Abstract
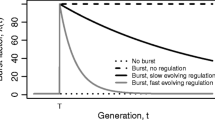
Insertion sequences (ISs) are transposable genetic elements in bacterial genomes. IS elements are common among bacteria but are generally rare within free-living species, probably because of the negative fitness effects they have on their hosts. Conversely, ISs frequently proliferate in intracellular symbionts and pathogens that recently transitioned from a free-living lifestyle. IS elements can profoundly influence the genomic evolution of their bacterial hosts, although it is unknown why they often expand in intracellular bacteria. We designed a laboratory evolution experiment with Escherichia coli K-12 to test the hypotheses that IS elements often expand in intracellular bacteria because of relaxed natural selection due to (1) their generally small effective population sizes (N e) and thus enhanced genetic drift, and (2) their nutrient rich environment, which makes many biosynthetic genes unnecessary and thus selectively neutral territory for IS insertion. We propagated 12 populations under four experimental conditions: large N e versus small N e, and nutrient rich medium versus minimal medium. We found that relaxed selection over 4,000 generations was not sufficient to permit IS element expansion in any experimental population, thus leading us to hypothesize that IS expansion in intracellular symbionts may often be spurred by enhanced transposition rates, possibly due to environmental stress, coupled with relaxed natural selection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergthorsson U, Ochman H (1995) Heterogeneity of genome sizes among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:5784–5789
Bergthorsson U, Ochman H (1998) Distribution of chromosome length variation in natural isolates of Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol 15:6–16
Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, Davis NW, Kirkpatrick HA, Goeden MA, Rose DJ, Mau B, Shao Y (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453–1462
Brinster S, Lamberet G, Staels B, Trieu-Cuot P, Gruss A, Poyart C (2009) Type II fatty acid synthesis is not a suitable antibiotic target for Gram-positive pathogens. Nature 458:83–86
Capy P, Gasperi G, Biémont C, Bazin C (2000) Stress and transposable elements: co-evolution or useful parasites? Heredity 85:101–106
Chain PSG, Hu P, Malfatti SA, Radnedge L, Larimer F, Vergez LM, Worsham P, Chu MC, Andersen GL (2006) Complete genome sequence of Yersinia pestis strains Antiqua and Nepal516: evidence of gene reduction in an emerging pathogen. J Bacteriol 188:4453–4463
Chandler M, Mahillon J (2002) Insertion sequences revisited. In: Craig NL, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz A (eds) Mobile DNA II, vol 5/6. ASM Press, Washington, pp 305–366
Chao L, McBroom SM (1985) Evolution of transposable elements: an IS10 insertion increases fitness in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol 2:359–369
Conlon KM, Humphreys H, O’Gara JP (2004) Inactivations of rsbU and sarA by IS256 represent novel mechanisms of biofilm phenotypic variation in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol 186:6208–6219
Cooper VS, Schneider D, Blot M, Lenski RE (2001) Mechanisms causing rapid and parallel losses of ribose catabolism in evolving populations of Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol 183:2834–2841
Cornelis G (1980) Transposition of Tn951 (Tnlac) and cointegrate formation are thermosensitive processes. J Gen Microbiol 117:243–247
Doolittle WF, Sapienza C (1980) Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284:601–603
Dougherty KM, Plague GR (2008) Transposable element loads in a bacterial symbiont of weevils are extremely variable. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7832–7834
Duchaud E, Rusniok C, Frangeul L, Buchrieser C, Taourit S, Bocs S, Boursaux-Eude C, Chandler M, Dassa E, Derose R, Derzelle S, Freyssinet G, Gaudriault S, Givaudan A, Médigue C, Lanois A, Powell K, Siguier P, Wingate V, Zouine M, Glaser P, Boemare N, Danchin A, Kunst F (2003) The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat Biotechnol 21:1307–1313
Dykhuizen DE (1990) Experimental studies of natural selection in bacteria. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 21:373–398
