Abstract
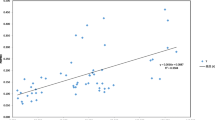
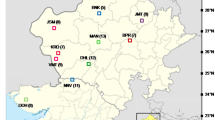
Lamiophlomis rotata (Lamiaceae), a perennial medicinal herb, is endemic to the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. A total of 188 individuals from eight natural populations of L. rotata in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (four from Tibet, two from Yunnan, and two from Qinghai) were analyzed using intersimple sequence repeats (ISSR) and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) techniques. Our results revealed that the level of genetic variation in L. rotata was relatively high (P = 94.85%, I = 0.440 ± 0.220, H T = 0.289 ± 0.028). Three genetic groups corresponding to the three geographic regions were detected, suggesting significant geographic structure. Our results suggest that the highly structured geographic pattern found in L. rotata might represent diverging evolutionary processes associated with the uplifting of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and Quaternary climatic oscillations. These findings imply that as many populations as possible should be preserved in situ for the conservation of this species. Given their genetic variability and peripheral distribution, Qinghai and Yunnan populations should be assigned priority for conservation. Optimal harvesting strategies, domestication and tissue culture of L. rotata should be developed as soon as possible to guarantee its sustainable use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya–Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411:62–66
Aparicio A, Albaladejo RG, Porras M, Ceballos G (2000) Isozyme evidence for natural hybridization in Phlomis (Lamiaceae): hybrid origin of the rare P. x margaritae. Ann Bot 85:7–12
Batygina TB (1999) Genetic heterogeneity of seeds in terms of embryology. Russian J Plant Physiol 46:374–388
Ben FN, Boussaid M (2004) Genetic diversity in wild Tunisian populations of Mentha pulegium L. (Lamiaceae). Genet Resour Crop Evol 51:309–321
Bossart JL, Prowell DP (1998) Genetic estimates of population structure and gene flow: limitations, lessons and new directions. Trends Ecol Evol 13:202–206
Chen SL, Xia T, Chen SY, Zhou YJ (2005) RAPD profiling in detecting genetic variation in endemic Coelonema (Brassicaceae) of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau of China. Biochem Genet 43:189–201
Chung HG, Chung JM, Chung MG (1998) Allozyme variation in six flowering plant species characterizing Ullung Island, Korea. Jpn J Bot 73:241–247
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Dominguez CA, Abarca CA, Eguiarte LE, Molina FF (2005) Local genetic differentiation among populations of the mass-flowering tropical shrub Erythroxylum havanens (Erythroxylaceae). New Phytol 166:663–672
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Fracaro F, Zacaria J, Echeverrigaray S (2005) RAPD based genetic relationships between populations of three chemotypes of Cunila galioides Benth. Biochem Syst Ecol 33:409–417
Ge XJ, Zhang LB, Yuan YM, Hao G, Chiang TY (2005) Strong genetic differentiation of the East-Himalayan Megacodon stylophorus (Gentianaceae) detected by Inter-Simple Sequence Repeats (ISSR). Biodivers Conserv 14:849–861
Godt MJW, Walker J, Hamrick JL (2004) Allozyme diversity in Macbridea alba (Lamiaceae), an Endemic Florida Mint. J Hered 95:244–249
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1996) Effect of life history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philos Trans R Soc London B Biol Sci 351:1291–1298
Harris SA (1999) RAPDs in systematics—a useful methodology? In: Hollingsworth PM, Bateman RM, Gornall RJ (eds) Molecular systematics and plant evolution, Taylor and Francis, London, UK, pp. 221–228
Hewitt GM (2004) Genetic consequences of climatic oscillations in the Quaternary. Philos Trans R Soc London B Biol Sci 359:183–195
Holsinger KE, Lewis PO (2003) Hickory: a package for analysis of population genetic data v.1.0. Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, USA
Isabel N, Beaulieu J, Theriault P, Bousquet J (1999) Direct evidence for biased gene diversity estimates from dominant random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprints. Mol Ecol 8:477–483
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles rescherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44:223–270
Jiao K, Shan Y (2003) The quaternary glaciations and glacier properties in the Tanggula range. J Glaci Geocry 25:34–42
Judd WS, Campbell CS, Kellog EA, Stevens PF (1999) A phylogenetic approach in plant systematics. Sinauer, Sunderland MA, USA
Levin DA (1970) Developmental instability and evolution in peripheral isolates. Am Nat 104:343–353
Lewontin RC (1984) Detecting population differences in quantitative characters as opposed to gene frequencies. Am Nat 123:115–124
Li HL, Hao MA, Wang BT, Bai L (2002) Studies on the analgesic action of Tibetan Herb Lamiphlomis inhibiting pain induced by cancer. J Hebei Medi 24:146–147
