Abstract
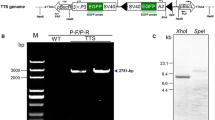
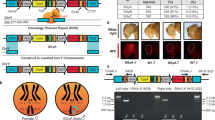
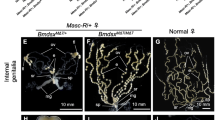
In deletion-mapping of W-specific RAPD (W-RAPD) markers and putative female determinant gene (Fem), we used X-ray irradiation to break the translocation-carrying W chromosome (WZe). We succeeded in obtaining a fragment of the WZe chromosome designated as Ze W, having 3 of 12 W-RAPD markers (W-Bonsai, W-Yukemuri-S, W-Yukemuri-L). Inheritance of the Ze W fragment by males indicates that it does not include the Fem gene. On the basis of these results, we determined the relative positions of W-Yukemuri-S and W-Yukemuri-L, and we narrowed down the region where Fem gene is located. In addition to the Ze W fragment, the Z chromosome was also broken into a large fragment (Z1) having the +sch (1-21.5) and a small fragment (Z2) having the +od (1-49.6). Moreover, a new chromosomal fragment (Ze WZ2) was generated by a fusion event between the Ze W and the Z2 fragments. We analyzed the genetic behavior of the Z1 fragment and the Ze WZ2 fragment during male (Z/Z1 Ze WZ2) and female (Z1 Ze WZ2/W) meiosis using phenotypic markers. It was observed that the Z1 fragment and the Z or the W chromosomes separate without fail. On the other hand, non-disjunction between the Ze WZ2 fragment and the Z chromosome and also between the Ze WZ2 fragment and the W chromosome occurred. Furthermore, the females (2A: Z/Ze WZ2/W) and males (2A: Z/Z1) resulting from non-disjunction between the Ze WZ2 fragment and the W chromosome had phenotypic defects: namely, females exhibited abnormal oogenesis and males were flapless due to abnormal indirect flight muscle structure. These results suggest that Z2 region of the Z chromosome contains dose-sensitive gene(s), which are involved in oogenesis and indirect flight muscle development.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Ohbayashi F, Harada T, Shimada T, Yokoyama T, Kobayashi M, Oshiki T (1996) An application of DNA diagnosis method for preservation of the susceptible strain to densonucleosis virus type-1 of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Sericult Sci Jpn 65:196–200 (in Japanese with English summary)
Abe H, Kanehara M, Terada T, Ohbayashi F, Shimada T, Kawai S, Suzuki M, Sugasaki T, Oshiki T (1998) Identification of novel random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) on the W chromosome of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori, and the wild silkworm, B. mandarina, and their retrotransposable element-related nucleotide sequences. Genes Genet Syst 73:243–254
Abe H, Seki M, Ohbayashi F, Tanaka N, Yamashita J, Fujii T, Yokoyama T, Takahashi M, Banno Y, Sahara K, Yoshido A, Ihara J, Yasukochi Y, Mita K, Ajimura M, Suzuki MG, Oshiki T, Shimada T (2005a) Partial deletions of the W chromosome due to reciprocal translocation in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Mol Biol 14:339–352
Abe H, Mita K, Yasukochi Y, Oshiki T, Shimada T (2005b) Retrotransposable elements on the W chromosome of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:144–151
Bainbridge D (2003) The X in Sex. Harvard University Press, London
Ball E, Ball SP, Sparrow JC (1985) A mutation affecting larval muscle development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet 6:77–92
Bernstein AI, Mogami K, Donady JJ, Emerson CP (1983) Drosophila muscle myosin heavy chain encoded by a single gene in a cluster of muscle mutations. Nature 302:393–397
Bortoluzzi S, Rampoldi L, Simionati B, Zimbello R, Barbon A, d’Alessi F, Tiso N, Pallavicini A, Toppo S, Cannata N, Valle G, Lanfranchi G, Danieli GA (1998) A comprehensive, high-resolution genomic transcript map of human skeletal muscle. Genome Res 8:817–825
Cripps RM, Ball E, Stark M, Lawn A, Sparrow JC (1994) Recovery of dominant, autosomal flightless mutants of Drosophila melanogaster and identification of a new gene required for normal muscle structure and function. Genetics 137:151–164
Doira H (1978) Genetic stocks of the silkworm: In: Tazima Y (ed), The silkworm, an important laboratory tool. Kodansha Ltd., Japan
Eric JV, Bruce TL (2004) How mammalian sex chromosome acquired their peculiar gene content. BioEssays 26:159–169
Fujii H, Banno Y, Doira H, Kihara H, Kawaguchi Y (1998) Genetical stocks and mutations of Bombyx mori: important genetic resources. 2nd edn. Institute of Genetic Resources, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, p54
Fujii T, Tanaka N, Yokoyama T, Ninagi O, Oshiki T, Ohnuma A, Tazima Y, Banno Y, Ajimura M, Mita K, Seki M, Ohbayashi F, Shimada T, Abe H (2006) The female-killing chromosome of the silkworm, Bombyx mori, was generated by translocation between Z and W chromosomes. Genetica 127:253–265
Fujiwara H, Ninaki O, Kobayashi M, Kusuda J, Maekawa H (1991) Chromosomal fragment responsible for genetic mosaicism in larval body marking of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genet Res 57:11–16
Fujiwara H, Maekawa H (1994) RFLP analysis of chromosomal fragments in genetic mosaic strain of Bombyx mori. Chromosoma 103:468–474
Hasimoto H (1933) The role of the W-chromosome in the sex determination of Bombyx mori. Jpn J Genet 8:245–247 (in Japanese)
Hasimoto H (1948) Sex-limited zebra, an X-ray mutation in the silkworm. J Sericult Sci Jpn 16:62–64 (in Japanese with English summary)