Edwards RJ, Brookfield JFY (2003) Transiently beneficial insertions could maintain mobile DNA sequences in variable environments. Mol Biol Evol 20:30–37
Elena SF, Ekunwe L, Hajela N, Oden SA, Lenski RE (1998) Distribution of fitness effects caused by random insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. Genetica 102(103):349–358
Fraser C, Hanage WP, Spratt BG (2007) Recombination and the nature of bacterial speciation. Science 315:476–480
Haren L, Bétermier M, Polard P, Chandler M (1997) IS911-mediated intramolecular transposition is naturally temperature sensitive. Mol Microbiol 25:531–540
Herzer PJ, Inouye S, Inouye M, Whittam TS (1990) Phylogenetic distribution of branched RNA-linked multicopy single-stranded DNA among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:6175–6181
Kang Y, Durfee T, Glasner JD, Qiu Y, Frisch D, Winterberg KM, Blattner FR (2004) Systematic mutagenesis of the Escherichia coli genome. J Bacteriol 186:4921–4930
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kimura M, Ohta T (1969) The average number of generations until fixation of a mutant gene in a finite population. Genetics 61:763–771
Kothary MH, Babu US (2001) Infective dose of foodborne pathogens in volunteers: a review. J Food Saf 21:49–73
Kretschmer PJ, Cohen SN (1979) Effect of temperature on translocation frequency of the Tn3 element. J Bacteriol 139:515–519
Leavis HL, Willems RJL, van Wamel WJB, Schuren FH, Caspers MPM, Bonten MJM (2007) Insertion sequence-driven diversification creates a globally dispersed emerging multiresistant subspecies of E. faecium. PLoS Pathog 3:e7
Lederberg J (2004) E. coli K-12. Microbiol Today 31:116
Lee B-M, Park Y-J, Park D-S, Kang H-W, Kim J-G, Song E-S, Park I-C, Yoon U-H, Hahn J-H, Koo B-S, Lee G-B, Kim H, Park H-S, Yoon K-O, Kim J-H, Jung C-h, Koh N-H, Seo J-S, Go S-J (2005) The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Nucleic Acids Res 33:577–586
Lenski RE, Rose MR, Simpson SC, Tadler SC (1991) Long-term experimental evolution in Escherichia coli. I. Adaptation and divergence during 2,000 generations. Am Nat 138:1315–1341
Lind PA, Berg OG, Andersson DI (2010) Mutational robustness of ribosomal protein genes. Science 330:825–827
Lynch M (2007) The origins of genome architecture. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Lynch M, Conery JS (2003) The origins of genome complexity. Science 302:1401–1404
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Moran NA, Plague GR (2004) Genomic changes following host restriction in bacteria. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:627–633
Moran NA, Wernegreen JJ (2000) Lifestyle evolution in symbiotic bacteria: insights from genomics. Trends Ecol Evol 15:321–326
Neidhardt FC, Bloch PL, Smith DF (1974) Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol 119:736–747
Newton ILG, Bordenstein SR (2011) Correlations between bacterial ecology and mobile DNA. Curr Microbiol 62:198–208
Nuzhdin SV (1999) Sure facts, speculations, and open questions about the evolution of transposable element copy number. Genetica 107:129–137
Ochman H, Davalos LM (2006) The nature and dynamics of bacterial genomes. Science 311:1730–1733
Ochman H, Moran NA (2001) Genes lost and genes found: evolution of bacterial pathogenesis and symbiosis. Science 292:1096–1098
Ochman H, Wilson AC (1987) Evolutionary history of enteric bacteria. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. ASM Press, Washington, pp 1649–1654
Ohta T (1973) Slightly deleterious mutant substitutions in evolution. Nature 246:96–98
Ohtsubo Y, Genka H, Komatsu H, Nagata Y, Tsuda M (2005) High-temperature-induced transposition of insertion elements in Burkholderia multivorans ATCC 17616. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1822–1828
Orgel LE, Crick FHC (1980) Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284:604–607
Papadopoulos D, Schneider D, Meier-Eiss J, Arber W, Lenski RE, Blot M (1999) Genomic evolution during a 10,000-generation experiment with bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3807–3812
Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, Holden MT, Churcher CM, Bentley SD, Mungall KL, Cerdeño-Tarraga AM, Temple L, James K, Harris B, Quail MA, Achtman M, Atkin R, Baker S, Basham D, Bason N, Cherevach I, Chillingworth T, Collins M, Cronin A, Davis P, Doggett J, Feltwell T, Goble A, Hamlin N, Hauser H, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Leather S, Moule S, Norberczak H, O’Neil S, Ormond D, Price C, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutter S, Sanders M, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Unwin L, Whitehead S, Barrell BG, Maskell DJ (2003) Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet 35:32–40
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Pfaffl MW (2004) Quantification strategies in real-time PCR. In: Bustin SA (ed) A-Z of quantitative PCR, vol 2–3. International University Line Press, La Jolla, pp 87–120
Pfeifer F, Blaseio U (1990) Transposition burst of the ISH27 insertion element family in Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6921–6925
Plague GR, Dunbar HE, Tran PL, Moran NA (2008) Extensive proliferation of transposable elements in heritable bacterial symbionts. J Bacteriol 190:777–779
Riley M (1993) Functions of the gene products of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 57:862–952
Russell DG (2005) Where to stay inside the cell: a homesteader’s guide to intracellular parasitism. In: Cossart P, Boquet P, Normark S, Rappuoli R (eds) Cellular microbiology, 2nd edn. ASM Press, Washington, pp 227–253
Safi H, Barnes PF, Lakey DL, Shams H, Samten B, Vankayalapati R, Howard ST (2004) IS6110 functions as a mobile, monocyte-activated promoter in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol Microbiol 52:999–1012
Schmitz-Esser S, Tischler P, Arnold R, Montanaro J, Wagner M, Rattei T, Horn M (2010) The genome of the amoeba symbiont “Candidatus Amoebophilus asiaticus” reveals common mechanisms for host cell interaction among amoeba-associated bacteria. J Bacteriol 192:1045–1057
Song Y, Tong Z, Wang J, Wang L, Guo Z, Han Y, Zhang J, Pei D, Zhou D, Qin H, Pang X, Han Y, Zhai J, Li M, Cui B, Qi Z, Jin L, Dai R, Chen F, Li S, Ye C, Du Z, Lin W, Wang J, Yu J, Yang H, Wang J, Huang P, Yang R (2004) Complete genome sequence of Yersinia pestis strain 91001, an isolate avirulent to humans. DNA Res 11:179–197
Todd ECD, Greig JD, Bartleson CA, Michaels BS (2008) Outbreaks where food workers have been implicated in the spread of foodborne disease. Part 4. Infective doses and pathogen carriage. J Food Prot 71:2339–2373
Touchon M, Rocha EPC (2007) Causes of insertion sequences abundance in prokaryotic genomes. Mol Biol Evol 24:969–981
Treves DS, Manning S, Adams J (1998) Repeated evolution of an acetate-crossfeeding polymorphism in long-term populations of Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol 15:789–797
Wahl LM, Gerrish PJ (2001) The probability that beneficial mutations are lost in populations with periodic bottlenecks. Evolution 55:2606–2610
Whittam TS, Ake SE (1993) Genetic polymorphisms and recombination in natural populations of Escherichia coli. In: Takahata N, Clark AG (eds) Mechanisms of molecular evolution. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 223–245
Woyke T, Teeling H, Ivanova NN, Huntemann Ml, Richter M, Gloeckner FO, Boffelli D, Anderson IJ, Barry KW, Shapiro HJ, Szeto E, Kyrpides NC, Mussmann M, Amann R, Bergin C, Ruehland C, Rubin EM, Dubilier N (2006) Symbiosis insights through metagenomic analysis of a microbial consortium. Nature 443:950–955
Yang F, Yang J, Zhang X, Chen L, Jiang Y, Yan Y, Tang X, Wang J, Xiong Z, Dong J, Xue Y, Zhu Y, Xu X, Sun L, Chen S, Nie H, Peng J, Xu J, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Wen Y, Yao Z, Shen Y, Qiang B, Hou Y, Yu J, Jin Q (2005) Genome dynamics and diversity of Shigella species, the etiologic agents of bacillary dysentery. Nucleic Acids Res 33:6445–6458
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Boyer, B. Jackson, K. McConnell, and G. Voltaire for assistance in the lab, and two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant 1R15GM081862-01A1. This is contribution number 255 of the Louis Calder Center—Biological Field Station, Fordham University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plague, G.R., Dougherty, K.M., Boodram, K.S. et al. Relaxed natural selection alone does not permit transposable element expansion within 4,000 generations in Escherichia coli . Genetica 139, 895–902 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-011-9593-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-011-9593-x