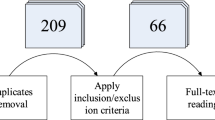
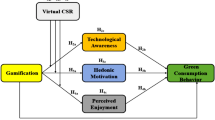
Abstract
Gamification has attracted the attention of many scholars of different fields such as education, commerce, management, urban planning, and citizen science since a decade ago. The review of the related literature indicates that there is a plethora of research on the implications of gamification in various fields. However, to the best of the researcher, these studies have not been synthesized yet. The main purpose of the study was to synthesize the relevant studies through a qualitative meta-analysis study. In so doing, different electrical database sources, including Google Scholar, Academia, Linked-in, Research gate, etc. were searched for the keywords: gamification, gamification implication, gamified* participation, etc. The data of the study were synthesized thorough qualitative meta-analysis. The findings were thematically analyzed and coded. Results showed that gamification has implications in education, e-learning, commerce, management, citizen participation, and motivation. The findings can be used by urban planners to provide citizens with playgrounds to play different games.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact the corresponding author for data requests.
References
Alawadhi, S., Scholl, H. J., Janssen, M., Wimmer, M. A., Moe, C. E., Flak, L. S., et al., Aldama-Nalda, A., Chourabi, H., Gil-Garcia, J. R., Leung, S., Mellouli, S., Nam, T., Pardo, T. A., & Walker, S. (Eds.). (2012). Building understanding of smart city initiatives: Electronic government. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Albino, V., Berardi, U., & Dangelico, R. (2015). Smart cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. Journal of Urban Technology, 22(1), 75–98.
Ampatzidou, C., Gugerell, K., Constantinescu, T., Devisch, O., Jauschneg, M., & Berger, M. (2018). All work and no play: Facilitating serious games and gamified applications in participatory urban planning and governance'. Urban Planning, 3(1), 34–46.
Angelakis, V., Tragos, E., Pöhls, H. C., Kapovits, A., & Bassi, A. (Eds.). (2017). Designing, developing, and facilitating smart cities: Urban dDesign to IOT solutions. Cham: Springer.
Barata, G., Gama, S., Fonseca, M., & Gonçalves, D. (2013). Improving student creativity with gamification and virtual worlds.. Gamification'13. Stratford, ON, Canada: ACM.
Basten, D. (2017). Gamification, software technology. IEEE Software. https://doi.org/10.1109/MS.2017.3571581.
Bilgihan, A., Kandampully, J., & Zhang, T. (2016). Towards a unified customer experience in online shopping environments: antecedents and outcomes. International Journal of Quality Service Sciences, 8(1), 102–119.
Bowser, A., Hansen, D., & Preece, J. (2013). Gamifying citizen science: Lessons and futuredirections. In Workshop on designing gamification: Creating gameful and playful experiences.
Bowser, A., Hansen, D., Preece, J., He, Y., Boston, C., & Hammock, J. (2014). Gamifying citizen science: a study of two user groups. In Proceedings of the companion publication of the 17th ACM conference on Computer supported cooperative work and social computing pp. (137–140)
Brown, E., & Cairns, P.(2004). A grounded investigation of game immersion. In Extended abstracts of the 2004 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI 2004, Vienna, Austria, April 24–29, 2004.
Brown, S. L., & Vaughan, C. C. (2009). Play: How it shapes the brain, open the imagination and invigorates the soul. New York: A Very Publishing Group.
Buck, M. F. (2017). Gamification of learning and teaching in schools: A critical stance. International Journal of Media, Technology and Lifelong Learning, 13(1), 35–54.
Budthimedhee, K., Li, J. H., & Pallathucheril, V. (2002). e Planning: A snapshot of the literature on using the world wide web in urban planning. Journal of Planning Literature, 17(2), 20–36.
Buscher, V., Tabet, M., Ashley, G., Doody, L., McDermott, J. & Tomordy, M. (2010) ‘Smart Cities Transforming the 21st century city via the creative use of technology’, Arup's IT & Communications Systems team.