Li JJ, Zheng BX, Yang XJ, Xie YQ, Zhang LY, Ma ZH, Xu SY (1986) The quaternary glaciation in the Taggula range. In: Xu SY (ed) Glaciers of Xizang (Tibet). Science Press, Beijing, pp 238–242
Li XW (1989) The geographical distribution of Labiatae in HengDuan Mountains. Bull Bot Res 9:103–112
Liu JQ, Wang YJ, Wang AL, Hideaki O, Abbott RJ (2006a) Radiation and diversification within the Ligularia–Cremanthodium–Parasenecio complex (Asteraceae) triggered by uplift of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Mol Phylogenet Evol 38:31–49
Liu JQ, Gao TG, Chen ZD, Lu AM (2002) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau endemic Nannoglottis (Asteraceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:307–325
Liu ZM, Zhao AM, Kang XY, Zhou SL, López-Pujol J (2006b) Genetic diversity, population structure, and conservation of Sophora moorcroftiana (Fabaceae), a shrub endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Plant Biol 8:81–92
López-Pujol J, Orellana MR, Bosch M, Simon J, Blanché C (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on allozyme diversity and conservation status of the coastal sand dunes plant Stachys maritima (Lamiaceace) in the Iberian Peninsula. Plant Biol 5:504–512
Macey JR, Schulte JA, Larson A, Fang ZL, Wang YZ, Tuniyev BS, Papenfuss TJ (1998) Phylogenetic relationships of toads in the Bufo bufo species group from the eastern escarpment of the Tibetan plateau: a case of vicariance and dispersal. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9:80–87
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:175–178
Mattner J, Zawko G, Rossetto M, Krauss SL, Dixon KW, Sivasithamparam K (2002) Conservation genetics and implications for restoration of Hemigenia exilis (Lamiaceae), a serpentine endemic from Western Australia. Conserv Biol 107:37–45
Mayr E (1963) Animal species and evolution. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Miller MP (1997) Tools for population genetic analysis. Version 1.3. Department of Biological Sciences, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff
Morden CW, Loeffler W (1999) Fragmentation and genetic differentiation among subpopulations of the endangered Hawaiian mint Haplostachys haplostachya (Lamiaceae). Mol Ecol 8:617–625
Moritz C (1994) Defining evolutionarily significant units for conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 9:373–375
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetics distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Nei M, Maruyama T, Chakraborty R (1975) The bottleneck effect and genetic variability in populations. Evolution 29:1–10
Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol Ecol 13:1143–1155
Olmstead RG (1990) Biological and historical factors influencing genetic diversity in the Scutellaria angustifolia complex (Labiatae). Evolution 44:54–70
Palombi MA, Damiano C (2002) Comparison between RAPD and ISSR molecular markers in detecting genetic variation in kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa A. Chev). Plant Cell Rep 20:1061–1066
Pang J, Wang Y, Zhong Y, Hoelzel AR, Papenfuss TJ, Zeng X, Ananjeva NB, Zhang YP (2003) A phylogeny of Chinese species in the genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:398–409
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (1999) A comparison of the taxonomic richness of vascular plants in China and the United States. Am Nat 154:160–181
Qian W, Ge S, Hong DY (2001) Genetic variation within and among populations of a wild rice Oryza granulata from China detected by RAPD and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 102:440–449
Qu YH, Ericson PG, Lei FM, Li SH (2005) Postglacial colonization of the Tibetan plateau inferred from the matrilineal genetic structure of the endemic red-necked snow finch, Pyrgilauda ruficollis. Mol Ecol 14(6):1767–1781
Renau-Morata B, Nebauer SG, Sales E, Arrillaga I, Caligari P, Segura J (2005) Genetic diversity and structure of natural and managed populations of Cedrus atlantica (Pinaceae) assessed using random amplified polymorphic DNA. Am J Bot 92:875–884
Richards AJ (1986) Plant breeding systems. George Allen and Unwin, London, UK
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.02. Exeter Software, Setauket, NY, USA
Roslin T (2001) Spatial population structure in a patchily distributed beetle. Mol Ecol 10:823–837
Ryder OA (1986) Conservation and systematics: the dilemma of subspecies. Trends Ecol Evol 1:9–10
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin ver. 2.000: a software for population genetics data analysis. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Switzerland
Shi YF, Li JJ, Li BY, Pan BT, Fang XM, Yao CD, Wang SM, Cui ZJ, Li SJ (1998) Uplift and environmental evolution of Qinghai–Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau. In: Sun H, Zheng D (eds) Formation, evolution and development of Qinghai–Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau, Guangdong Science & Technology Press. Guangzhou, pp. 73–138
