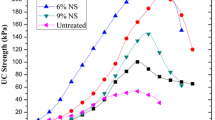
Abstract
The properties of clay can be altered with the addition of nanomaterials such as nano alumina. Previous studies have shown that nano alumina (Al) can be used to improve the Atterberg limits, compaction, permeability, swelling and shrinkage of fine-grained soil. The current study investigated the effect of the addition of 0%, 2%, 4% or 6% nano Al on the shear and unconfined compressive strength of kaolinite clay using direct shear and unconfined compressive strength tests, respectively. SEM images of the soil microstructure were analyzed. The results showed that the addition of 6% nano Al (by weight of dry soil) increased the shear strength of the soil to about 1.5 times that of soil without nanoparticles. The unconfined compressive strength of the soil increased by 15% with the addition of 4% nano Al. The SEM images showed that nano Al decreased the size of the soil pores by filling the soil voids and this compaction further increased the shear strength and unconfined compressive strength of the soil. Shear strength and unconfined compressive strength parameters should be considered for soil stabilization and have not previously been investigated. The research gap for the application of nano alumina in soil has been examined in the present investigation by means of unconfined compressive strength and direct shear testing. The inconsistencies in earlier studies have been cleared up by looking at the Atterberg limits.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Some or all data, models, and codes that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Al-Mansob RA, Wong WF, Alsharef JMA, Jassam TM, Ng JL, Ali SIA, Yusof ZBM (2021) Unconfined compressive strength characteristic of soft soil mixed with lime and nano alumina. In: AIP conference proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC, pp 020010
Al-Murshedi AD, Karkush MO, Karim HH (2020) Collapsibility and shear strength of gypseous soil improved by nano silica fume (NSF). In: Key engineering materials. Trans Tech Publ., pp 292–301
ASTM D2166 (2006) Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D2487 (2017) Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system) 1. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D3080 (2011) Standard test method for direct shear test of soils under consolidated drained conditions. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D422 (2007) Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D4318 (2010) Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM D698 (2007) Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using standard effort (12 400 Ft-lbf/ft3 (600 KN-m/m3)) 1. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Changizi F, Haddad A (2015) Strength properties of soft clay treated with mixture of nano-SiO2 and recycled polyester fiber. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7:367–378
Cui H, Jin Z, Bao X, Tang W, Dong B (2018) Effect of carbon fiber and nanosilica on shear properties of silty soil and the mechanisms. Constr Build Mater 189:286–295
Ghasabkolaei N, Choobbasti AJ, Roshan N, Ghasemi SE (2017) Geotechnical properties of the soils modified with nanomaterials: a comprehensive review. Arch Civ Mech Eng 17:639–650
Haddad A, Changizi F (2016) Effect of nano-SiO2 on the geotechnical properties of cohesive soil. Geotech Geol Eng 34:725–733
Hariprasad Reddy S, Mir BA (2020) Influence of nano-materials on compaction and strength behavior of clayey soils. In: Gali ML, Rao PR (eds) Geotechnical characterization and modelling. Springer, Berlin
Jahromi SG, Zahedi H (2018) Investigating the effecting of nano aluminum on mechanical and volumetric properties of clay. Amirkabir J Civ Eng 50:597–606
Kalhor A, Ghazavi M, Roustaei M, Mirhosseini SM (2019) Influence of nano-SiO2 on geotechnical properties of fine soils subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 161:129–136
Kalhor A, Ghazavi M, Roustaei M (2022) Impacts of nano-silica on physical properties and shear strength of clayey soil. Arab J Sci Eng 47:5271–5279
Kananizadeh N, Ebadi T, Khoshniat SA, Mousavirizi SE (2011) The positive effects of nanoclay on the hydraulic conductivity of compacted Kahrizak clay permeated with landfill leachate. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 39:605–611
Luo H-L, Hsiao D-H, Lin D-F, Lin C-K (2012) Cohesive soil stabilized using sewage sludge ash/cement and nano aluminum oxide. Int J Transp Sci Technol 1:83–99
Mir BA, Hariprasad Reddy S (2021) Enhancement in shear strength characteristics of soft soil by using nanomaterials. In: Reddy KR, Agnihotri AK, Yukselen-Aksoy Y, Dubey BK, Bansal A (eds) Sustainable environment and infrastructure. Springer, Berlin
Mir BA, Reddy SH (2021) Mechanical behaviour of nano-material (Al2O3) stabilized soft soil. Int J Eng 34:636–643
Ng CWW, Coo JL (2015) Hydraulic conductivity of clay mixed with nanomaterials. Can Geotech J 52:808–811
Shahin SS, Fayed LAEM, Ahmad EH (2015) Review of nano additives in stabilization of soil. In: Seventh international conference on nano technology in construction
Taha MR (2018) Recent developments in nanomaterials for geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering. In: MATEC web of conferences. EDP Sciences, pp 02004
Taha OME, Taha MR (2016) Soi–water characteristic curves and hydraulic conductivity of nanomaterial–soil–bentonite mixtures. Arab J Geosci 9:1–14
Tanzadeh R, Vafaeian M, Fard MY (2019) Effects of micro-nano-lime (CaCO3) particles on the strength and resilience of road clay beds. Constr Build Mater 217:193–201
Thomas S, Chandrakaran S, Sankar N (2022) Nanocomposites are state-of-the-art in the field of ground improvement-a review. Mater Today Proc 65:877–882
Wang W, Zhang C, Li N, Tao F, Yao K (2018) (2018) Characterisation of nano magnesia–cement-reinforced seashore soft soil by direct-shear test. J Mar Georesour Geotechnol 14:1–10
Wong JKH, Kok ST, Wong SY (2020) Fibers, geopolymers, nano and alkali-activated materials for deep soil mix binders. Civil Eng J 6:830–847
Yao K, An D, Wang W, Li N, Zhang C, Zhou A (2020) Effect of nano-MgO on mechanical performance of cement stabilized silty clay. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 38:250–255
Zhang G (2007) Soil nanoparticles and their influence on engineering properties of soils. In: Advances in measurement and modeling of soil behavior
Zhang H, Hu H, Lai Y, Niu F (2019) Mechanism for soil reinforcement by electroosmosis incorporated with nanoclay. Dry Technol 37:1290–1299
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out at the Soil Mechanics Laboratory of the Civil Engineering Department in the School of Engineering at the Shahed University. The assistance and constructive suggestions of all experts and personnel of the lab, especially Mr. Naseri are greatly appreciated.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parsaei, M., Rojhani, M. & Seyedahmadian, S. Effect of the Addition of Nano Alumina on the Mechanical Properties of Clay. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 3767–3779 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02488-4