Canter, M. (2010). Building a Digital City: Our Communal History, Infrastructure and Culture–to be. Digital City Mechanics, Inc. http://builddigcity.pbworks.com/f/Building_a_Digital_City_-_10-18-10.pdf.
Chakraborty, A. (2011). Enhancing the role of participatory scenario planning processes: Lessons from reality check exercises. Futures, 43(4), 387–399.
Clanton, C.(1998). An interpreted demonstration of computer game design. In Proceedings of ACM CHI 1998 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems: Summary, April 18–23, pp. 1–2.
Danowska‐Florczyk, E., & Mostowski, P. (2012). Gamification as a new direction in teaching Polish as a foreign language. ICT for Language Learning 5th edition. Accessed from https://www.pixel‐ online.org/
Dicheva, D., Dichev, C., Agre, G., & Angelova, G. (2015). Gamification in education: A systematic mapping study. Educational Technology and Society, 18(3), 75–88.
de Lange, M. (2015). The playful city Using play and games to foster participation. Lithuania: Mykolas Romeris University.
da Silva, R., Rodrigues, R. G., & Leal, C. T. P. (2019). Gamification in management education: A systematic literature review. Brazilian Administration Review, 6(2), 1–31.
Furdu, I., Tomozei, C., & Köse, U. (2017). Pros and cons gamification and gaming in classroom. Broad Research in Artificial Intelligence and Neuroscience, 8(2), 56–62.
Gafni, R., Achituv, D. B., Eidelman, S., & Chatsky, T. (2018). The effects of gamification elements in e-learning platforms. Online Journal of Applied Knowledge Management, 6(2), 37–53.
Hamari, J. (2011). Transforming homo economicus into homo ludens: A field experiment on gamification in a utilitarian peer-to-peer trading service. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 12(4), 236–245.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R. & Nacke, L. (2011). From game design elements to gamefulness: defining gamification. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, 9–15, ACM.
Devlin, S., Cowling, P., Kudenko, D., Goumagias, N., Nucciareli, A., & Cabras, I., … others. (2014). Game intelligence. In Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), 2014 IEEE Conference, 1–8.
Domínguez, A., de Navarrete, J. S., de Marcos, L., Fernández-Sanz, L., Pagés, C., et al. (2013). Gamifying learning experiences: Practical implications and outcomes. Computer Education, 63(1), 380–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.12.020.
Doumanis, I., & Smith, S. (2015). A framework for research in gamified mobile guide applications using embodied conversational agents (ECAs). International Journal of Serious Games, 2(3), 21–40.
Edwards, M., & Haines, A. (2007). Evaluating dmart Growth. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 27(1), 70–97.
Enders, B. (2013). Gamification, games and learning: What managers and practitioners need to know. The e-learning Guild.
Franzoni, C., & Sauermann, H. (2014). Crowd science: The organization of scientific research in open collaborative projects. Research Policy, 43(1), 1–20.
Glover, I. (2013). Play as you learn: Gamification as a technique for motivating learners. In Proceedings of the world conference on educational multimedia, hypermedia and telecommunications (MHT’13). AACE (pp. 1999–2008).
Ermi, L., & Mäyrä, F. (2004). Player-centred game design: Experiences in using scenario study to inform mobile game design. The International Journal of Computer Game Research., 5(1), 1–10.
Ermi, L., & Mäyrä, F. (2005). Fundamental components of the gameplay experience: Analysing immersion. In: Proceedings of the 2005 DiGRA. International Conference: Changing Views: Worlds in Play, DiGRA 2005, Vancouver, Canada.
Flanagan, M. (2009). Critical play: Radical game design. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press.
Freeman, M. (2013). The Game of things; A look at the new conceptual formation in the field of cyberspace and its applications: Hierarchy of concept and content studies, center for the development of Information technology and digital media.
Gabarron, E., Schopf, T., Serrano, J. A., Fernandez-Luque, L., & Dorronzoro, E. (2012). Gamification strategy on prevention of STDs for youth. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 192, 1066–1066.
