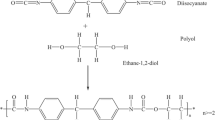
Abstract
Using chemical additives such as ordinary Portland cement is conventional for ground improvement purposes. Still, there are specific situations that require innovative solutions because the employment of traditional binders may lead to unpleasant issues. Organic polymers emerge as an option to deal with those drawbacks whilst promoting enhancements in the material’s mechanical response. Thus, the present study uses polyester [poly(glycerol isophthalate)], whose main source of raw material is glycerol, an abundant by-product derived from biodiesel production, in the improvement of uniform quartzitic sand. Thence, a series of mechanical tests were carried out on compacted sand-polymer-cement blends to evaluate the effect of variables such as polymer content, amount of cement, and curing temperature through a central composite design scheme. This enables the assessment of first and second-order effects as well as the curvature of the evaluated responses. In general, the polymer addition has led to substantial enhancement in the material’s response, particularly concerning the decrease in hydraulic conductivity. This highlights the usefulness of this polymer for geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Abbawi ZWS (2015) Studying strength and stiffness characteristics of sand stabilized with cement and lime additives. Eng Technol J 33:1857–1875
Abebe B, Murthy HCA, Amare E (2018) Summary on adsorption and photocatalysis for pollutant remediation: mini review. JEAS 08:225–255. https://doi.org/10.4236/jeas.2018.84012
Alelvan GM, Casagrande M, Consoli NC (2022a) Mechanical behavior analysis of polymer stabilized gold ore tailings. Soils Rocks 45(2):1–18. https://doi.org/10.28927/sr.2022.075421
Alelvan GM, Casagrande M, Consoli NC (2022b) Mechanical behavior analysis of polymer stabilized gold ore tailings. Soils Rocks 45:1–8. https://doi.org/10.28927/SR.2022.075421
ANP—Brazilian Agency for Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (2022a) Brazilian statistical yearbook of oil, natural gas and biofuels-Base year 2021, Biofuels, 2022a.
ANP (2022b) Oil, natural gas and biofuels statistical yearbook 2022b. Brasil
ASTM (2011) Test method for splitting tensile strength of cylindrical concrete specimens - ASTM C496. ASTM International
ASTM (2016a) Test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil - ASTM D2166. ASTM International
ASTM (2016b) Test methods for measurement of hydraulic conductivity of saturated porous materials using a flexible wall permeameter - ASTM D5084. ASTM International
ASTM (2017) Practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (Unified Soil Classification System) - ASTM D2487. ASTM International
ASTM (2020) Test method for consolidated drained triaxial compression test for soils - ASTM D7181. ASTM International
ASTM (2021) Test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using standard effort (12,400 ft-lbf/ft3 (600 kN-m/m3)) - ASTM D698. ASTM International
Ateş A (2013) The effect of polymer-cement stabilization on the unconfined compressive strength of liquefiable soils. International Journal of Polymer Science 2013:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/356214
Behera S, Mahanwar PA (2020) Superabsorbent polymers in agriculture and other applications: a review. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Materials 59:341–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2019.1647239
Bruschi GJ, Santos CP, Tonini de Araújo M (2021) Green stabilization of bauxite tailings: mechanical study on alkali-activated materials. J Mater Civ Eng 33:06021007. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003949
Buchmann C, Bentz J, Schaumann GE (2015) Intrinsic and model polymer hydrogel-induced soil structural stability of a silty sand soil as affected by soil moisture dynamics. Soil and Tillage Research 154:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.06.014
Clayton CRI, Khatrush SA (1986) A new device for measuring local axial strains on triaxial specimens. Géotechnique 36:593–597. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1986.36.4.593
Consoli NC, Foppa D, Festugato L, Heineck KS (2007) Key parameters for strength control of artificially cemented soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 133:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:2(197)
Consoli NC, Festugato L, da Rocha CG, Cruz RC (2013) Key parameters for strength control of rammed sand–cement mixtures: Influence of types of Portland cement. Constr Build Mater 49:591–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.08.062
Consoli NC, Carretta MS, Festugato L (2021a) Ground waste glass–carbide lime as a sustainable binder stabilising three different silica sands. Géotechnique 71:480–493. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.18.P.099
Consoli NC, Párraga Morales D, Saldanha RB (2021b) A new approach for stabilization of lateritic soil with Portland cement and sand: strength and durability. Acta Geotech 16:1473–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01136-y