Hurst LD, Randerson JP (1999) An exceptional chromosome. Trends Genet 15:383–385
Kawamura N (1988) The egg size determining gene, Esd, is a unique morphological marker on the W chromosome of Bombyx mori. Genetica 76:195–201
Kawaguchi Y (1995) Genetic analysis of the soft and elongated trunk mutant in Bombyx mori. J Sericult Sci Jpn 64:31–34
Koike Y, Mita K, Suzuki MG, Maeda S, Abe H, Osoegawa K, deJong PJ, Shimada T (2003) Genomic sequence of a 320-kb segment of the Z chromosome of Bombyx mori containing a kettin ortholog. Mol Gen Genomics 269:137–149
Kondoh Y, Obara Y (1982) Anatomy of motoneurones innervating mesothoracic indirect flight muscles in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Exp Biol 98:23–27
Marec F, Mirchi R (1990) Genetic control of the pest Lepidoptera: gamma-ray induction of translocations between sex chromosomes of Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Stored Prod Res 26:109–116
Marec F (1996) Synaptonemal complex in insects. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 25:205–233
Marec F, Neven LG, Robinson AS, Vreysen M, Goldsmith MR, Nagaraju J, Franz G (2005) Development of Genetic sexing strains in Lepidoptera: from traditional to transgenic approaches. J Econ Entomol 98:248–259
Marec F, Tothova A, Sahara K, Traut W (2001) Meiotic pairing of sex chromosome fragments and its relation to atypical transmission of a sex-linked marker in Ephestia kuehniella (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Heredity 87:659–671
Mogami K, O’Donnell PT, Bernstein SI, Wright TRF, Emerson CP (1986) Mutations of the Drosophila myosin heavy-chain gene: effects on transcription, myosin accumulation, and muscle function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1393–1397
Mogami K, Hotta Y (1981) Isolation of Drosophila flightless mutants which affect myofibrillar proteins of indirect flight muscle. Mol Gen Genet 183:409–417
Murakami A, Imai HT (1974) Cytological evidence for holocentric chromosomes of the silkwoms, Bombyx mori and B. mandarina (Bombycidae, Lepidoptera). Chromosoma 47:167–178
Nagaraja GM, Mahesh G, Satish V, Madhu M, Muthulakshmi M, Nagaraju J (2005) Genetic mapping of Z chromosome and identification of W chromosome-specific markers in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Heredity 95:148–157
Newman SM, Wright TRF (1983) lethal(1)fibrillardysgenesis. A mutation affecting muscle development in the embryo of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet 4:329–345
Ohnuma A (1988) Synthesis of balanced sex-linked lethal strain in the silkworm. Rep Silk Sci Res Inst (Tokyo, Japan) 36:17–25 (in Japanese with English summary)
Sahara K, Yoshido A, Kawamura N, Ohnuma A, Abe H, Mita K, Oshiki T, Shimada T, Asano S-I, Bando H, Yasukochi Y (2003) W-derived BAC probes as a new tool for identification of the W chromosome and its aberrations in Bombyx mori. Chromosoma 112:48–55
Saifi GM, Chandra HS (1999) An apparent excess of sex- and reproduction-related genes on the human X chromosome. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 266:203–209
Strunnikov VA (1975) Sex control in silkworms. Nature 255:111–113
Sturtevant AH (1915) No crossing over in the female of the silkworm moth. Am Nat 49:42–44
Suzuki MG, Shimada T, Kobayashi M (1998) Absence of dosage compensation at the transcription level of a sex-linked gene in a female heterogametic insect, Bombyx mori. Heredity 81:275–283
Suzuki MG, Shimada T, Kobayashi M (1999) Bm kettin, homologue of the Dorosophila kettin gene, is located on the Z chromosome in Bombyx mori and is not dosage compensated. Heredity 82:170–179
Tanaka Y (1913a) A study of mendelian factors in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Coll Agric Sapporo 5:61–113
Tanaka Y (1913b) Gametic coupling and repulsion in silkworms. J Coll Agric Sapporo 5:115–148
Tanaka Y (1916) Genetic studies in the silkworm. J Coll Agric Sapporo 6:1–33
Tanaka Y (1923) Inheritance of elongate (a preliminary note). Sanshikaiho 32:21–23
Traut W, Sahara K, Otto TD, Marec F (1999) Molecular differentiation of sex chromosome probed by comparative genomic hybridization. Chromosoma 108:173–180
Warmke JW, Kreuz AJ, Falkenthal S (1989) Co-localization to chromosome bands 99E1-3 of the Drosophila melanpgaster myosin light chain-2 gene and a haplo-insufficient locus that affects flight behavior. Genetics 122:139–151
Yokoyama T, sugai E, Oshiki T, Pan Q (1990) Induction of the triploid silkworm, Bombyx mori, by the hot-water treatment to the inseminated eggs immediately after oviposition. J Sericult Sci Jpn 59:281–224
Yoshido A, Bando H, Yasukochi Y, Sahara K (2005) The Bombyx mori karyotype and the assignment of linkage groups. Genetics 170(2):675–685
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from BRAIN (to. K. M.), Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, MEXT (Nos. 17052006, 16011263, and 17018007) and JSPS (No. 16208006), the Insect Technology Project, MAFF/NIAS (No. 1216), and the National Bioresource Project, MEXT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, T., Yokoyama, T., Ninagi, O. et al. Isolation and characterization of sex chromosome rearrangements generating male muscle dystrophy and female abnormal oogenesis in the silkworm, Bombyx mori . Genetica 130, 267–280 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9104-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9104-7