Goehle, G. (2013). Gamification and web-based homework. PRIMUS, 23(3), 234–246.
Gordillo, A., Gallego, D., Barra, E., & Quemada, J. (2013). The city as a learning gamified platform. Frontiers in Education Conference (pp. 372–378). IEEE.
Gordon, M. (2014). Manual of nursing diagnosis. Burlington, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Gordon, E., & Baldwin-Philippi, J. (2014a). Playful civic learning: Enabling lateral trust and reflection in game-based public participation. International Journal of Communication., 8, 28.
Gordon, E., & Baldwin-Philippi, J. (2014b). Civic learning through civic gaming: Community plan it and the development of trust and reflective participation. International Journal of Communication, 8, 759–786.
Greenhill. A., Holmes. K., Lintott. C., Simmons. B., Masters. K., Cox, J., & Graham. G. (2014) Playing with science: Gamised aspects of gamification found on the online citizen science project-zooniverse. In GAMEON'2014 (pp. 15–24). EUROSIS.
Hamari, J., & Lehdonvirta, V. (2010). Game design as marketing: How game mechanics create demand for virtual goods. International Journal of Business Science and Applied Management, 5(1), 14–29.
Hamari, J., Koivisto, J., & Sarsa, H. (2014). Does gamification work? A literature review of empirical studies on gamification. In Proceedings of the annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences (pp. 3025–3034).
Hamari, J., & Koivisto, J. (2015). Working out for likes an empirical study on social influence in exercise gamification. Computers in Human Behavior, 50(4), 333–347.
Huotari, K., & Hamari, J. (2012) Defining gamification: a service marketing perspective. In Proceedings of the 16th international academic MindTrek conference (pp. 17–22).
Iacovides, I., Jennett, C., Cornish-Trestrail, C., & Cox, A. L. (2013). Do games attract or sustain engagement in citizen science? A study of volunteer motivations. In CHI’13 extended abstracts on human factors in computing systems (pp. 1101–1106).
Insley, V., & Nunan, D. (2013). Gamification and the online retail experience. International Journal Retail Distribution Manage, 42(5), 340–351.
Jennett, C., Cox, A. L., Cairns, P., Dhoparee, S., Epps, A., Tijs, T., Walton, A. (2008). Measuring and defining the experience of immersion in games. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 66(9), 641–661.
Kajan, E., Mahmood, Z., Dolićanin, Ć., Randjelović, D., & Stojanović, B. (2015). Handbook of research on democratic strategies and citizen-centered E-Government services. Hershey: IGI Global.
Kapp, K. M. (2012). The gamification of learning and instruction: Game-based methods and strategies for training and education (1st ed.). San Francisco: Wiley.
Kapp, K. M., Blair, L., & Mesch, R. (2014). The gamification of learning and instruction field book: Ideas into practice/Karl M. Lucas Blair, Rich Mesch, San Francisco, CA: Wiley
Karac, J., & Stabauer, M. (2017). Gamification in E-commerce: A survey based on the Octalysis framework. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317172222
Kazhamiakin, R., Marconi, A., Perillo, M., Pistore, M., Piras, L., Avesani, F., Perri, N. & Valetto, G.(2015). Using gamification to incentivize sustainable urban mobility. In 2015 IEEE first international smart cities conference (ISC2) (pp. 1–6). IEEE
Klimmt, C. (2003). Dimensions and determinants of the enjoyment of playing digital games: A three level model. Paper presented at the level up: Digital Games Research Conference, Utrecht, Netherlands.
Kozel, S. (2013). 18 Sinews of ubiquity: A corporeal ethics for ubiquitous computing. In U. Eackman (Ed.), Throughout: Art and culture emerging with ubiquitous computing (pp. 337–350). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Lerner, J. A. (2014). Making democracy fun: How game design can empower citizens and transform politics. MIT Press.
Li, C., Dong, Z., Untch, R. H., & Chasteen, M. (2013). Engaging computer science collaborative learning environment. International Journal of Information and Educational Technology, 3(1), 72–77.
