Abstract
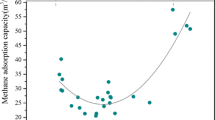
The emission of gas from the coal seams is one of the most important issues during the underground coal mining operation. Each year, coal gas emission from the underground stopes leads to the death of a large number of miners and is one of the biggest threats to workplace safety. In addition, ventilating and releasing coal gas outside of the mine is too expensive and, in most cases, might be impossible. Therefore, it is necessary to increase gas emissions and improve the efficiency of methane drainage for securing the mining workplace. The main aim of this paper is to investigate the capacity of the drainage system in the Parvadeh Tabas Coal Mine, Iran. For this purpose, the effect of the specification of the drilling pattern such as the length and drilling direction of the drilled boreholes on the methane gas concentration was investigated. The results of this study show that, with the change in the length of the borehole and the angle of the boreholes according to the axis of the tailgates, the volume of the methane drainage changes, significantly. The boreholes with lengths between 60 and 80 m drilled in lines with 16-degree division from a line perpendicular to the tailgate have the highest methane concentration.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Adhikari P, Ng KW, Gebreslasie YZ, Wulff SS (2022) New static analysis methods and LRFD recommendations for steel H-piles in rock-based intermediate geomaterials. Geotech Geol Eng 40(5):2553–2567
Barham WS, Rabab’ah SR, Aldeeky HH, Al Hattamleh OH (2020) Mechanical and physical based artificial neural network models for the prediction of the unconfined compressive strength of rock. Geotech Geol Eng 38:4779–4792
Brunner DJ, Schwoebel JJ (2018) Directional drilling for methane drainage and exploration in advance of mining recent advances and applications, REI Drilling, Inc., Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 10 p. http://www.reidrilling.com/dotAsset/1ef1002c-412d-40c2-a228-d287d4434b17
Cao J, Liu T, Shi Y, Lin B, Shen J, Xu Y, Gong X, Liu Y (2023) Strata movement of overburden-separation grouting working face and its influence on gas emission during mining. Sustainability 15(17):12792
Dougherty HN, Karacan CÖ (2011) A new methane control and prediction software suite for longwall mines. Comput Geosci 37(9):1490–1500
George D, Mallery P (2019) IBM SPSS statistics 26 step by step: a simple guide and reference. Routledge, London
Höglund-Isaksson L, Gómez-Sanabria A, Klimont Z, Rafaj P, Schöpp W (2020) Technical potentials and costs for reducing global anthropogenic methane emissions in the 2050 timeframe–results from the GAINS model. Environm Res Commun 2(2):025004
Hosseini Alaee N, Mozafari A, Mirzaee M, Faghihi A, Tolouei K (2019) Fuzzy evaluation method for the identification of subsidence susceptibility in an underground mine (case study in Tabas coal mine of Iran). Nat Hazards 99:797–806
Hou Y, Cui J, Liu R (2022) Study on the long-distance gas pre-drainage technology in the heading face by directional long borehole. Energies 15(17):6304
Hu S, Zhang A, Feng G, Guo X, Miu X, Li C, Han D, Wang J, Kang L (2018) Methane extraction from abandoned mines by surface vertical wells: a case study in China. Geofluids 2018:1–9
Hu S, Hao G, Feng G, Guo H, Wu D (2020) A method for improving the methane extraction concentrations of in-seam boreholes. Fuel 265:117006
Hu J, Huang R, Xu F (2022) Data mining in coal-mine gas explosion accidents based on evidence-based safety: a case study in China. Sustainability 14(24):16346
Jia L, Li K, Shi X, Zhao L, Linghu J (2021) Application of gas wettability alteration to improve methane drainage performance: a case study. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(4):621–629
Kamani M, Ajalloeian R (2019) Evaluation of engineering properties of some carbonate rocks through corrected texture coefficient. Geotech Geol Eng 37:599–614
Kędzior SS, Dreger M (2023) Time variability of methane extraction from hard coal deposits in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin (Poland) in relation to geological and mining conditions. J Sustain Min. https://doi.org/10.46873/2300-3960.1379
Khatti J, Samadi H, Grover KS (2023) Estimation of settlement of pile group in clay using soft computing techniques. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02643-x
King AP, Eckersley R (2019) Statistics for biomedical engineers and scientists: how to visualize and analyze data. Academic Press, Cambridge