Consoli NC, Scheuermann Filho HC, Leon HB (2021c) General relationships controlling loss of mass, stiffness and strength of sustainable binders amended sand. Transportation Geotechnics 27:100473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2020.100473
de Brioude M, M, Guimarães DH, Fiúza R da P, et al (2007) Synthesis and characterization of aliphatic polyesters from glycerol, by-product of biodiesel production, and adipic acid. Mat Res 10:335–339. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392007000400003
Donohue MD, Aranovich GL (1998) Classification of Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Adv Coll Interface Sci 76–77:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00044-X
Du S, Ge X, Zhao Q (2022) Central composite design-based development of eco-efficient high-volume fly ash mortar. Construction and Building Materials 358:129411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129411
Farmer VC, Palmieri F (1975) The characterization of soil minerals by infrared spectroscopy. In: Gieseking JE (ed) Soil Components. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 573–670
Feng Y-S, Du Y-J, Reddy KR, Xia W-Y (2018) Performance of two novel binders to stabilize field soil with zinc and chloride: Mechanical properties, leachability and mechanisms assessment. Constr Build Mater 189:1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.072
Gibson N, Kuchenbecker P, Rasmussen K (2020) Volume-specific surface area by gas adsorption analysis with the BET method. In: Characterization of Nanoparticles. Elsevier, pp 265–294
Gong W, Zang Y, Liu B (2016) Effect of using polymeric materials in ecological sand-fixing of Kerqin Sandy Land of China. J Appl Polym Sci 133. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44102
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, surface area and porosity, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Guimarães DH, Brioude MM, Fiúza RP (2007) Synthesis and characterization of polyesters derived from glycerol and phthalic acid. Mat Res 10:257–260. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392007000300007
Head KH (2006) Manual of soil laboratory testing, 3rd edn. Whittles publishing, Dunbeath
Hong SH, Lee EY (2016) Restoration of eroded coastal sand dunes using plant and soil-conditioner mixture. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 113:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.021
Joel M, Agbede IO (2011) Mechanical-cement stabilization of laterite for use as flexible pavement material. J Mater Civ Eng 23:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000148
Kolay PK, Dhakal B, Kumar S, Puri VK (2016) Effect of liquid acrylic polymer on geotechnical properties of fine-grained soils. Int J of Geosynth and Ground Eng 2:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-016-0071-5
Komolafe OO, Osinubi KJ (2019) Stabilization of lateritic soil with cement – oil palm empty fruit bunch ash blend for California Bearing Ratio base course requirement. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 640:012085. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/640/1/012085
Lahalih SM, Ahmed N (1998) Effect of new soil stabilizers on the compressive strength of dune sand. Constr Build Mater 12:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(98)00024-5
Latifi N, Rashid ASA, Siddiqua S, Horpibulsuk S (2015) Micro-structural analysis of strength development in low- and high swelling clays stabilized with magnesium chloride solution — A green soil stabilizer. Appl Clay Sci 118:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.10.001
Li Y, Cui J, Zhang T (2009) Effectiveness of sand-fixing measures on desert land restoration in Kerqin sandy land, northern China. Ecol Eng 35:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.09.013
Liu J, Shi B, Lu Y (2012) Effectiveness of a new organic polymer sand-fixing agent on sand fixation. Environ Earth Sci 65:589–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1106-9
Liu J, Qi X, Zhang D (2017) Study on the Permeability Characteristics of Polyurethane Soil Stabilizer Reinforced Sand. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2017:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5240186
Liu J, Bai Y, Song Z (2020) Stabilization of sand using different types of short fibers and organic polymer. Construction and Building Materials 253:119164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119164
Ma G, Ran F, Feng E (2015) Effectiveness of an Eco-friendly Polymer Composite Sand-Fixing Agent on Sand Fixation. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2490-7
Mao L, Xue R, An L (2004) Quantitative analysis on SEM image of microstructure with MATLAB. J Chin Electron Microsc 1:579–583
Montgomery DC (2020) Design and analysis of experiments, 10th edn. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Mousavi F, Abdi E, Rahimi H (2014) Effect of polymer stabilizer on swelling potential and CBR of forest road material. KSCE J Civ Eng 18:2064–2071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0137-7