MacDonald, E., Case, N., Clayton, J., Hall, M., Heavner, M., Lalone, N., et al. (2015). Aurorasaurus: A citizen science platform for viewing andreporting the aurora. Space Weather, 13(9), 548–559.
Manzini, E. (2015). Design, when everybody designs: An introduction to design for social Innovation. Massachusetts: MIT Press.
Mayer, I. S. (2009). The gaming of policy and the politics of gaming: A review. Simulation and Gaming, 40(6), 825–862.
Meske, C., Brockmann, T., Wilms, K., & Stieglitz, S. (2016). Social collaboration and gamification (pp. 93–109). Cham: Springer.
Moccozet, L., Tardy, C., Opprecht, W., & Léonard, M. (2013). Interactive collaborative learning (ICL). In International conference on interactive collaborative learning (ICL) (pp. 171–179). IEEE.
Morris, B. J., Croker, S., Zimmerman, C., Gill, D., & Romig, C. (2013). Gaming science: the “gamification” of scientific thinking. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00607.
Neuhofer, B., Buhalis, D., & Ladkin, A. (2012). Conceptualising technology enhanced destination experiences. Journal of Destination Marketing and Management, 1(1–2), 36–46.
Nijholt, A. (2017a) Humans as avatars in smart and playable cities, International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW) (pp. 190–193). IEEE.
Nijholt, A. (Ed.). (2017). Playable cities: The city as a digital playground. Springer: Singapore.
Nijholt, A., Romão, T. & Reidsma, D. (2012). Advances in computer entertainment: 9th International Conference, ACE 2012, Kathmandu, Nepal, November 3–5 2012: proceedings/Anton Nijholt, Teresa Romão, Dennis Reidsma (eds.) [Online], Heidelberg: Springer
Okeleke, K., Rogers, M., & Pedros, X. (2017). The mobile economy 2017. GSMA Intelligence. Accessed from https://www.gsmaintelligence.com/research/?
Oliver, R. L. (1997). Emotional expression in the satisfaction response. Satisfaction: A behavioral perspective on the consumer. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Olszewski, R., Turek, A., & Łączyński, M. (Eds.) (2016).Urban gamification as a source of information for spatial data analysis and predictive participatory modelling of a city’s development (5th ed).
Oudenampsen, M. (2013). Aldo van Eyck and the City as Playground. http://www.merijnoudenampsen.org/2013/03/27/aldo-van-eyck-and-the-city-asplayground.
Pine B, J., & Gilmore H, J. (1999) The experience economy: Work is theatre and every business a stage. Boston: Harvard Business Press.
Prestopnik, N. R., & Tang, J. (2015). Points, stories, worlds, and diegesis: Comparing player experiences in two citizen science games. Computers in Human Behavior, 52(2015), 492–506.
Popa, D. M. (2013). Design case: Gamification of ERP—A user centered design approach. Paper presented at the CHI 2013 workshop: Designing gamification: Creating gameful and playful experiences. Paris, France. Retrieved from http://gamification-research.org/wpcontent/uploads/2013/03/Popa.pdf
Queiroz, F., & Spitz, R. (2016). The lens of the lab: Design challenges in scientific software. The International Journal of Design Management and Professional Practice, 10(3), 17–45.
Ratti, C. (2014). The Sense-able City: We don’t need to build new cities—a simple reboot of the existing ones will do. The European. Accessed from https://www.theeuropean
Rehm, S., Foth, M., & Mitchell, P. (2018). DoGood: Examining gamification, civic engagement, and collective intelligence. AI and SOCIETY, 33(1), 27–37.
Robson, K., Plangger, K., Kietzmann, J. H., McCarthy, I., & Pitt, L. (2016). Game on: Engaging customers and employees through gamification. Business Horizons, 59(1), 29–36.
Rouse, K. (2013). Gamification in science education: The relationship of educational games to motivation and achievement. Hattiesburg: The University of Southern Mississippi.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68–78.