Kulkarni BN, Kulkarni NB, Anantharama V (2022) An empirical analysis of surface-level methane emission from anthropogenic sources in India. J Clean Prod 346:131101
Li P, Cheng Z, Chen L, Wang H, Cao J (2021) Improvement of gas drainage efficiency via optimization of sealing depth of cross-measure boreholes. Adv Civil Eng 2021:1–13
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Gao Y, Zhang Y (2012) Numerical simulating research on orifice pre-splitting blasting in coal seam. Procedia Eng 45:322–328
Liu P, Fan J, Jiang D, Li J (2021) Evaluation of underground coal gas drainage performance: mine site measurements and parametric sensitivity analysis. Process Saf Environ Prot 148:711–723
Malozyomov BV, Golik VI, Brigida V, Kukartsev VV, Tynchenko YA, Boyko AA, Tynchenko SV (2023) Substantiation of drilling parameters for undermined drainage boreholes for increasing methane production from unconventional coal-gas collectors. Energies 16(11):4276
Mishra P, Pandey CM, Singh U, Gupta A, Sahu C, Keshri A (2019a) Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann Card Anaesth 22(1):67
Mishra P, Pandey CM, Singh U, Keshri A, Sabaretnam M (2019b) Selection of appropriate statistical methods for data analysis. Ann Card Anaesth 22(3):297
Mohtasham Seyfi M, Khademi Hamidi J, Monjezi M, Hosseini A (2018) Estimation of coal seams gas content for evaluating potential use of methane drainage system in Tabas coal mine. J Min Environ 9(3):667–677
Nawrat S, Napieraj S (2012) Utilization of the methane from polish mines. AGH J Min Geoeng 36(3):269–282
Nguyen PMV, Walentek A, Wierzbinski K, Zmarzły M (2022) Prediction of the absolute methane emission rate for longwall caving extraction based on rock mass modelling—a case study. Energies 15:4958
Rahimdel MJ, Mirzaei M (2021) Optimum operational conditions of mining trucks based on the vibrational health risk of the driver. Int J Heavy Veh Syst 28(2):226–241
Rahimdel MJ, Mirzaei M, Sattarvand J, Hoseinie SH (2017) Health risk of whole body vibration in mining trucks during various operational conditions. J Central South Univer 24:1808–1816
Rahimdel MJ, Aryafar A, Vaziri S (2022) Fuzzy FMEA for the safety risk analysis of underground coal mining (a case study in Iran). Min Technol 131(2):104–114
Ran D, Cheng J, Zhang R, Wang Y, Wu Y (2021) Damages of underground facilities in coal mines due to gas explosion shock waves: an overview. Shock Vibr 2021:1–11
Slastunov S, Kolikov K, Batugin A, Sadov A, Khautiev A (2022) Improvement of intensive in-seam gas drainage technology at Kirova mine in Kuznetsk Coal Basin. Energies 15(3):1047
Smalheiser N (2017) Data literacy: how to make your experiments robust and reproducible. Academic Press, Cambridge
SPSS (2013) IBM SPSS statistics 22. IBM Corp, New York
Szlązak N, Swolkień J, Kamiński P (2023) Design of coal seam exploitation in methane hazard conditions: a case study. Energies 16(1):365
Szott W, Słota-Valim M, Gołąbek A, Sowiżdżał K, Łętkowski P (2018) Numerical studies of improved methane drainage technologies by stimulating coal seams in multi-seam mining layouts. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 108:157–168
Tabas Parvadeh Coal Company, TPCC (2018) Technical report of the of the 1st mechanized coal mine of Parvadeh Tabas, https://en.stic.ir/tabas_parvardeh/
Tang B, Tang Y, Wang C, Li Y, Yu Y, Dai M, Wang Z (2020) Rapid co-extraction of coal and coalbed methane techniques: a case study in Zhangji coal mine, China. IOP Conf Series: Earth Environ Sci 446(5):052012
Tian CHEN, Manfei XU, Justin TU, Hongyue WANG, Xiaohui NIU (2018) Relationship between Omnibus and Post-hoc Tests: an Investigation of performance of the F test in ANOVA. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry 30(1):60
Yi M, Wang L, Hao C, Liu Q, Wang Z (2021) Method for designing the optimal sealing depth in methane drainage boreholes to realize efficient drainage. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8:1400–1410
Yue G, Li M, Wang L, Liang W (2019) Optimal layout of blasting holes in structural anisotropic coal seam. PLoS ONE 14(6):0218105
Zheng C, Jiang B, Xue S, Chen Z, Li H (2019) Coalbed methane emissions and drainage methods in underground mining for mining safety and environmental benefits: a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 127:103–124
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimdel, M.J., Javanshir Giv, M. & Bahonar, M.R. Selecting the Optimal Borehole Drilling Pattern for Methane Drainage in Underground Coal Mining: A Case Study in Iran. Geotech Geol Eng 42, 2641–2655 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02695-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02695-z