Muttakin M, Mitra S, Thu K (2018) Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int J Heat Mass Transf 122:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.01.107
Pereira dos Santos C, Bruschi GJ, Mattos JRG, Consoli NC (2022) Stabilization of gold mining tailings with alkali-activated carbide lime and sugarcane bagasse ash. Transportation Geotechnics 32:100704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100704
Pirie A, Singh B, Islam K (2005) Ultra-violet, visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopic techniques to predict several soil properties. Soil Res 43:713. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR04182
Rezaeimalek S, Huang J, Bin-Shafique S (2017) Evaluation of curing method and mix design of a moisture activated polymer for sand stabilization. Constr Build Mater 146:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.093
Saldanha RB, Consoli NC (2016) Accelerated mix design of lime stabilized materials. J Mater Civ Eng 28:06015012. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001437
Saldanha RB, Scheuermann Filho HC, Ribeiro JLD, Consoli NC (2017) Modelling the influence of density, curing time, amounts of lime and sodium chloride on the durability of compacted geopolymers monolithic walls. Constr Build Mater 136:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.023
Scheuermann Filho HC, Miguel GD, Consoli NC (2022) Porosity/cement index over a wide range of porosities and cement contents. J Mater Civ Eng 34:06021011. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004115
Servi S, Lotero A, Silva JPS, Bastos C, Consoli NC (2022) Mechanical response of filtered and compacted iron ore tailings with different cementing agents: Focus on tailings-binder mixtures disposal by stacking. Construction and Building Materials 349:128770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128770
Shrivastava AK, Jain D, Vishwakarma S (2016) Frictional resistance of drilling fluids as a borehole stabilizers. Geo-Engineering 7:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40703-016-0026-7
Silvani C, Ibraim E, Scheuermann Filho HC, Diambra A, Festugato L, Consoli NC (2022) Sand-fly ash-lime blends: Mechanical behavior under multiaxial stress condition. J Mater Civ Eng 34:04022059. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004199
Silverstein RM, Bassler GC, Morrill TC (1991) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Sing KSW (1982) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Provisional). Pure Appl Chem 54:2201–2218. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198254112201
Sousa Junior JGA, Demattê JAM, Genú AM (2008) Comportamento espectral dos solos na paisagem a partir de dados coletados por sensores terrestre e orbital. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 32:727–738. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832008000200027
Suksiripattanapong C, Jenpiyapong K, Tiyasangthong S (2022) Mechanical and thermal properties of lateritic soil mixed with cement and polymers as a non-bearing masonry unit. Case Studies in Construction Materials 16:e00962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e00962
Tonini de Araújo M, Tonatto Ferrazzo S, Mansur Chaves H, et al (2023) Mechanical behavior, mineralogy, and microstructure of alkali-activated wastes-based binder for a clayey soil stabilization. Construction and Building Materials 362:129757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129757
Vendruscolo MA (2003) Estudo do comportamento de materiais compósitos fibrosos para aplicação como reforço de base de fundações superficiais. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Tese de Doutorado
Vieira GA (2016) Síntese e caracterização de polímeros verdes: Poliésteres do glicerol e do ácido isoftálico. Universidade Federal do Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri, Dissertação de Mestrado
Zhang M, Guo H, El-Korchi T et al (2013) Experimental feasibility study of geopolymer as the next-generation soil stabilizer. Constr Build Mater 47:1468–1478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.06.017
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to explicit their appreciation to MCT-CNPq (Editais INCT-REAGEO & Produtividade em Pesquisa), and MEC-CAPES (PROEX) for the support of the research group.
Funding
The funding was provided by CNPq, INCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GV: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—original draft. HCSF: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. NCC: Conceptualization, General Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicting interests that could inappropriately bias this work, and the authors still declare their interest in the development of this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, G.A., Scheuermann Filho, H.C. & Consoli, N.C. Geotechnical Enhancement of a Quartzitic Sand Using a Green Polymer. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 3971–3984 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02499-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02499-1