Abstract
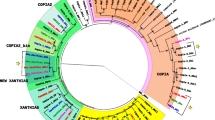
In silico searches for sequences homologous to hAT elements in 12 Drosophila genomes have allowed us to identify 37 new hAT elements (8 in D. ananassae, 11 in D. mojavensis, 2 in D. sechellia, 1 in D. simulans, 2 in D. virilis, 3 in D. yakuba, 3 in D. persimilis, 1 in D. grimshawi, 5 in D. willistoni and 1 in D. pseudobscura). The size of these elements varies from 2,359 to 4,962 bp and the terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) show lengths ranging from 10 to 24 bp. Several elements show intact transposase ORFs, suggesting that they are active. Conserved amino acid motifs were identified that correspond to those important for transposase activity. These elements are highly variable and phylogenetic analysis showed that they can be clustered into four different families. Incongruencies were observed between the phylogenies of the transposable elements and those of their hosts, suggesting that horizontal transfer may have occurred between some of the species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW (2006) MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W369–W373
Besansky JN, Mukabayire O, Bedell AJ, Lusz H (1996) Pegasus, a small inverted repeat transposable element found in the white gene of Anopheles gambiae. Genetica 98:119–129
Biémont C, Vieira C (2006) Junk DNA as an evolutionary force. Nature 443:521–524
Borsatti F, Azzoni P, Mandrioli M (2003) Identification of a new hobo element in the cabbage moth, Mamestra brassicae (Lepidoptera). Hereditas 139:151–155
Calvi BR, Hong TJ, Findley SD, Gelbart WM (1991) Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of inverted repeat transposons in Drosophila and plants: hobo, Activator, and Tam3. Cell 66:465–471
Capy P, Bazin C, Higuet D, Langin T (eds) (1998) Dynamics and evolution of transposable elements. Landes Bioscience, Austin, Texas
Casola C, Lawing AM, Betrán E, Feschotte C (2007) PIF-like transposons are common in Drosophila and have been repeatedly domesticated to generate new host genes. Mol Biol Evol 24:1872–1888
Clark AG, Eisen MB, Smith DR, Bergman CM, Oliver B, Markow TA, Kaufman T, Kellis M, Gelbart W et al (2007) Evolution of genes and genomes on the Drosophila phylogeny. Nature 450:203–218
Coates CJ, Johnson KN, Perkins HD, Howells AJ, O’Brochta DA, Atkinson PW (1996) The hermit transposable element of the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina, belongs to the hAT family of transposable elements. Genetica 97:23–31
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Daniels SB, Chovnick A, Boussy A (1990) Distribution of hobo transposable elements in the genus Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 7:589–606
EMBOSS (2007) EMBOSS. http://emboss.sourceforge.net. Cited 12 Sept 2007
Essers L, Kunze R (1995) Transposable elements Bg (Zea mays) and Tag1 (Arabidopsis thaliana) encode protein sequences with homology to Ac like transposases. Maize Genet Coop Newslett 69:38–41
Essers L, Adolphs RH, Kunze R (2000) A highly conserved domain of the maize Activator transposase is involved in dimerization. Plant Cell 12:211–224
Ferris PJ (1989) Characterization of a Chlamydomonas transposon, Gulliver, resembling those in higher plants. Genetics 122:363–377
FlyBase BLAST Service (2007) FlyBase. http://flybase.bio.indiana.edu/blast. Cited 12 Sept 2007
GenBank (2007) National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Cited 12 Sept 2007
Handler AM (2003) Isolation and analysis of a new hopper hAT transposon from the Bactrocera dorsalis white eye strain. Genetica 118:17–24
Handler AM, Gomez SP (1997) A new hobo, Ac, Tam3 transposable element, hopper, from Bactrocera dorsalis is distantly related to hobo and Ac. Gene 185:133–135
Henikoff S, Henikoff JG, Alford WJ, Pietrokovski S (1995) Automated construction and graphical presentation of protein from unaligned sequences. Gene 163:GC17–GC26
Hickman AB, Perez ZN, Zhou LQ, Musingarimi P, Ghirlando R, Hinshaw JE, Craig NL, Dyda F (2005) Molecular architecture of a eukaryotic DNA transposase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:715–721
Kaminker JS, Bergman CM, Kronmiller B, Carlson J, Svirskas R, Patel S, Frise E, Wheeler DA, Lewis SE, Rubin GM, Ashburner M and Celniker SE (2002) The transposable elements of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatin: a genomics perspective. Genome Biol 3: research0084.1–84.2
Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Jurka J (2003) HAT1_AG: a family of autonomous hAT-like DNA transposons from African malaria mosquito. Repbase Reports, vol 3, p 58