Scholl, H. J., & Scholl, M. C. (2014). Smart governance: A roadmap for research and practice. In conference 2014 proceedings. http://hdl.handle.net/2142/47408.
Simmons, B., Lintott, C., Masters, K., Greenhill, A., Graham, G., & Holmes, K. (2015). Defining and measuring success in online citizen science: A case study. Computing in Science and Engineering, 17(4), 28–36.
Schiano, D. J., & White, S. (1998). The first noble truth of cyberSpace: People are people (even when they MOO). In Proceeding of the CHI '98 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Los Angeles, California, USA, April 18–23, 1998.
Schrope, M. (2013). Solving tough problems with games. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(18), 7104–7106.
Seaborn, K., & Fels, D. I. (2015). Gamification in theory and action: a survey. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 74, 14–31.
Spitz, R., Junior, C. P., Queiroz, F., Leite, L. C., Dam, P., Ferranti, M. P., et al. (2017). Gamification, citizen science and civic engagement: In search of the common good. Strategic Design Research Journal, 11(3), 263–273.
Thiel, S.-K. (2017). ‘Let’s play urban planner: The use of game elements in public participation platforms. Next Generation Planning, 4(1), 58–75. https://doi.org/10.24306/plnxt.2017.04.005.
Thiel, S. K., & Lenher, U. (2015). Exploring the effects of game elements in m-participation. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/300204780.
Upton, L. (2016). How gamification of travel is aiming to boost ridership in Italy. London: SMARTRAIL WORLD.
Urh, M., Goran, V., Eva, J., & Rok, P. (2015). The model for introduction of gamification into e-learning in higher Education. Procedia-Social Behaviour Science, 197(2015), 388–397.
Vargo, S. L., & Lusch, R. F. (2008). Service-dominant logic: Continuing the evolution. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 36(1), 1–10.
Velibeyoglu, K. (1999). Impacts of new information technologies upon built environment. http://www.angelfire.com/ar/corei/infotech.html
Villagrasa, S., & Duran, J. (2013). Gamification for learning 3D computer graphics arts. In Proceedings of the first international conference on technological ecosystem for enhancing multiculturality (pp. 429‐433). ACM.
Wanick, V., & Bui, H. (2019). Gamification in management: analysis and research directions. International Journal of Serious Games, 6(2), 57–74.
Watson, D., Hancock, M., & Mandryk, R. L. (2013). Gamifying behavior that leads to learning. In Gamification'13 (pp. 87–90).
Weiser, M. (1991). The computer for the 21st century. Scientific American, 265(3), 66–75.
Wolfinbarger, M., & Gilly, M. C. (2001). Shopping online for freedom, control and fun. California Management Review, 43, 34–55.
Wongso, O., Rosmansyah, Y., & Bandung, Y. ( 2014). Gamification framework model, based on social engagement in e-learning 2.0. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Technology, Informatics, Management, Engineering and Environment, Aug. 19–21, Bandung: IEEE Xplore Press, pp. 10–14.
Xu, C., Li, M. F., Wu, J. K., Guo, H., Li, Q., Zhang, Y. E., Chai, J. J., Li, T. Z., & Xue, Y. B. (2013). Identification of a canonical SCF(SLF) complex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility of Pyrus (Rosaceae). Plant Molecular Biology, 81, 245–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9995-x.
Zichermann, G., & Cunningham, C. (2011). Gamification by design: Implementing game mechanics in web and mobile apps. Sebastopol: O'Reilly.
Zichermann, G., & Linder, J. (2013). The gamification revolution: How leaders leverage game mechanics to crush the competition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Funding
Funding is not applicable to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GRL guided the study and edited the English version. MPM and HAK researchers compiled the study and translated it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal rights
Hereby, it is declared that all ethical considerations were taken into account and this study has no side effects on environment and human beings.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Latifi, G.R., Monfared, M.P. & Khojasteh, H.A. Gamification and citizen motivation and vitality in smart cities: a qualitative meta-analysis study. GeoJournal 87, 1217–1230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10295-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10295-0