivity of family GH11 bacillus amyloliquefaciens xylanase A (BaxA) and the T33I mutant to Oryza sativa xylanase inhibitor protein (OsXIP): an experimental and computational study. Enzyme Microb Technol 156:109998. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2022.109998
Liu X, Zhang D, Yu Z et al (2022b) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-Box gene family in almond reveal its expression features in different flowering periods. Genes (basel) 13:1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/GENES13101764
Liu Z, Zhu X, Liu W et al (2023a) Characterization of the REVEILLE family in rosaceae and role of PbLHY in flowering time regulation. BMC Genomics 24:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12864-023-09144-4
Liu W, Wang M, Zhong M et al (2023b) Genome-wide identification of bZIP gene family and expression analysis of BhbZIP58 under heat stress in wax gourd. BMC Plant Biol 23:598. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04580-6
Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E et al (2014) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Research 42:D490–D495. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1178
Magali L, Patrice D, Gert T et al (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Michael ES, Keiichiro O, Johannes R et al (2011) Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27:431–432. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675
Moscetti I, Tundo S, Janni M et al (2013) Constitutive Expression of the Xylanase Inhibitor TAXI-III delays fusarium head blight symptoms in durum wheat transgenic plants. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 26:1464-1472. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-04-13-0121-R
Nian L, Liu X, Yang Y et al (2021) Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic, and expression analysis under abiotic stress conditions of LIM gene family in Medicago sativa L. PLoS ONE 16:e0252213. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252213
Paës G, Berrin JG, Beaugrand J (2012) GH11 xylanases: Structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol Adv 30:564–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.10.003
Qian W, Liao BY, Chang AYF, Zhang J (2010) Maintenance of duplicate genes and their functional redundancy by reduced expression. Trends Genet 26:425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIG.2010.07.002
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P et al (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Sang Q, Fan L, Liu T et al (2023) MicroRNA156 conditions auxin sensitivity to enable growth plasticity in response to environmental changes in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36774-9
Sonah H, Chavan S, Katara J et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and characterization of Xylanase inhibitor protein (XIP) genes in cereals. Indian J Gen Plnt Bree 76:159–166. https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-6906.2016.00036.5
Sun RJ, Xu Y, Hou CX et al (2018) Expression and characteristics of rice xylanase inhibitor OsXIP, a member of a new class of antifungal proteins. Biol Plant 62:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10535-018-0787-2
Tao J, Jia H, Wu M et al (2022) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the TIFY gene family in kiwifruit. BMC Genomics 23:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12864-022-08398-8
Tian Y, Dong Q, Ji Z et al (2015) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-box gene family in apple. Gene 555:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GENE.2014.11.018
Tokunaga T, Esaka M (2007) Induction of a novel XIP-type xylanase inhibitor by external ascorbic acid treatment and differential expression of XIP-family genes in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 48:700–714. https://doi.org/10.1093/PCP/PCM038
Tokunaga T, Miyata Y, Fujikawa Y, Esaka M (2008) RNAi-mediated knockdown of the XIP-type endoxylanase inhibitor gene, OsXIP, has no effect on grain development and germination in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1122–1127. https://doi.org/10.1093/PCP/PCN080
Tundo S, Moscetti I, Faoro F et al (2015) Fusarium graminearum produces different xylanases causing host cell death that is prevented by the xylanase inhibitors XIP-I and TAXI-III in wheat. Plant Sci 240:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLANTSCI.2015.09.002
Tundo S, Mandalà G, Sella L et al (2022) Xylanase inhibitors: defense players in plant immunity with implications in agro-industrial processing. Int J Mol Sci 23:14994. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS232314994
Vaghela B, Vashi R, Rajput K, Joshi R (2022) Plant chitinases and their role in plant defense: a comprehensive review. Enzyme Microb Technol 159:110055. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2022.110055
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD et al (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e49–e49. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKR1293
Wang J, Mei J, Ren G (2019) Plant microRNAs: Biogenesis, homeostasis, and degradation. Front Plant Sci 10:433008. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00360
Wang W, Fang H, Aslam M et al (2022) MYB gene family in the diatom phaeodactylum tricornutum revealing their potential functions in the adaption to nitrogen deficiency and diurnal cycle. J Phycol 58:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.13217
Wicker T, Buchmann JP, Keller B (2010) Patching gaps in plant genomes results in gene movement and erosion of colinearity. Genome Res 20:1229–1237. https://doi.org/10.1101/GR.107284.110
Xin Z, Wang Q, Yu Z et al (2014) Overexpression of a Xylanase inhibitor gene, OsHI-XIP, enhances resistance in rice to herbivores. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11105-013-0661-5
Xinbin D, Patrick XZ (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–W159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr319
Yu N, Niu QW, Ng KH, Chua NH (2015) The role of miR156/SPLs modules in Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant J 83:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/TPJ.12919
Zhan Y, Sun R, Sun X et al (2017) Expression regulation of a xylanase inhibitor gene riceXIP in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Revista Brasileira De Botanica 40:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40415-017-0400-5
Zhang B (2015) MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 66:1749–1761. https://doi.org/10.1093/JXB/ERV013
Zhao L, Guo L, Lu X et al (2022) Structure and character analysis of cotton response regulator genes family reveals that GhRR7 responses to draught stress. Biol Res 55:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/S40659-022-00394-2
Zhou Y, Tao J, Ahammed GJ et al (2019a) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of aquaporin gene family related to abiotic stress in watermelon. Genome 62:643–656. https://doi.org/10.1139/GEN-2019-0061
Zhou Y, Wang X, Song M et al (2019b) A secreted microRNA disrupts autophagy in distinct tissues of Caenorhabditis elegans upon ageing. Nat Commun 10:4827. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12821-2
Zhou T, Chen J, Huang Y et al (2022) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in zanthoxylum armatum DC. Agriculture (switzerland) 12:1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRICULTURE12091318
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Department of Education Anhui Natural Science Foundation (KJ2020A0119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.C.W., Y.X. and G.S. conceived and designed research. M.Z., Z.L., J.G., C.Y., A.L., Q.H. and H.Y. conducted experiments. D.C.W. and Y.X. contributed new reagents or analytical tools. M.Z., Z.L. and D.C.W. analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. G.S. edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest:
This manuscript or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal has not be under consideration by any other journal. No material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights, or the rights of a third party. All authors have approved the manuscript. The authors have declared that no conflict interests exist.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Liu, Z., Gan, J. et al. Identification and expression analysis of XIP gene family members in rice. Genetica (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-024-00207-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-024-00207-2