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2005a) hAT-1_DP, a family of autonomous hAT transposons from Drosophila pseudoobscura. Repbase Reports, vol 5, p 44
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2005b) hAT-2_AG: a family of autonomous hAT DNA transposons from African malaria mosquito. Repbase Reports, vol 5, p 46
Karolchik D, Baertsch R, Diekhans M, Furey TS, Hinrichs A, Lu YT, Roskin KM, Schwartz M, Sugnet CW, Thomas DJ, Weber RJ, Haussler D, Kent WJ (2003) The UCSC genome browser database. Nucleic Acids Res 31:51–54
Karolchik D, Hinrichs AS, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Sugnet CW, Haussler D, Kent WJ (2004) The UCSC table browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D493–D496
Kempken F, Kück U (1996) Restless, an active Ac-like transposon from the fungus Tolypocladium inflatum: structure, expression, and alternative RNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol 16:6563–6572
Kempken F, Windhofer F (2001) The hAT family: a versatile transposon group common to plants, fungi, animals, and man. Chromosoma 110:1–9
Kent WJ (2002) BLAT – the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res 12:656–664
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (2001) Perspective: transposable elements, parasitic DNA, and genome evolution. Evolution 55:1–24
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Le Rouzic A, Capy P (2005) The first steps of transposable elements invasion: parasitic strategy versus genetic drift. Genetics 169:1033–1043
Marchler-Bauer A, Bryant SH (2004) CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Nucleic Acids Res 32(W):327–331
Michel K, O’Brochta DA, Atkinson PW (2003) The C-terminus of the Hermes transposase contains a protein multimerization domain. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:959–970
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr (1997) GeneDoc: a tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments. http://www.psc.edu/biomed/genedoc
ORF Finder (Open Reading Frame Finder) (2006) National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html. Cited 12 Sept 2007
Pardue ML, DeBaryshe PG (2003) Retrotransposons provide an evolutionarily robust non-telomerase mechanism to maintain telomeres. Annu Rev Genet 37:485–511
Pinkerton AC, Whyard S, Mende HA, Coates CJ, O’Brochta DA, Atkinson PW (1999) The Queensland fruit fly, Bactrocera tryoni, contains multiple members of the hAT family of transposable elements. Insect Mol Biol 8:423–434
Rubin E, Lithwick G, Levy AA (2001) Structure and evolution of the hAT transposon superfamily. Genetics 158:949–957
Saiton N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstruction of phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Silva JC, Kidwell MG (2000) Horizontal transfer and selection in the evolution of P elements. Mol Biol Evol 17:1542–1557
Simmons G (1992) Horizontal transfer of hobo transposable elements within the Drosophila melanogaster species complex: evidence from DNA sequencing. Mol Biol Evol 9:1050–1060
Streck RD, MacGaffey JE, Beckendorf SK (1986) The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J 5:3615–3623
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Volff J-N (2006) Turning junk into gold: domestication of transposable elements and the creation of new genes in eukaryotes. BioEssays 28:913–922
Warren WD, Atkinson PW, O’Brochta (1994) The Hermes transposable element from the house fly, Musca domestica, is a short inverted repeat-type element of the hobo, Ac, and Tam3 (hAT) element family. Genet Res 64:87–97
Warren WD, Atkinson PW, O’Brochta (1995) The Australian bushfly Musca vetustissima contains a sequence related to transposons of the hobo, Ac and Tam3 family. Gene 154:133–134
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, Paux E, SanMiguel P, Schulman AH (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Drosophila genome projects for making sequences freely available to the scientific community; M. Sc. Lizandra Robe and Nina R. Mota for help with the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from FAPERGS (0411965 and 07511528) and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Freitas Ortiz, M., Loreto, E.L.S. Characterization of new hAT transposable elements in 12 Drosophila genomes. Genetica 135, 67–75 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9259-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9259-5