Souframanien J, Gopalakrishna T (2004) A comparative analysis of genetic diversity in blackgram genotypes using RAPD and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:1687–1693
Sun H (2002) Tethys retreat and Himalayas–Hengduanshan mountains uplift and their significance on the origin and development of the Himalayan elements and alpine flora. Acta Bot Yunnanica 24:273–288
Van Treuren R, Bijlsma R, Van Delden W, Ouborg NJ (1991) The significance of genetic erosion in the process of extinction. I. Genetic differentiation in Salvia pratensis and Scabiosa columbaria in relation to population size. Heredity 66:181–189
Vazquez JL, Gomez-Mercado F, Guerrero JLG, Rodriguez-Garcia I, Garcia-Maroto F (1999) Genetic relationships and population structure within taxa of the endemic Sideritis pusilla (Lamiaceae) assessed using RAPDs. Bot J Linn Soc 129:345–358
Vinceti B, Van Breuge P, Amaral1 W (2004) The practical implications of research outputs from forest genetic studies. In: Vinceti B, Amaral W, Meilleur B (eds) Challenges in managing forest genetic resources for livelihoods, International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, pp 245–267
Wallace LE (2002) Examining the effects of fragmentation on genetic variation in Platanthera leucophaea (Orchidaceae): inferences from allozyme and random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Plant Spec Biol 17:37–49
Wang A, Yang M, Liu J (2005) Molecular phylogeny, recent radiation and evolution of gross morphology of the rhubarb genus Rheum (Polygonaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA trnL-F sequences. Ann Bot (Lond) 96:489–498
Wang G (2001) Studies on the therapeutic effects of rheumatic arthritis of 72 cases using Duyiwei Pian. Chinese Tradit Med Inform J 8:72
Waples RS (1991) Pacific salmon, Oncorynchus spp., and the definition of a “species” under the Endangered Species Act. Mar Fish Rev 53:11–22
Wu CY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing
Wu CY, Li XW (1982) On the evolution and distribution in Labiatae. Acta Bot Yunnanica 4:97–118
Wu CY (1987) Flora of Tibet. Vol. 5. Science Press, Beijing
Wu CY, Li XW (1977) Flora of China. Vol. 65(2). Science Press, Beijing
Wu SG, Yang YP, Fei Y (1995) On the flora of the alpine region in the Qinghai–Xizang (Tibet) plateau. Acta Bot Yunnanica 17:233–250
Xia T, Chen SL, Chen SY, Ge XJ (2005) Genetic variation within and among populations of Rhodiola alsia (Crassulaceae) native to the Tibetan Plateau as detected by ISSR markers. Biochem Genet 43:87–101
Yang ZR (2003) The effects of thymic factor D and DuYiWei treatment for MDR-TB. Chinese Clini New Med 3:52
Yeh FC, Yang R, Boyle T (1997) POPGENE Version 1.32. Ag/For Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta and Center for International Forestry Research
Yi JH, Yan XZ, Luo ZY, Zhong ZC (1995) Study on chemical components in root of Lamiophlomis rotata, a Tibetan medicine. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 30:206–210
Yi JH, Zhang GL, Li BG, Chen YZ (1999) Phenylpropanoid glycosides from Lamiophlomis rotata. Phytochemistry 51:825–828
Yuan W, Song YC, Liang ZF (2003) Comparison of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory action of Tibetan herb Lamiphlomis from different growing area in mice. China Pharm 14:716–717
Zeng Y, Chen XJ, Chen ZL (2001) Advances in studies on traditional Tibetan herb Lamiophlomis rotata. Chinese Traditional Herbal Drugs 32:1141–1143
Zhang D, Fengquan L, Jianmin B, (2000) Eco-environmental effects of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau uplift during the Quartenary in China. Environ Geol 39:1352–1358
Zhang FM, Kong H, Ge S (2003) Allozyme variation and population differentiation of the Aconitum delavayi complex (Ranunculaceae) in the Hengduan Mountains of China. Biochem Genet 41:47–55
Zhang YJ (2004) Studies on the therapeutic effects of breast swelling of 101 cases using Duyiwei Jiaonang. Chinese Tradit Patent Med 26:15
Zhang ZY, Chen YY, Li DZ (2005a) Detection of low genetic variation in a critically endangered chinese pine, Pinus squamata, using RAPD and ISSR markers. Biochem Genet 43:239–249
Zhang Q, Chiang TY, George M, Liu JQ, Abbott RJ (2005b). Phylogeography of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau endemic Juniperus przewalskii (Cupressaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence variation. Mol Ecol 14:3513–3524
Zheng HB, Powell CM, An ZS, Dong GR (2000) Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibet Plateau. Geology 8:715–718
Zhou JP (2004) Studies on the therapeutic effects of breast swelling of 86 cases using Duyiwei Jiaonang. Youjiang Med J 32:378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wang, L., Geng, Y. et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of Lamiophlomis rotata (Lamiaceae), an endemic species of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Genetica 128, 385–394 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-7517-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-7517-y